C++ STL
The C++ programming language offers various functionalities and features to the developers. It also supports object-oriented programming. In this tutorial, we are going to learn about the standard template libraries of C++. It is one of the most powerful features of the C++ programming language.
What is STL in C++?
In C++, the C++ STL is a very powerful feature and it is a set of C++ template classes. With the help of STL, you can make use of general-purpose classes and functions with templates. And these implement many popular and most used algorithms and data structures like vectors, lists, queues and stacks.
Components of C++ STL
There are four components of STL:-
- Containers
- Algorithms
- Function objects
- Iterators
1. Containers
The main purpose of containers is to manage collections of objects of a certain kind. In the following table, there are different types of containers:-
| Container | Description | Header file | iterator |
| vector | It is a class and it creates a dynamic array which allows insertion and deletion at the back. | <vector> | Random access |
| list | It allows insertions and deletions from anywhere. | <list> | Bidirectional |
| deque | It allows insertion and deletion from both ends. | <deque> | Random access |
| set | It is used for storing unique sets. | <set> | Bidirectional |
| multiset | It is used for storing non-unique sets. | <set> | Bidirectional |
| map | It is used for storing key-value pairs. And each key can be linked with only one value. | <map> | Bidirectional |
| multimap | It is used for storing key-value pairs. And each key can be linked with more than one value. | <map> | Bidirectional |
| stack | Follows last in first out(LIFO). | <stack> | No iterator |
| queue | Follows first in first out(FIFO). | <queue> | No iterator |
| Priority-queue | The highest priority is to remove the first element. | <queue> | No iterator |
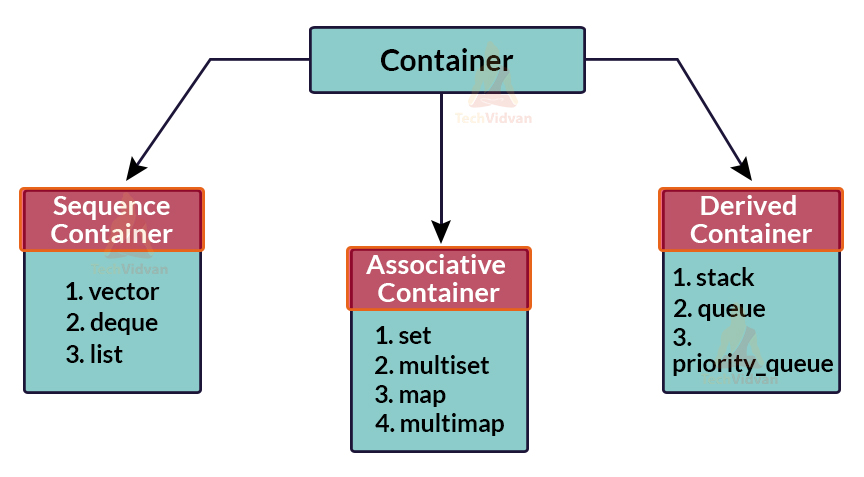
STL Containers Classifications
- Sequence Containers:- Vector, deque and list.
- Associative Containers:- Set, multiset, map and multimap.
- Derived Containers:- Stack, queue and priority_queue.
2. STL Iterator
The main purpose of iterators is to step through the elements of collections of objects. You can say that, iterators are pointer-like entities. And with the help of iterators, you can access individual elements in a container.
Iterators are made of mainly two functions:-
- begin():- This function helps you to return an iterator to the first element of the vector.
- end():- Returns an iterator to the last element of a container.
Categories of Iterators in C++ STL
1. Input Iterators:– It is used to read the values from a container. It is a one way iterator. You can increment an input iterator but it cannot be decremented.
2. Output Iterator:- It is used to modify the value of a container. But you cannot read a value from a container by using an output iterator. It is also a one way iterator. And it is only a write-only iterator.
3. Forward Iterator:– With the help of a forward iterator, you can navigate through the container one at a time using the ++ operator.
4. Bidirectional Iterator:– It is similar to the forward iterator but it also moves in backward direction. It is a two way iterator.
5. Random Access Iterator:– It is used to access a random element of a container. It is similar to the bidirectional iterator and it also has an additional feature such as pointer addition.
| iterator | Element access | Read | Write | Increment operation | Comparison |
| input | -> | v = *p | ++ | ==,!= | |
| output | *p = v | ++ | |||
| forward | -> | v = *p | *p = v | ++ | ==,!= |
| Bidirectional | -> | v = *p | *p = v | ++,– | ==,!= |
| Random access | ->,[ ] | v = *p | *p = v | ++,–,+,-,+=,–= | ==,!=,<,>,<=,>= |
3. Algorithms
Algorithms mainly act on containers. With the help of algorithms, you can perform initialization, sorting, searching and transforming of the elements of the containers. Using algorithms, you can save a lot of time and effort. To access the STL algorithms, you have to include the <algorithm> header file in the program code. To perform the complex operations, it provides 60 algorithm functions.
Algorithms can be further classified into:-
a. Mutating Algorithms:– Using this, you can change the value of a container. Using mutating algorithms, you can alter the order of the elements.
b. Non Mutating Algorithms:– You cannot change the value of a container and also cannot change the order of the elements.
c. Sorting Algorithms:– Used to sort the elements in a container.
d. Set Algorithms:– With this, you can perform some operations on a container which will help you in great efficiency. Also known as sorted range algorithms.
e. Relational Algorithms:– With the help of these algorithms, you can work with numeric datas. With this, you can perform all the mathematical operations to the elements of a container.
4. Function Objects in STL
STL includes classes that overload the function call operator. Function objects or Functors are the instances of such classes. Function object is a smart pointer and it has many advantages over the normal function.
Advantages of using the function objects
- It can have member functions and member attributes.
- It can be initialized before using it.
- Function objects are faster than the normal functions.
Example:-
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class func
{
public:
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a/b;
}
};
int main()
{
func fun;
int res = fun(10,5);
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
Output:-
2
In the above, fun is an object of the func class which defines an operator() function. So, you can use the fun object as a function to call the operator() function.
Example:- vector container
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v;
int x;
cout << "Size of vector: " << v.size() << endl;
for(x = 0; x < 2; x++) {
v.push_back(x);
}
cout << "Size extended: " << v.size() << endl;
for(x = 0; x < 2; x++) {
cout << "value of v["<<x<<"]: " << v[x] << endl;
}
vector<int>::iterator ve = v.begin();
while( ve != v.end()) {
cout << "value: " << *ve << endl;
ve++;
}
return 0;
}
Output:-
Size of vector: 0
Size extended: 2
value of v[0]: 0
value of v[1]: 1
value: 0
value: 1
Summary
In this tutorial, we discussed the C++ STL and its various components. We discussed why you should use function objects over normal functions. We also discussed various categories of iterators.
