chgrp command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
03 Nov, 2025
The `chgrp` command in Linux is used to change the group ownership of a file or directory. All files in Linux belong to an owner and a group. You can set the owner by using “chown” command, and the group by the "chgrp" command.
Here is the example of Changing Group Ownership of a Single File
sudo chgrp geeksforgeeks abc.txt
 For a single File
For a single FileHere the group name of the file abc.txt was changed from kcVirtual to geeksforgeeks. Note that when files are created the groupname of the file is the same as the owner under which the file was created.
Syntax of `chgrp` command in Linux
chgrp [OPTION]… GROUP FILE…chgrp [OPTION]… –reference=RFILE FILE…
Options available in `chgrp` command in Linux
First, we need to have administrator permission to add or delete groups. We can login as root for this purpose or use sudo. In order to add a new group, we can use:
sudo addgroup geeksforgeeks
1. `-c` or `--changes` Option
To describe the action for each File whose group actually changes.
Example:
sudo chgrp -c geeksforgeeks f1
 -c
-c2. `-f` Option
To suppress error messages.
Example:
sudo chgrp -f geeksforgeeks f2
 -f
-f3. `-v` Option
To describe the action or non-action taken for every File.
Example:
sudo chgrp -v geeksforgeeks f1
 -v
-v4. `--dereference` or `--no-dereference` Option
To change the group name of link files.
Example:
sudo chgrp --dereference geeksforgeeks symbolic_link
 --dereference
--dereferenceHere, symbolic_link is the link file for f1. When using the --dereference option, the group ownership of the actual file pointed to by symbolic_link gets changed.
Example:
sudo chgrp --no-dereference geeksforgeeks symbolic_link
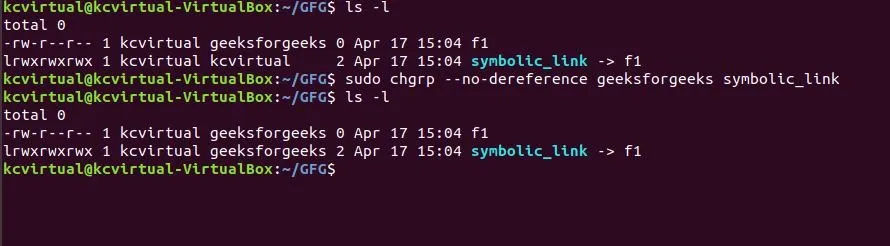
Here, symbolic_link is the link file for f1. When using the --no-dereference option, the group ownership of the symbolic_link itself is changed, rather than the target file it points to.
Examples of chgrp Command
Example 1: Changing Group Ownership of Multiple Files
The 'chgrp' command can also handle multiple files at once. For instance:
chgrp developers file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
Here, 'file1.txt', 'file2.txt', and 'file3.txt' will all be assigned to the 'developers' group.
Example 2: Changing Group Ownership of a Directory or Folder
To change the group ownership of a folder.
sudo chgrp geeksforgeeks GFG
 For directory or folder
For directory or folderExample 3: Recursively change the group ownership of a folder
To recursively change the group ownership of a folder and all of its contents.
sudo chgrp -R geeksforgeeks GFG
 Recursively
Recursively- As we can see the group of the folder GFG and its contents F1, F2 was all kcvirtual initially and they were changed to geeksforgeeks with the single command.
Example 4: Using the groupname of a reference file
Using the groupname of a reference file to change the group of another file or folder.
sudo chgrp -R --reference=abc.txt GFG
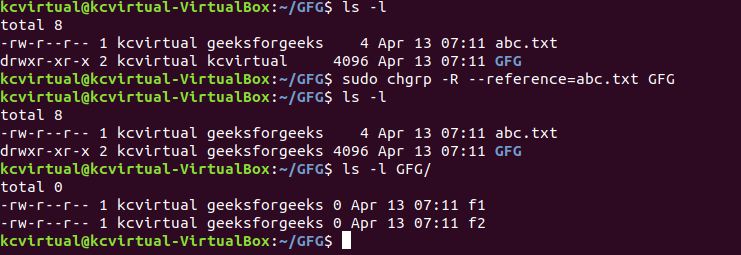 reference file
reference fileThe groupname of the reference file abc.txt was used to recursively change the group of the folder GFG and all its contents using the --reference option.
Which command changes the group ownership of the file notes.txt to the group students?
-
-
-
chown :students notes.txt
-
Explanation:
chgrp group file changes only the group ownership.
Which command updates the group of multiple files (a.txt, b.txt) to devteam?
-
chgrp devteam a.txt b.txt
-
chgrp -R devteam a.txt b.txt
-
chgrp -v a.txt b.txt devteam
-
Explanation:
Passing multiple files directly after the group applies group ownership to all of them.
Which command ensures that a symbolic link itself, and not the file it points to, receives the updated group ownership engineers?
-
chgrp --dereference engineers linkfile
-
-
chgrp --no-dereference engineers linkfile
-
chgrp -R engineers linkfile
Explanation:
--no-dereference updates only the symlink, not the referenced target.
Which command recursively applies the group of the reference file template.cfg to the directory project/ and all of its contents?
-
chgrp -R --reference=template.cfg project/
-
chgrp --from=template.cfg -R project/
-
chgrp -v project/ template.cfg
-
chgrp --copy-group template.cfg project/
Explanation:
--reference=file copies the group, and -R applies it recursively.
You must update the group ownership of /srv/archive to backupops, but only report files whose group actually changed, ignoring unchanged items. Which command accomplishes this with strict change-logging semantics?
-
chgrp -v backupops /srv/archive
-
chgrp -c backupops /srv/archive
-
chgrp --from=backupops -c /srv/archive
-
chgrp -f -c backupops /srv/archive
Explanation:
-c reports only when a file’s group actually changes, making the output concise and accurate.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Linux Administrator System