RESTful Blogging API with Node and Express.js
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Blogs Websites have become very popular nowadays for sharing your thoughts among the users over internet. In this article, you will be guided through creating a Restful API for the Blogging website with the help of Node, Express, and MongoDB.
Prerequisites:
Approach to Creating Restful Blogging App:
- To create a Restful Blog API, first, we will have to define how much field is required for the blog and then create the blog schema according to that.
- Create a collection in the MongoDB to store the blogs.
- Connect the application with MongoDB and create routes of creating, editing, deleting, and viewing the blogs, and to save it in the database.
- The application must do CRUD operation so that the content of the blogs can easily be manipulated and managed.
Steps to Create the Project:
Step 1: First check if the node and npm is installed in your system.
node -v
npm -v
Step 2: Create the folder for your application.
mkdir BLOG-API
cd BLOG-API
Step 3: To initialize the node project run the following command.
npm init -y
It will initialize your project and create a package.json file containing your project details.
Step 4: Install the required dependencies for the project.
npm i express mongoose nodemon
Dependencies: You can verify the all required dependencies are installed in package.json
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.18.2",
"mongoose": "^8.2.0",
"nodemon": "^3.1.0"
}Folder Structure:
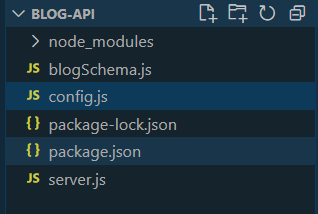
Step 5: Create a server.js file and start the server with the following command.
nodemon server.js
Step 6: Create a Database:
So we will use MongoDB Compass to create our blog_api database on our laptop/pc.
- Installed and opened the MongoDB Compass
- Click on the connect button to connect [localhost](http://localhost/) Database
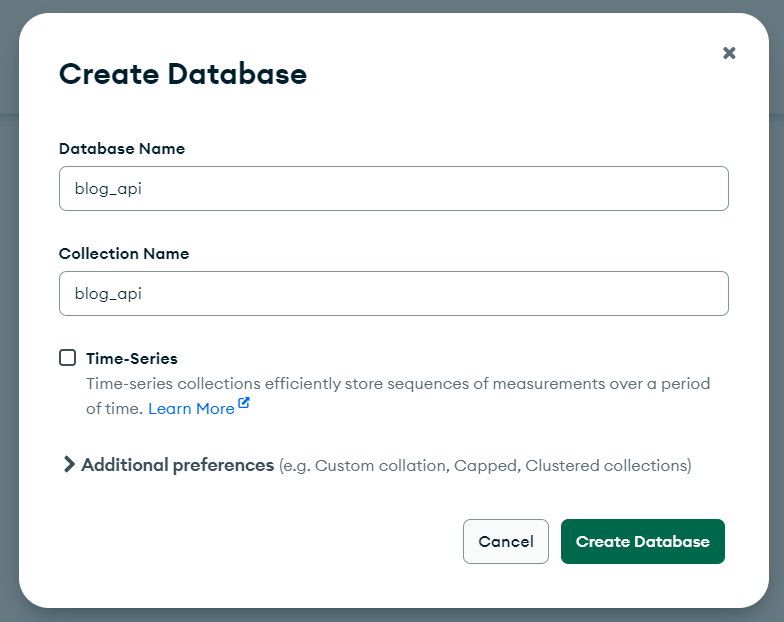
- Now it is time to create a blog_api database
 create-db
create-db- Click on connect to create database
 db_create
db_createDatabase is created successfully.
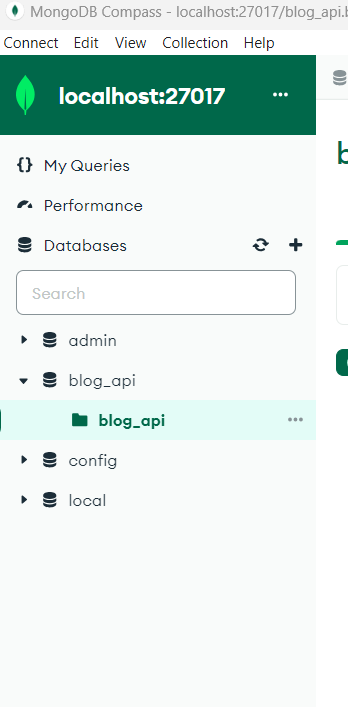 database
databaseStep 7: Connecting MongoDB to the Application
- For this, we will create a new file ‘config.js’ in the same folder and write the implementation code there after that, we will connect this file to our server.js file.
JavaScript
//config.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
await mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/blog_api");
console.log("MongoDB connected");
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.message);
process.exit(1);
}
};
module.exports = connectDB;
- Connect the application to MongoDB using Mongoose by adding the below code to the server.js file
JavaScript
const connectDB = require("./config");
connectDB();
- Now run the server.js file to check Database is Connected or not ?
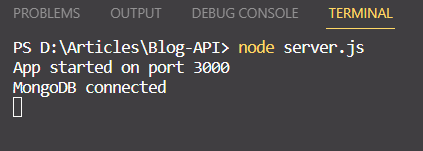 connect_db
connect_dbStep 8: Define the Blog schema using Mongoose.
- blog schema includes title, content & author field
JavaScript
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const blogSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: String,
content: String,
author: String,
created_at: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
});
const Blog = mongoose.model("Blog", blogSchema);
module.exports = Blog;
Step 9: Implement CRUD operations:
1. Create a Blog:
JavaScript
app.post("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.create(req.body);
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This route handler for creating a new blog post.
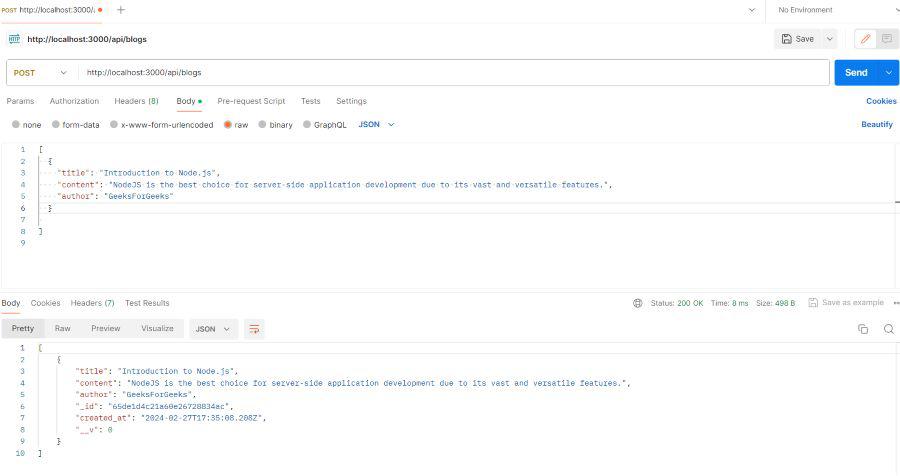 create_post
create_post2. Get All Blog:
JavaScript
app.get("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blogs = await Blog.find();
res.json(blogs);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This route handler for fetching all blog posts.
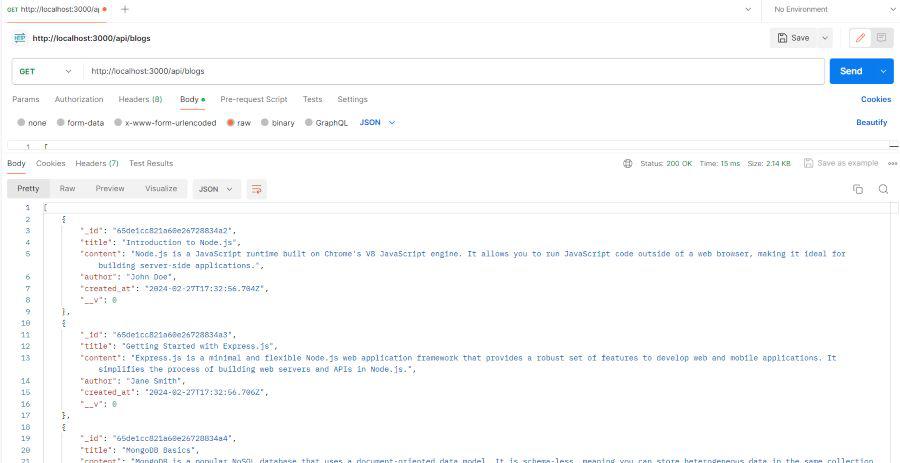 get_all
get_all3. Get Blog by Id:
JavaScript
app.get("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findById(req.params.id);
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This route handler for fetching a single blog post by its id from the database.
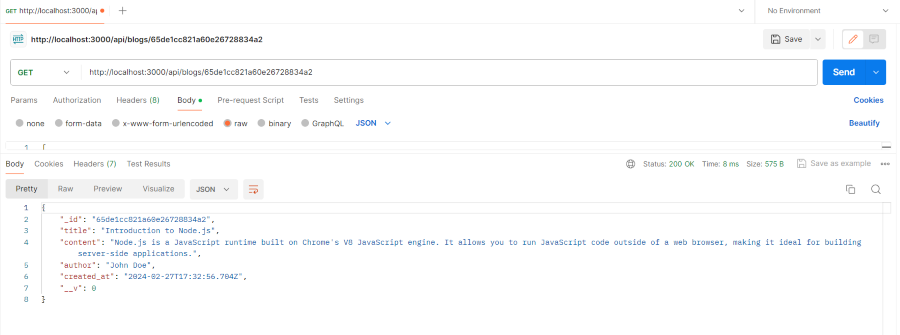 get_by_id
get_by_id4. Edit Blog:
JavaScript
app.put("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, req.body, {
new: true,
});
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This route handler allows updating a blog post by its id.
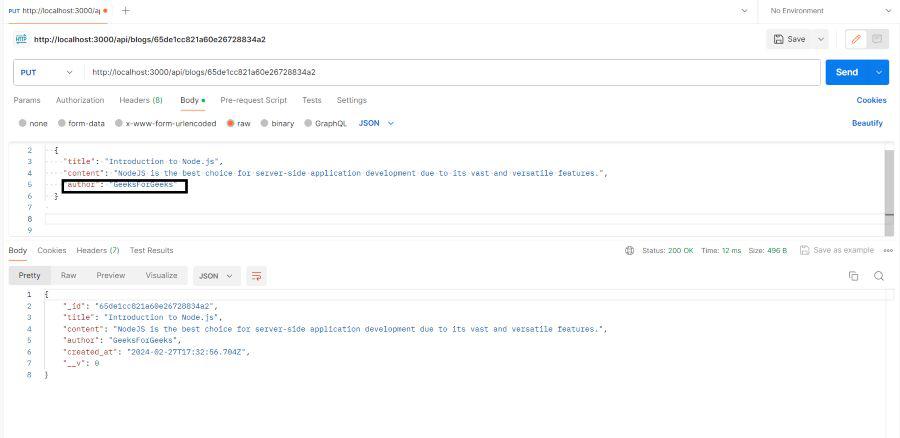 edit
edit5. Delete All Blog:
JavaScript
app.delete("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
await Blog.deleteMany();
res.json({ message: "All blogs deleted successfully" });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This route handler deletes all blog posts.
 delete-all
delete-all6. Delete Blog by Id:
JavaScript
app.delete("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id);
res.json({ message: "Blog deleted successfully", deletedBlog: blog });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
- This is a route handler for deleting a blog post by id using Mongoose in a Node.js/Express application.
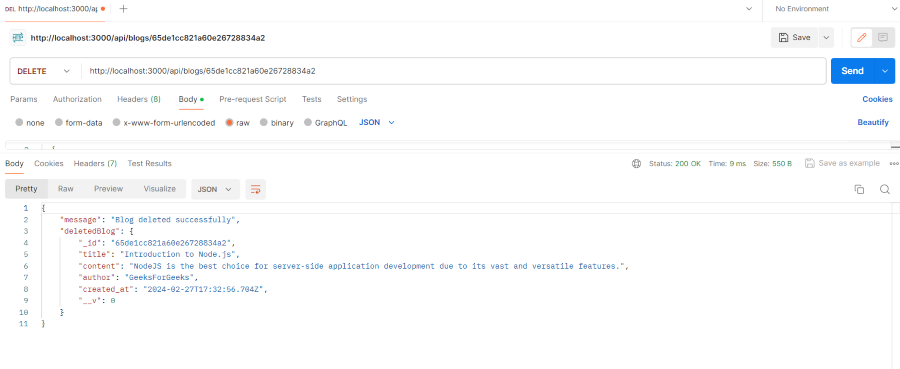 deletebyid
deletebyidFinal Code:
JavaScript
//server.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const connectDB = require("./config");
const Blog = require('./blogSchema')
app.use(express.json());
connectDB();
app.post("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.create(req.body);
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
app.get("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blogs = await Blog.find();
res.json(blogs);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
app.get("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findById(req.params.id);
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
app.put("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, req.body, {
new: true,
});
res.json(blog);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
app.delete("/api/blogs", async (req, res) => {
try {
await Blog.deleteMany();
res.json({ message: "All blogs deleted successfully" });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
app.delete("/api/blogs/:id", async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id);
res.json({ message: "Blog deleted successfully", deletedBlog: blog });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5000;
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`));
//blogSchema.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const blogSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: String,
content: String,
author: String,
created_at: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
});
const Blog = mongoose.model("Blog", blogSchema);
module.exports = Blog;
//config.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
await mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/blog_api");
console.log("MongoDB connected");
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.message);
process.exit(1);
}
};
module.exports = connectDB;
Output:
Conclusion:
Creating a RESTful API for a blogging website using Node.js, Express, and MongoDB involves setting up a Node project with necessary dependencies, connecting to MongoDB for data storage, defining a Mongoose schema for blogs, and implementing CRUD operations. This approach allows for efficient management of blog posts through endpoints for creating, reading, updating, and deleting content, ensuring a scalable and robust backend solution for a blogging application.
Explore
Introduction & Installation
Node.js Modules , Buffer & Streams
Node.js Asynchronous Programming
Node.js NPM
Node.js Deployments & Communication
Resources & Tools