Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Python3 1==
Python3 1==
Output:
 Example #2: Using
Example #2: Using
Python3 1==
Output:

Dataframe.add_prefix() function can be used with both series as well as dataframes.
- For Series, the row labels are prefixed.
- For DataFrame, the column labels are prefixed.
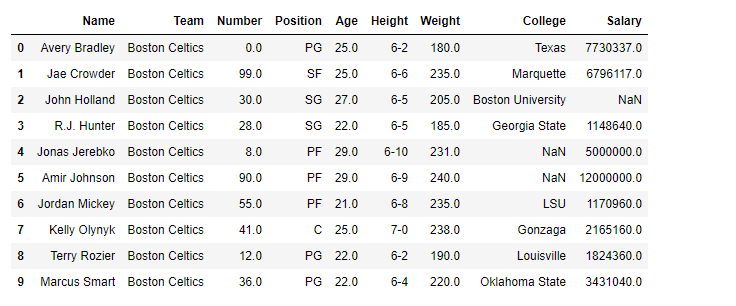
Syntax: DataFrame.add_prefix(prefix) Parameters: prefix : string Returns: with_prefix: type of callerFor link to CSV file Used in Code, click here Example #1: Prefix
col_ in each columns in the dataframe
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Making data frame from the csv file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
# Printing the first 10 rows of the
# dataframe for visualization
df[:10]

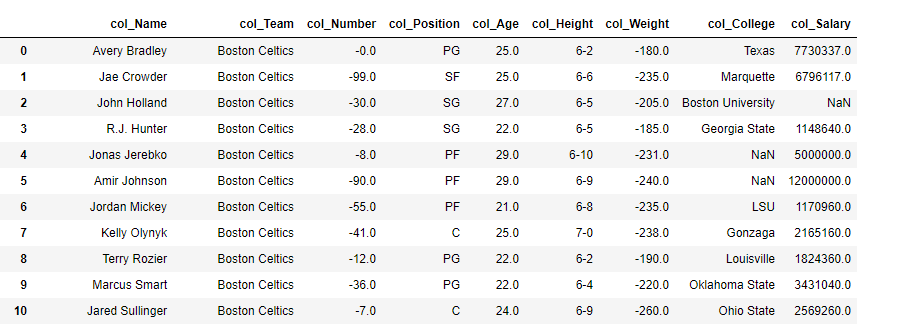
# Using add_prefix() function
# to add 'col_' in each column label
df = df.add_prefix('col_')
# Print the dataframe
df
 Example #2: Using
Example #2: Using add_prefix() with Series in pandas
add_prefix() alters the row index labels in the case of series.
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating a Series
df = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 21, 4])
# This will prefix 'Row_' in
# each row of the series
df = df.add_prefix('Row_')
# Print the Series
df
