How to Use Multiple DataSources in Spring Batch with H2 and MySQL
Overview: Why Use Multiple DataSources in Spring Batch?
Learn how to configure multiple datasources in a Spring Batch application.
This is useful when you want to store Spring Batch metadata in an H2 database and business data in MySQL or other databases. It also helps when production environments restrict metadata table creation.The other situation may occur where in production environment you do not have permission to create meta data tables for spring batch then you can use H2 database for storing meta data related information.
Setting Up the Maven Project
Create a Maven-based Spring Boot project and include dependencies for Spring Batch, H2, and MySQL. H2 will store batch metadata, while MySQL stores business data.
You can use the following pom.xml file for your project.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-multiple-datasources</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.release>22</maven.compiler.release>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.4</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Configuring MySQL in application.properties
I am using only MySQL database configurations in src/main/resources/application.properties file and you don’t need to configure the H2 database as it is in-memory database, so it will be available as long as the application is live.
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/roytuts
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=trueThe spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true override the implementations of spring beans when you want to override the definition or implementation of any spring bean.
Creating the MySQL Table for Business Data
The following MySQL table stores the person details from CSV file which is used in the spring batch example.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `roytuts`;
USE `roytuts`;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `persons` (
`id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(150) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;Defining Multiple DataSources and Transaction Managers
Configure H2 and MySQL datasources and transaction managers. Mark one as @Primary to avoid ambiguity.
The following configuration class defines the data sources for H2 database and MySQL database. It also defines the transaction managers for both databases. Whenever you are working with multiple data sources or transaction managers you need to make one of them as primary.
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Primary
@Bean(name = "h2DataSource")
public DataSource h2DataSource() {
EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder embeddedDatabaseBuilder = new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder();
return embeddedDatabaseBuilder.addScript("classpath:org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-h2.sql")
.addScript("classpath:org/springframework/batch/core/schema-h2.sql").setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2)
.build();
}
@Bean(name = "mySQLDataSource")
public DataSource mySQLDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().driverClassName(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.driverClassName"))
.url(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"))
.username(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.username"))
.password(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.password")).build();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager mySQLDataSourceTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(mySQLDataSource());
}
@Bean
public NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate() {
return new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(mySQLDataSource());
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "platformTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(h2DataSource());
}
}Mapping CSV Fields to Java Objects
Use FieldSetMapper to map CSV fields to the User object.
The field set mapper is used to set the value to the appropriate object after reading from the input source.
public class UserFieldSetMapper implements FieldSetMapper<User> {
@Override
public User mapFieldSet(FieldSet fieldSet) throws BindException {
User user = new User();
user.setName(fieldSet.readString(0));
user.setEmail(fieldSet.readString(1));
return user;
}
}Transforming Data with ItemProcessor
Use ItemProcessor to transform each record before writing. For example, convert names to uppercase and generate email addresses.
public class UserItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<User, User> {
@Override
public User process(final User user) throws Exception {
final String domain = "roytuts.com";
final String name = user.getName().toUpperCase();
final String email = user.getName() + "@" + domain;
final User transformedUser = new User(name, email);
System.out.println("Converting [" + user + "] => [" + transformedUser + "]");
return transformedUser;
}
}Writing Data to MySQL Using PreparedStatement
Use ItemPreparedStatementSetter to write transformed data to the MySQL table.
public class PersonsPreparedStatementSetter implements ItemPreparedStatementSetter<User> {
@Override
public void setValues(User item, PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, item.getName());
ps.setString(2, item.getEmail());
}
}Spring Batch Configuration: Jobs, Steps, and Components
Configure JobRepository, ItemReader, ItemProcessor, ItemWriter, and define Job and Step beans.
You don’t need to use @EnableBatchProcessing in spring batch 5 version. The @Configuration annotation is enough for configuring the batch things.
@Configuration
public class SpringBatchConfig {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("h2DataSource")
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
private static final String QUERY_INSERT_PERSONS = "INSERT " + "INTO persons(name, email) " + "VALUES (?, ?)";
@Bean
public JobRepository jobRepository() throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setTransactionManager(platformTransactionManager);
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
// creates an item reader
public ItemReader<User> reader() {
FlatFileItemReader<User> reader = new FlatFileItemReader<User>();
// look for file user.csv
reader.setResource(new ClassPathResource("person.csv"));
// line mapper
DefaultLineMapper<User> lineMapper = new DefaultLineMapper<User>();
// each line with comma separated
lineMapper.setLineTokenizer(new DelimitedLineTokenizer());
// map file's field with object
lineMapper.setFieldSetMapper(new UserFieldSetMapper());
reader.setLineMapper(lineMapper);
return reader;
}
@Bean
// creates an instance of our UserItemProcessor for transformation
public ItemProcessor<User, User> processor() {
return new UserItemProcessor();
}
@Bean
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
// creates item writer
public ItemWriter<User> writer() {
JdbcBatchItemWriter<User> batchItemWriter = new JdbcBatchItemWriter<>();
batchItemWriter.setJdbcTemplate(namedParameterJdbcTemplate);
batchItemWriter.setSql(QUERY_INSERT_PERSONS);
ItemPreparedStatementSetter<User> valueSetter = new PersonsPreparedStatementSetter();
batchItemWriter.setItemPreparedStatementSetter(valueSetter);
return batchItemWriter;
}
@Bean
public Job importUserJob(Step step) throws Exception {
// need incrementer to maintain execution state
return new JobBuilder("importUserJob", jobRepository()).incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer()).flow(step).end()
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step step1(ItemReader<User> reader, ItemWriter<User> writer, ItemProcessor<User, User> processor)
throws Exception {
// chunk uses how much data to write at a time
// In this case, it writes up to five records at a time.
// Next, we configure the reader, processor, and writer
return new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository()).<User, User>chunk(5, platformTransactionManager).reader(reader)
.processor(processor).writer(writer).build();
}
}CSV Input File Format
The input file (person.csv) is a CSV (Comma Separated Value) file which has simply first name and last name pairs. This file is kept under class path folder src/main/resources.
The input file person.csv contains comma-separated name pairs like:
soumitra,roy
souvik,sanyal
arup,chatterjee
suman,mukherjee
debina,guha
liton,sarkar
debabrata,poddarUser Value Object (VO) Class
The Value Object class is a simple class which has two attributes for first and last names.
public class User {
private String name;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name: " + name + ", email:" + email;
}
}Main Class to Launch Spring Boot Application
A class is having main method and @SpringBootApplication annotation is enough to start the spring boot application.
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBatch.class, args);
}
}Output Example
Here is the output of the spring batch application when run by executing the main class.
Converting [name: soumitra, email:roy] => [name: SOUMITRA, email:[email protected]]
Converting [name: souvik, email:sanyal] => [name: SOUVIK, email:[email protected]]
Converting [name: arup, email:chatterjee] => [name: ARUP, email:[email protected]]
Converting [name: suman, email:mukherjee] => [name: SUMAN, email:[email protected]]
Converting [name: debina, email:guha] => [name: DEBINA, email:[email protected]]
Converting [name: liton, email:sarkar] => [name: LITON, email:[email protected]]
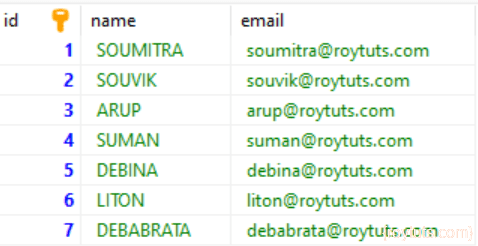
Converting [name: debabrata, email:poddar] => [name: DEBABRATA, email:[email protected]]Data in the MySQL database table gets inserted as:
And the insert statements when exported be like the following:
INSERT INTO `persons` (`id`, `name`, `email`) VALUES
(1, 'SOUMITRA', '[email protected]'),
(2, 'SOUVIK', '[email protected]'),
(3, 'ARUP', '[email protected]'),
(4, 'SUMAN', '[email protected]'),
(5, 'DEBINA', '[email protected]'),
(6, 'LITON', '[email protected]'),
(7, 'DEBABRATA', '[email protected]');Hope you got an idea how to use multiple datasources in spring batch application.
Source Code
Conclusion
Using multiple datasources in Spring Batch is a powerful approach when you need to separate metadata storage from business data processing. This setup is especially useful in production environments where database access is restricted or where different databases serve different purposes. By configuring H2 for Spring Batch metadata and MySQL for business data, you maintain flexibility, scalability, and cleaner separation of concerns. With the right configuration of datasources, transaction managers, and batch components, your application becomes more robust and easier to maintain.
No comments