Progress Bar Widget in Kivy
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2025
A ProgressBar in Kivy is a display-only widget used to visualize the progress of a task. It currently supports only horizontal mode. The progress can be updated programmatically by changing the value property. Let's add a simple Progress Bar to a Kivy window.
Below program adds a horizontal progress bar to the Kivy window and sets a value to show progress.
Python
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.progressbar import ProgressBar
from kivy.uix.widget import Widget
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.clearcolor = (1, 1, 1, 1)
class BasicProgressBar(Widget):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
cx = Window.width / 2
self.pb = ProgressBar(max=100, value=50, size_hint=(None, None), width=300, height=30,pos=(cx - 150, Window.height - 100))
self.add_widget(self.pb)
class ProgressBarApp(App):
def build(self):
return BasicProgressBar()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ProgressBarApp().run()
Output

Explanation:
- ProgressBar(max=100, value=50): sets the maximum and current progress.
- size_hint=(None, None) and pos=(...): manually place the progress bar in the window.
- add_widget(pb): adds the progress bar to the Kivy window.
Syntax
ProgressBar(max=100, value=0, size_hint=(None,None), width=200, height=30)
Parameters:
- max: Maximum allowed value (default 100).
- value: Current value of the progress bar.
- size_hint, width, height: manual sizing.
Examples
Example 1: This program adds a button. Clicking it opens a popup containing a progress bar, which fills over time.
Python
Window.clearcolor = (0.98, 0.98, 1, 1)
class ProgressButton(Widget):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.pb = ProgressBar(max=100, value=0, size_hint=(1, None), height=30)
self.popup = Popup(title='Download', content=self.pb, size_hint=(0.5, 0.2))
self.popup.bind(on_open=self.start_progress)
btn = Button(text='Start Download', size_hint=(None,None), width=150, height=40,pos=(Window.width/2 - 75, Window.height - 100), on_release=self.show_popup)
self.add_widget(btn)
def show_popup(self, instance):
self.pb.value = 0
self.popup.open()
def start_progress(self, instance):
Clock.schedule_interval(self.update_progress, 1/25)
def update_progress(self, dt):
if self.pb.value >= 100:
return False
self.pb.value += 1
class ProgressBarApp(App):
def build(self):
return ProgressButton()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ProgressBarApp().run()
Output
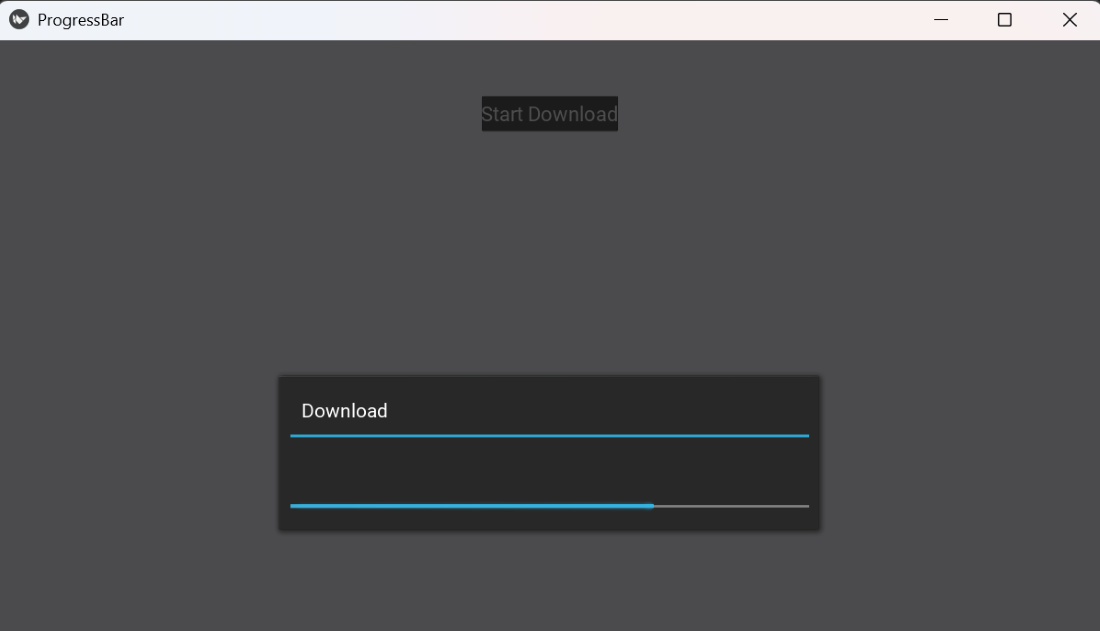
Explanation:
- Button(...): triggers the popup containing the progress bar.
- Popup(...): displays the progress bar in a separate window.
- Clock.schedule_interval(...): repeatedly calls update_progress to increment the bar.
- update_progress(...): stops updating when value reaches 100.
Example 2: This code shows a progress bar in the main window, updating automatically using Clock.
Python
Window.clearcolor = (1, 1, 0.95, 1)
class AutoProgress(Widget):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
cx = Window.width / 2
self.pb = ProgressBar(max=100, value=0, size_hint=(None,None), width=300, height=30,pos=(cx - 150, Window.height - 120))
self.add_widget(self.pb)
Clock.schedule_interval(self.update_progress, 1/20)
def update_progress(self, dt):
if self.pb.value < 100:
self.pb.value += 1
class ProgressBarApp(App):
def build(self):
return AutoProgress()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ProgressBarApp().run()
Output

Explanation:
- Clock.schedule_interval(...): updates the progress bar at regular intervals.
- update_progress(...): increments value until it reaches the maximum.
- No popup needed; the progress bar is displayed directly in the main window.
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice