Python Falcon - API Testing
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Python Falcon is a lightweight and fast web framework designed for building RESTful APIs. When it comes to API testing, Falcon provides a straightforward and efficient way to interact with your API endpoints. In this article, we'll explore three simple examples using Python Falcon: a basic API endpoint, form submission, and file upload with display.
Python Falcon - API Testing
Below, are the examples of Python Falcon - API Testing Tools.
Example 1: Basic API Endpoint
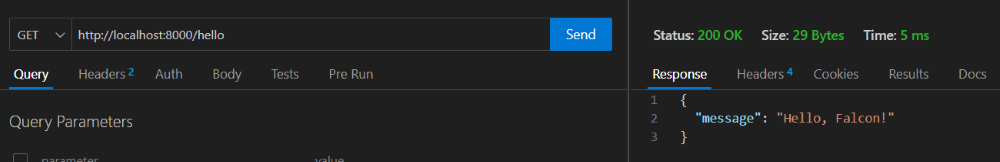
In this example, we've created a resource class HelloWorldResource with an on_get method, which is called when a GET request is made to the /hello endpoint. The response contains a JSON object with a greeting message.
Python3
import falcon
class HelloWorldResource:
def on_get(self, req, resp):
resp.status = falcon.HTTP_200
resp.media = {'message': 'Hello, Falcon!'}
# Create a Falcon application
app = falcon.App()
# Add a route for the HelloWorldResource
app.add_route('/hello', HelloWorldResource())
if __name__ == '__main__':
from wsgiref import simple_server
# Run the Falcon app
host = 'localhost'
port = 8000
httpd = simple_server.make_server(host, port, app)
print(f'Starting Falcon app on http://{host}:{port}')
httpd.serve_forever()
Output :
Example 2: Message Passing
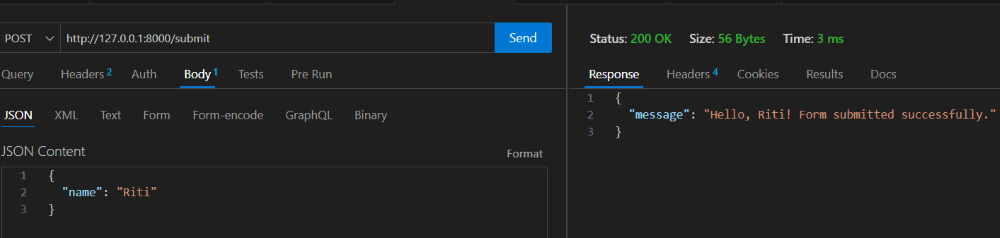
In this example, we've created a resource class FormSubmitResource with an on_post method, which is triggered when a POST request is made to the /submit endpoint. The submitted form data is accessed using req.media, and a personalized response is sent back.
Python3
import falcon
class FormSubmitResource:
def on_post(self, req, resp):
data = req.media
name = data.get('name', 'Guest')
resp.status = falcon.HTTP_200
resp.media = {'message': f'Hello, {name}! Form submitted successfully.'}
# Create a Falcon application
app = falcon.App()
# Add a route for the FormSubmitResource
app.add_route('/submit', FormSubmitResource())
if __name__ == '__main__':
from wsgiref import simple_server
# Run the Falcon app
host = 'localhost'
port = 8000
httpd = simple_server.make_server(host, port, app)
print(f'Starting Falcon app on http://{host}:{port}')
httpd.serve_forever()
Output :
Example 4: Query Parameters Handling
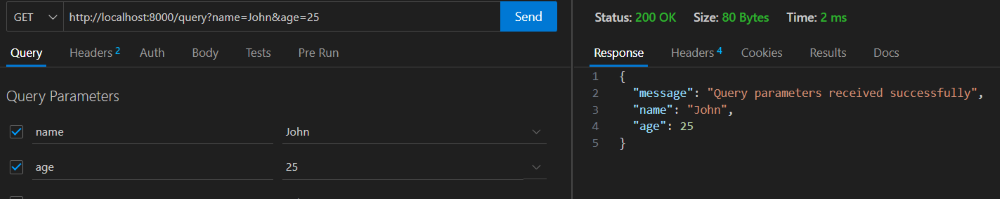
In this example, we've created a resource class QueryParamsResource with an on_get method. The method retrieves query parameters using Falcon's req.get_param and req.get_param_as_int methods. It then processes the parameters and generates a response JSON object.
Python3
import falcon
class QueryParamsResource:
def on_get(self, req, resp):
# Retrieve query parameters
name = req.get_param('name', default=None)
age = req.get_param_as_int('age', default=None)
# Process parameters and generate response
response = {'message': 'Query parameters received successfully'}
if name:
response['name'] = name
if age is not None:
response['age'] = age
resp.status = falcon.HTTP_200
resp.media = response
app.add_route('/query', QueryParamsResource())
Output :
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice