List View - Function based Views Django
Last Updated :
18 Nov, 2025
A List View is used to show multiple records from a database, such as posts, products, or users.
- Retrieves all required records from the database.
- Passes the data to a template for rendering.
- Displays the records in a clear format like a list or table.
- Provides an easy way to show collections of items on a page.
Example: Consider a project named 'geeksforgeeks' having an app named 'geeks'. After creating the project and app, the next step is to create a model, whose records will be displayed using the List View.
Step 1: Define a Model
In geeks/models.py:
Python
from django.db import models
class GeeksModel(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
description = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.title
Step 2: Apply Migrations
Run the following commands to create the corresponding database table
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
Step 3: Create Sample Data
Use Django's shell to create model instances:
python manage.py shell
Enter following commands in shell:
from geeks.models import GeeksModel
GeeksModel.objects.create(title="title1", description="description1")
GeeksModel.objects.create(title="title2", description="description2")
GeeksModel.objects.create(title="title3", description="description3")
 Snapshot of the Command in Shell
Snapshot of the Command in ShellNow we have everything ready for back end. To verify that instances have been created, exit the shell using exit() command and run the development server using this command:
python manage.py runserver
After running the command, visit the development url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/
Step 4: Create the List View
In geeks/views.py, define a function-based view to fetch and render the model instances:
Python
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import GeeksModel
def list_view(request):
context = {
"dataset": GeeksModel.objects.all()
}
return render(request, "list_view.html", context)
Step 5: Create the Template
In templates/list_view.html, add the following HTML to display the data:
html
<div class="main">
{% for data in dataset %}
<h3>{{ data.title }}</h3>
<p>{{ data.description }}</p>
<hr/>
{% endfor %}
</div>
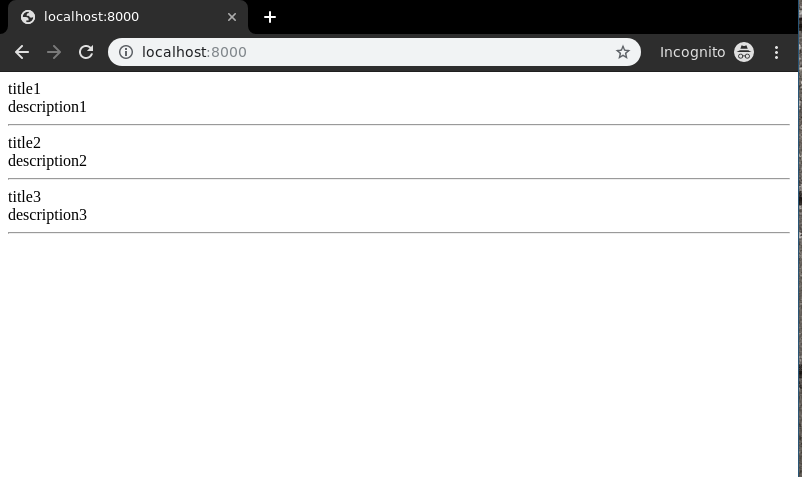
Run the development server and visit the URL http://127.0.0.1:8000/ to see the list view in action.
Output:
Sorting the List (Descending Order)
You can order the results in reverse (newest first) by modifying the view:
Python
def list_view(request):
context = {
"dataset": GeeksModel.objects.all().order_by("-id")
}
return render(request, "list_view.html", context)
order_by("-id"): sorts the items in descending order of their ID.
Output:

Filtering the List
You can also filter the data shown in the list view. For example, let’s add a new entry:
Launch the shell using the below command:
python manage.py shell
Enter the following commands in shell:
from geeks.models import GeeksModel
GeeksModel.objects.create(title = "Naveen", description = "GFG is Best").save()

To display only items with the word “title” in their title, update the view:
Python
def list_view(request):
context = {
"dataset": GeeksModel.objects.filter(title__icontains="title")
}
return render(request, "list_view.html", context)
title__icontains="title" filters entries whose title contains the word "title", case-insensitively.
Run the development server and visit the URL http://127.0.0.1:8000/ again to see the filtered output.

What does a function-based List View in Django typically do?
-
Shows a form to create a new record
-
Deletes all records of a model
-
Displays multiple records from a model in a list or table
-
Explanation:
A List View fetches all (or filtered) objects from the database and renders them in a template for display.
In a function-based List View, which code snippet correctly obtains all objects from a model named MyModel?
-
dataset = MyModel.objects.all()
-
dataset = MyModel.get_all()
-
dataset = MyModel.objects.filter()
-
dataset = MyModel.objects.list()
Explanation:
objects.all() returns a QuerySet of all instances of MyModel, which can then be passed to template context.
After fetching objects in a List View, how is the data typically sent to the template for rendering?
-
-
Using render(request, template_name, context) with context containing the dataset
-
Printing dataset directly to console
-
Returning HttpResponse(dataset)
Explanation:
The view sends the data via context dict to the template so that template engine can display each item in list format.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/3
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/3
1/3
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice