Python Project – Slide Puzzle Game
Master programming with our job-ready courses: Enroll Now
The Slide Puzzle Game is developed using Python and Tkinter. This project aims to create a user-friendly slide puzzle game that allows users to test their game skills.
About Python Slide Puzzle Game
- Develop a slide puzzle game with a graphical user interface.
- Implement functionalities for shuffling tiles and moving tiles.
- The game can be easily reset and replayed.
Project Setup
Required Libraries
The project requires the following standard Python libraries:
- Tkinter: For graphical user interface.
- random: For reshuffling tiles randomly.
- time: For tracking game duration.
Prerequisites for Python Slide Puzzle Game
- Basic understanding of Python programming.
- Familiarity with Tkinter for GUI development.
Download Python Slide Puzzle Game Project Code
Please download the source code of the Python Slide Puzzle Game Project: Python Slide Puzzle Game Project Code.
Steps to Implement Python Slide Puzzle Game
1. Importing Libraries
This helps to import necessary libraries for the GUI of the Alarm Clock:-
- tkinter: Used for creating the graphical user interface (GUI).
- random: This is used to generate random tiles on reset.
- time: Provides time-related functions.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox import random import time
2. Class SlidePuzzle
- In the constructor for the class SlidePuzzle self.root stores the main tkinter window as an instance.
- The game is initialized with self.size, self.tiles & self.moves.
- Game widgets are set using self.buttons, self.create_widets, and self.shuffle_time. All this initializes an empty list to create a layout for puzzle tiles and shuffle them.
class SlidePuzzle:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("PythonGeeks Slide Puzzle Game")
self.size = 4
self.tiles = list(range(1, self.size * self.size)) + [0]
self.moves = 0
self.start_time = None
self.buttons = []
self.create_widgets()
self.shuffle_tiles()
3. Create Widgets
- frame = tk.Frame(self.root): This is used to form a Frame widget (frame) within the main Tkinter window/
- frame.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=10): Used to place frames in grid layout at row 0, column 0 with 10 pixels of padding on all sides.
- The nested loop iterates over rows (i) and columns (j) to create buttons for each tile in the puzzle.
- tk.Button(frame, width=4, height=2, font=(“Arial”, 18), command=lambda i=i, j=j: self.move_tile(i, j)): It creates a button within the frame widget of given dimensions and font.
- button.grid(row=i, column=j): Places the button in the grid layout at position (i, j) within the frame
- self.moves_label=tk.Label(self.root, text=”Moves: 0″, font=(“Arial”, 14)): This is used as a label to display the number of moves.
- self.moves_label.grid(row=1, column=0, pady=5): Places the moves label in the grid layout at row 1, column 0 with padding.
- reset_button = tk.Button(self.root, text=”Reset”, command=self.reset_game, font=(“Arial”, 14)): It creates a button (reset_button) labeled “Reset” that calls the self.reset_game() method when clicked.
- reset_button.grid(row=3, column=0, pady=5): It places the reset button in the grid layout at row 3, column 0, with padding.
- quit_button = tk.Button(self.root, text=”Quit”, command=self.root.quit, font=(“Arial”, 14)): It creates a button (quit_button) labeled “Quit” that exits the application when clicked (self.root.quit).
- quit_button.grid(row=4, column=0, pady=5): This places the quit button in the grid layout at row 4, column 0, with padding.
def create_widgets(self):
frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
frame.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
for i in range(self.size):
row = []
for j in range(self.size):
button = tk.Button(frame, width=4, height=2, font=("Arial", 18), command=lambda i=i, j=j: self.move_tile(i, j))
button.grid(row=i, column=j)
row.append(button)
self.buttons.append(row)
self.moves_label = tk.Label(self.root, text="Moves: 0", font=("Arial", 14))
self.moves_label.grid(row=1, column=0, pady=5)
self.timer_label = tk.Label(self.root, text="Time: 0s", font=("Arial", 14))
self.timer_label.grid(row=2, column=0, pady=5)
reset_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Reset", command=self.reset_game, font=("Arial", 14))
reset_button.grid(row=3, column=0, pady=5)
quit_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Quit", command=self.root.quit, font=("Arial", 14))
quit_button.grid(row=4, column=0, pady=5)
4. Shuffle & Update Tiles
- random.shuffle(self.tiles): It randomly shuffles tiles on positions from 1 to 15 in the puzzle.
- self.update_buttons(): It calls update_buttons to update the display of buttons.
- self.start_time = time.time(): This records the start time using time.time() to calculate game time.
- Buttons’ values are updated using update_buttons(), which iterates in a nested loop to change the value using self.buttons[i][j].config(text=text).
def shuffle_tiles(self):
random.shuffle(self.tiles)
self.update_buttons()
self.start_time = time.time()
self.update_timer()
def update_buttons(self):
for i in range(self.size):
for j in range(self.size):
tile = self.tiles[i * self.size + j]
text = str(tile) if tile != 0 else ""
self.buttons[i][j].config(text=text)
5. Move Tiles & Update Timer
- empty_index = self.tiles.index(0): It finds the index of empty space.
- We check if the player wants to move an adjacent space and if that space is empty or not using if abs(empty_row – i) + abs(empty_col – j) == 1:
- self.moves += 1: It implements the user moves by Incrementing the self.moves counter to track the number of moves made by the player.
- self.update_buttons(): This updates the GUI display to reflect the new positions of tiles after the move.
- self.moves_label.config(text=f”Moves: {self.moves}”): This updates the moves label to display the current number of moves.
- update_timer(): It checks for elapsed time by int(time.time() – self.start_time) and self.root.after(1000, self.update_timer) allows the method to run again after 1 second, thus creating a recursive loop that updates the timer display every second.
def move_tile(self, i, j):
empty_index = self.tiles.index(0)
empty_row, empty_col = divmod(empty_index, self.size)
if abs(empty_row - i) + abs(empty_col - j) == 1:
self.tiles[empty_row * self.size + empty_col], self.tiles[i * self.size + j] = self.tiles[i * self.size + j], self.tiles[empty_row * self.size + empty_col]
self.moves += 1
self.update_buttons()
self.moves_label.config(text=f"Moves: {self.moves}")
self.check_win()
def update_timer(self):
if self.start_time:
elapsed_time = int(time.time() - self.start_time)
self.timer_label.config(text=f"Time: {elapsed_time}s")
self.root.after(1000, self.update_timer)
6. Check Win & Reset Game
- self.tiles: It checks if the current state of the tiles (self.tiles) matches the solved state.
- end_time = time.time(): IT records the game time at which the puzzle is solved.
- A winning message is displayed on completing the game.
- To reset the game self.reset() is called sets all moves and time to 0
def check_win(self):
if self.tiles == list(range(1, self.size * self.size)) + [0]:
end_time = time.time()
duration = int(end_time - self.start_time)
messagebox.showinfo(f"You solved the puzzle in {self.moves} moves and {duration} seconds!")
self.reset_game()
def reset_game(self):
self.moves = 0
self.moves_label.config(text="Moves: 0")
self.timer_label.config(text="Time: 0s")
self.shuffle_tiles()
7. Main Function
- root = tk.Tk(): It forms the main application window using tkinter function.
- game = SlidePuzzle(root): This is done to form an instance of AlarmClock class passing root as argument. It initializes the alarm clock application
- root.mainloop(): It starts the Tkinter event loop, which listens for events and updates the GUI.
if __name__ == "__main__": root = tk.Tk() game = SlidePuzzle(root) root.mainloop()
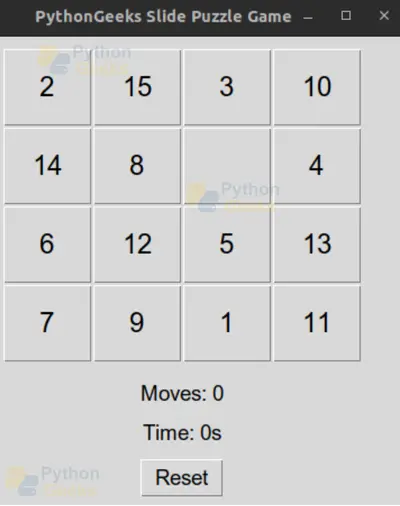
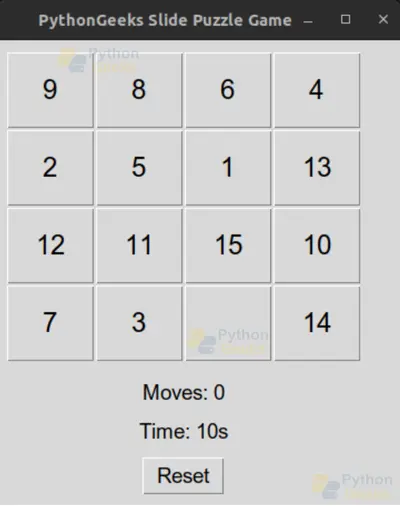
Python Slide Puzzle Game Output
Application Interface
On Reset
How to Play the Python Slide Puzzle Game
- Objective: The goal of this game is to arrange the tiles in numerical order, with the empty space at the bottom-right corner.
- Move Tiles: Click on a tile adjacent to the empty space to slide it into the empty space.
- Reset: Click the “Reset” button to shuffle the tiles and start a new game.
- Quit: Click the “Quit” button to exit the game.
Conclusion
The Slide Puzzle Game project shows how Python and Tkinter can be used to create a graphical user interface and handle game logic. The game provides a fun and challenging experience for users while showcasing concepts like event handling, GUI updates, and time management. Additional features such as different puzzle sizes, improved visual design, and more sophisticated shuffling algorithms can enhance the project.