Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Python3 1==
Python3 1==
Output:
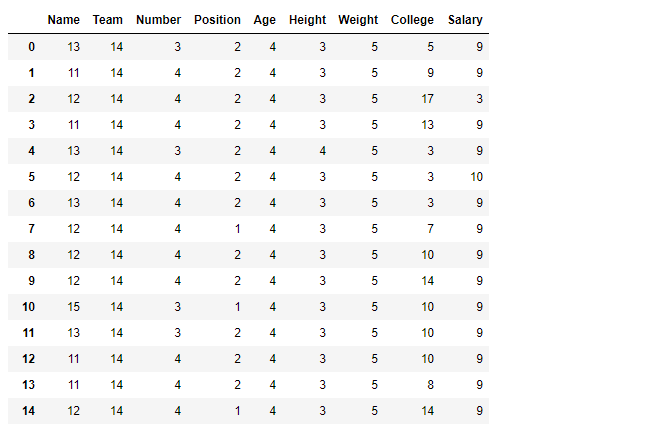 Notice how all nan value has been converted to string nan and their length is evaluated to be 3.
Example #2: Append
Notice how all nan value has been converted to string nan and their length is evaluated to be 3.
Example #2: Append
Python3 1==
Output:
Dataframe.applymap() method applies a function that accepts and returns a scalar to every element of a DataFrame.
Syntax: DataFrame.applymap(func) Parameters: func: Python function, returns a single value from a single value. Returns: Transformed DataFrame.For link to CSV file Used in Code, click here Example #1: Apply the
applymap() function on the dataframe to find the no. of characters in all cells.
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Making data frame from the csv file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
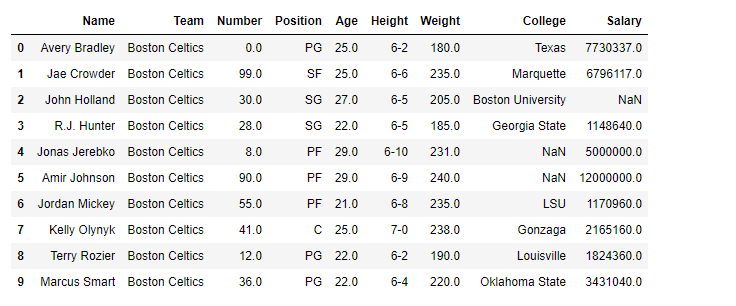
# Printing the first 10 rows of
# the data frame for visualization
df[:10]

# Using lambda function we first convert all
# the cell to a string value and then find
# its length using len() function
df.applymap(lambda x: len(str(x)))
 Notice how all nan value has been converted to string nan and their length is evaluated to be 3.
Example #2: Append
Notice how all nan value has been converted to string nan and their length is evaluated to be 3.
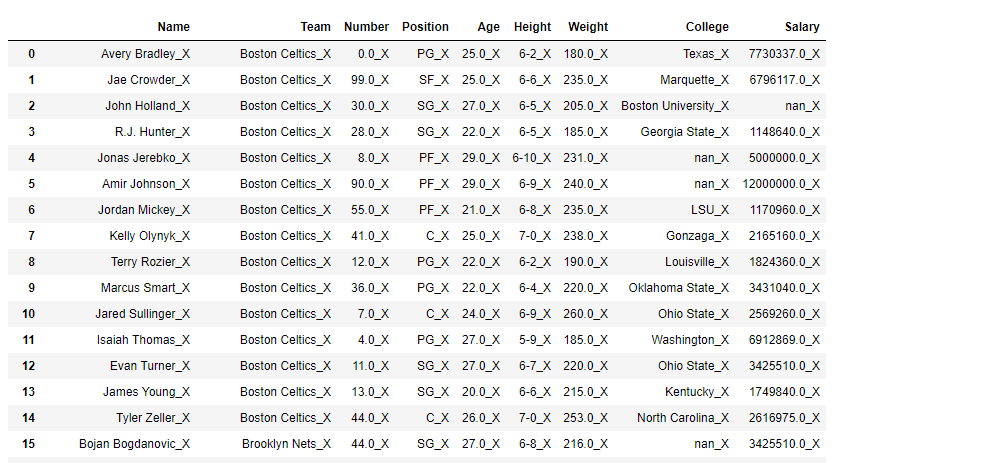
Example #2: Append _X in each cell using applymap() function.
In order to append _X in each cell, first convert each cell into a string.
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Making data frame from the csv file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
# Using applymap() to append '_X'
# in each cell of the dataframe
df.applymap(lambda x: str(x) + '_X')
