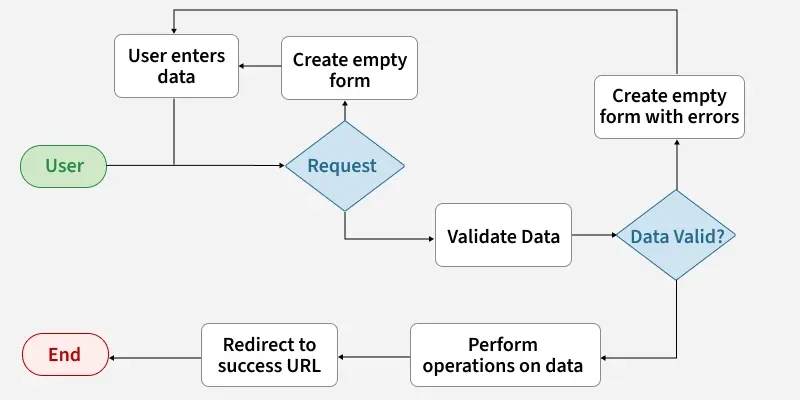
Django Forms are used to collect input from users, check if the input is correct, and process the data.
- Gather information through form fields such as text, email, or password.
- Automatically validate the data before processing.
- Can save the cleaned data to the database when needed.
- Provide a clean way to handle user input in web applications.
 Django Forms
Django Forms field_name = forms.FieldType(**options)
- field_name: Name of the form field.
- FieldType: Type of the field (e.g., CharField, EmailField, IntegerField).
- options: Optional keyword arguments such as max_length, required, initial, label, etc.
Before creating forms, make sure a Django project and app are already set up. Creating a form in Django is very similar to creating a model, it requires specifying the fields that the form will contain and their types.
To create a form, create a "forms.py" file in app folder:
Python
from django import forms
class InputForm(forms.Form):
first_name = forms.CharField(max_length=200)
last_name = forms.CharField(max_length=200)
roll_number = forms.IntegerField(help_text="Enter 6 digit roll number")
password = forms.CharField(widget=forms.PasswordInput())
Django form fields have several built-in methods to ease the work of the developer but sometimes one needs to implement things manually for customizing User Interface(UI). A form comes with 3 in-built methods that can be used to render Django form fields.
To render this form into a view, Create a home_view in views.py:
Python
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import InputForm
def home_view(request):
context = {}
context['form'] = InputForm()
return render(request, "home.html", context)
After defining the view, configure the URL patterns to connect it. Next, create an instance of the form class inside the view and set up a templates/home.html file to render the form and display it to users.
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Django Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Student Registration Form</h2>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Visit: http://localhost:8000/
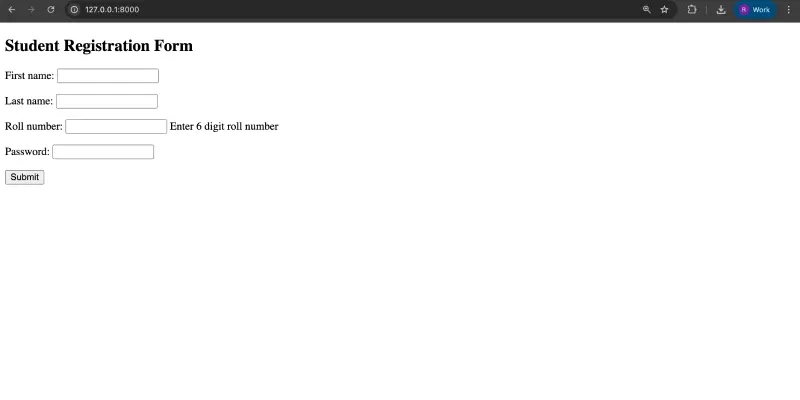 Basic-Django-forms
Basic-Django-formsDjango ModelForm is a class used to directly convert a model into a Django form. In database-driven applications, forms often map closely to Django models.
Once the project is ready, create a model in geeks/models.py:
Python
from django.db import models
# declare a new model with a name "GeeksModel"
class GeeksModel(models.Model):
# fields of the model
title = models.CharField(max_length = 200)
description = models.TextField()
last_modified = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True)
img = models.ImageField(upload_to = "images/")
# renames the instances of the model
# with their title name
def __str__(self):
return self.title
To create a form directly for this model, in geeks/forms.py:
Python
# import form class from django
from django import forms
# import GeeksModel from models.py
from .models import GeeksModel
# create a ModelForm
class GeeksForm(forms.ModelForm):
# specify the name of model to use
class Meta:
model = GeeksModel
fields = "__all__"
By visiting http://127.0.0.1:8000/, the form will be displayed and users can input data according to the fields defined in the model.
Django Forms provide a high-level interface for handling user input, rendering form elements, validating data, and processing submissions securely.
- Automatic field generation: Form fields are created and mapped to appropriate HTML input elements, reducing manual coding.
- Easy rendering: Django can render complete forms using helpers like {{ form.as_p }}, simplifying template integration.
- Built-in validation: Ensures submitted data is clean, complete, and correctly formatted without extra logic.
- Smooth model integration: Works seamlessly with Django models, enabling quick data saving and retrieval.
- Strong security: Includes CSRF protection and sanitizes input to prevent malicious data submission.
- Better maintainability: Centralizes form logic, making forms easier to update and debug as the application grows.
The most important part of a form and the only required part is the list of fields it defines. Fields are specified by class attributes. Here is a list of all Form Field types used in Django
Note: NullBooleanField (a boolean field that allowed True, False, or NULL) is deprecated. Use BooleanField(null=True, blank=True) instead.
Core Field Arguments
Core Field arguments are parameters provided to each field in a model to apply constraints or impart specific characteristics.For example, adding required=False to a CharField allows the field to be left blank by the user.
Each Field class constructor accepts at least these core arguments. Some Field classes may also accept additional, field-specific arguments, but the following are always supported:
| Field Options | Description |
|---|
| required | By default, each Field class assumes the value is required, so to make it not required you need to set required=False |
|---|
| label | The label argument lets you specify the “human-friendly” label for this field. This is used when the Field is displayed in a Form. |
|---|
| label_suffix | The label_suffix argument lets you override the form’s label_suffix on a per-field basis. |
|---|
| widget | The widget argument lets you specify a Widget class to use when rendering this Field. See Widgets for more information. |
|---|
| help_text | The help_text argument lets you specify descriptive text for this Field. If you provide help_text, it will be displayed next to the Field when the Field is rendered by one of the convenience Form methods.
|
|---|
| error_messages | The error_messages argument lets you override the default messages that the field will raise. Pass in a dictionary with keys matching the error messages you want to override. |
|---|
| validators | The validators argument lets you provide a list of validation functions for this field.
|
|---|
| localize | The localize argument enables the localization of form data input, as well as the rendered output. |
|---|
| disabled. | The disabled boolean argument, when set to True, disables a form field using the disabled HTML attribute so that it won’t be editable by users.
|
|---|
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice