Numpy hstack(), vstack(), reshape(), and flatten() Function
If you’re diving into the world of data manipulation and analysis using Python, you’ll likely come across the powerful numpy library. Numpy provides a varied range of functions and tools for working with arrays, and in this tutorial, we’ll explore four essential functions: numpy.hstack(), numpy.vstack(), numpy.reshape(), and numpy.flatten(). These functions are extremely crucial for reshaping and combining arrays, which is a basic necessity in data preprocessing and analysis.
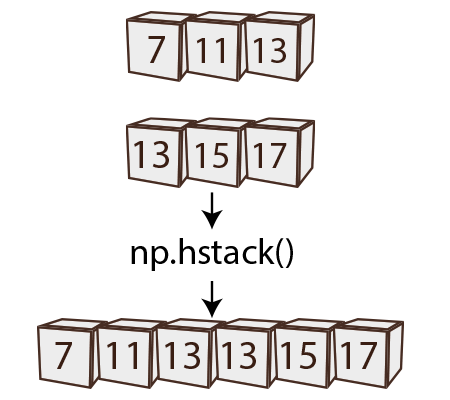
1. numpy.hstack()
numpy.hstack() stands for “horizontal stack”. It’s used to concatenate multiple arrays horizontally, meaning it combines arrays side by side.
When you use numpy.hstack(), the arrays within the tuple are combined along the second axis (axis 1), effectively joining their columns. It’s important that the arrays being stacked have compatible shapes along this axis.
Syntax:
numpy.hstack(tup)
tup: A tuple of arrays to be stacked horizontally.
Diagram:
Example:
import numpy as np array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) array2 = np.array([4, 5, 6]) horizontal_stack = np.hstack((array1, array2)) print(horizontal_stack)
Output:
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
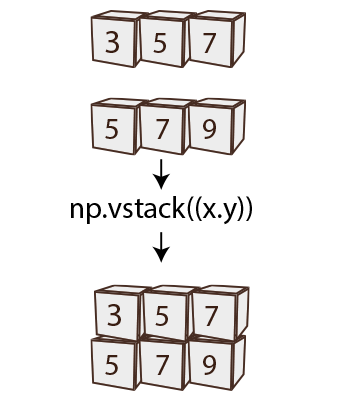
2. numpy.vstack()
numpy.vstack() stands for “vertical stack”. It’s used to concatenate multiple arrays vertically, meaning it stacks arrays on top of each other.
When you use numpy.vstack(), the arrays within the tuple are combined along the first axis (axis 0), effectively joining their rows. The arrays being stacked must have the same number of columns.
Syntax:
numpy.vstack(tup)
tup: A tuple of arrays to be stacked vertically.
Diagram:
Example
import numpy as np array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) array2 = np.array([4, 5, 6]) vertical_stack = np.vstack((array1, array2)) print(vertical_stack)
Output:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
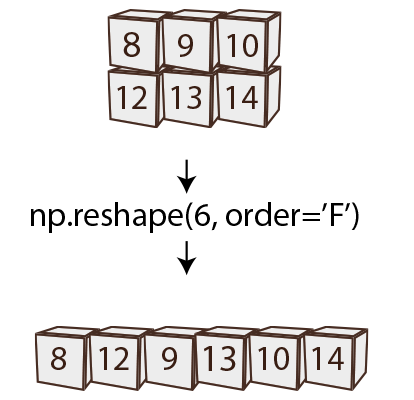
3. numpy.reshape()
numpy.reshape() is used to change the shape of an array without changing its data. This can be incredibly useful for converting between 1D, 2D, and higher-dimensional arrays.
numpy.reshape() alters the arrangement of elements in the array according to the new shape specified. It doesn’t modify the data itself, just the view of it. The new shape must have the same total number of elements as the original array.
Syntax
numpy.reshape(a, newshape)
a: The array to be reshaped.
newshape: The new shape you want for the array, represented as a tuple of integers.
Diagram:
Example
import numpy as np original_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) reshaped_array = np.reshape(original_array, (2, 3)) print(reshaped_array)
Output:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
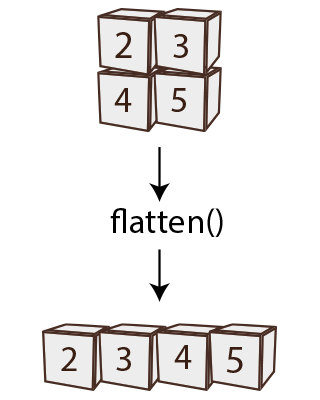
4. numpy.flatten()
numpy.flatten() is used to convert a multi-dimensional array into a 1D array.
numpy.flatten() collapses a multi-dimensional array into a 1D array by iterating through the elements in row-major order (unless otherwise specified). This can be helpful for certain operations or when dealing with algorithms that require 1D data.
Syntax
numpy.flatten(order='C')
order: The order in which the elements should be flattened. ‘C’ means row-major (default), and ‘F’ means column-major.
Diagram:
Example
import numpy as np multi_dimensional_array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) flattened_array = multi_dimensional_array.flatten() print(flattened_array)
Output:
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully completed this tutorial on NumPy’s hstack, vstack, flatten, and reshape functions. By mastering these array manipulation techniques, you’ve gained powerful tools to efficiently manage and transform data in Python. From combining arrays to reshaping their structures, you’re now equipped to handle diverse data challenges with confidence. Happy Coding with TechVidvan!