How to use sys.argv in Python
Last Updated :
08 Dec, 2025
In Python, sys.argv is used to handle command-line arguments passed to a script during execution. These arguments are stored in a list-like object, where the first element (sys.argv[0]) is the name of the script itself and the rest are arguments provided by the user.
This feature is helpful when you want to make your Python script interactive with input provided at runtime from the command line.
What is the sys Module?
The sys module in Python provides access to some variables used or maintained by the interpreter. It includes tools to interact with the runtime environment and sys.argv is one such variable used to handle command-line arguments.
Examples of sys.argv
Example 1: Basic Use of sys.argv
Python
import sys
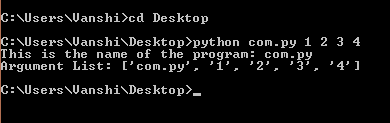
print("This is the name of the program:", sys.argv[0])
print("Argument List:", str(sys.argv))
Output
Explanation:
- sys.argv[0] returns the name of the script.
- str(sys.argv) prints the list of all command-line arguments including the script name.
Use the following command to run the script:
python script_name.py arg1 arg2
Commonly Used Functions with sys.argv
Python
import sys
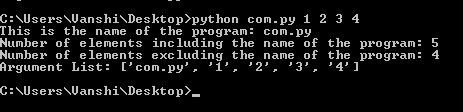
print("This is the name of the program:", sys.argv[0])
print("Number of elements including the name of the program:", len(sys.argv))
print("Number of elements excluding the name of the program:", len(sys.argv) - 1)
print("Argument List:", str(sys.argv))
Output
Explanation:
- len(sys.argv): gives the total number of command-line arguments.
- len(sys.argv) - 1: gives the number of actual arguments provided by the user, because sys.argv[0] is always the script name, not user input.
- str(): helps to display the list as a readable string.
Why Do We Exclude the Script Name?
sys.argv always stores the script name at index 0. So if you run: python script.py arg1 arg2. Then: sys.argv = ['script.py', 'arg1', 'arg2']. Here:
- len(sys.argv): 3 (script name + 2 arguments)
- len(sys.argv) - 1: 2 (only user-provided arguments)
That’s why we subtract 1 to ignore the script name and count only actual inputs from the user.
Example 2: Adding Numbers Using Command Line Arguments
Python
import sys
add = 0.0
n = len(sys.argv)
# Start from index 1 to skip the script name
for i in range(1, n):
add += float(sys.argv[i])
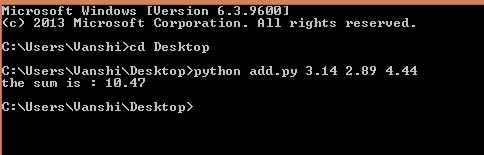
print("The sum is:", add)
Output
Explanation:
- This script accepts numeric inputs via command-line arguments.
- Converts them to float and adds them.
- Indexing starts from 1 to skip the script name.
Use the following command to run the script:
python script_name.py 3.5 4.2 2.3
Related articles: sys module
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice