Scrollview Widget in Kivy - Python
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2025
A ScrollView in Kivy provides a scrollable viewport that clips its child widget according to the scrollable area. Only one child is allowed. It supports horizontal and vertical scrolling through the properties scroll_x and scroll_y.
Let's add a simple Scrollview to a Kivy window.
Below example demonstrates a scrollable label in a Kivy window that allows vertical scrolling of long text.
Python
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.scrollview import ScrollView
from kivy.uix.label import Label
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.clearcolor = (1, 1, 1, 1)
class BasicScrollView(ScrollView):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
long_text = "You are learning Kivy! " * 100
lbl = Label(text=long_text,font_size=20,size_hint=(1, None), color=(0,0,0,1))
lbl.bind(texture_size=lambda inst, val: setattr(inst, 'height', val[1]))
lbl.text_size = (Window.width - 20, None)
self.add_widget(lbl)
class ScrollViewApp(App):
def build(self):
return BasicScrollView()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ScrollViewApp().run()
Output

Explanation:
- ScrollView creates a scrollable area.
- Label is added as the only child.
- size_hint=(1, None) allows manual height adjustment.
- lbl.bind(texture_size=...) updates height to fit text.
- lbl.text_size=(Window.width-20, None) wraps the text inside the scroll view.
Syntax
ScrollView(scroll_x=0, scroll_y=1, bar_width=10, bar_color=[1,0,0,1])
Parameters:
- scroll_x: horizontal scroll position (0-1).
- scroll_y: vertical scroll position (0-1).
- bar_width: width of the scroll bar.
- bar_color: RGBA color of the scroll bar.
Examples
Example 1: This code shows a vertical scroll view containing multiple labels, allowing scrolling to view all items.
Python
Window.clearcolor = (1, 1, 1, 1)
class MultiLabelScrollView(ScrollView):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
layout = BoxLayout(orientation='vertical', size_hint_y=None)
layout.bind(minimum_height=layout.setter('height'))
for i in range(20):
lbl = Label(text=f"Item {i+1}", size_hint_y=None, height=40, font_size=20, color=(0,0,0,1))
layout.add_widget(lbl)
self.add_widget(layout)
class ScrollViewApp(App):
def build(self):
return MultiLabelScrollView()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ScrollViewApp().run()
Output
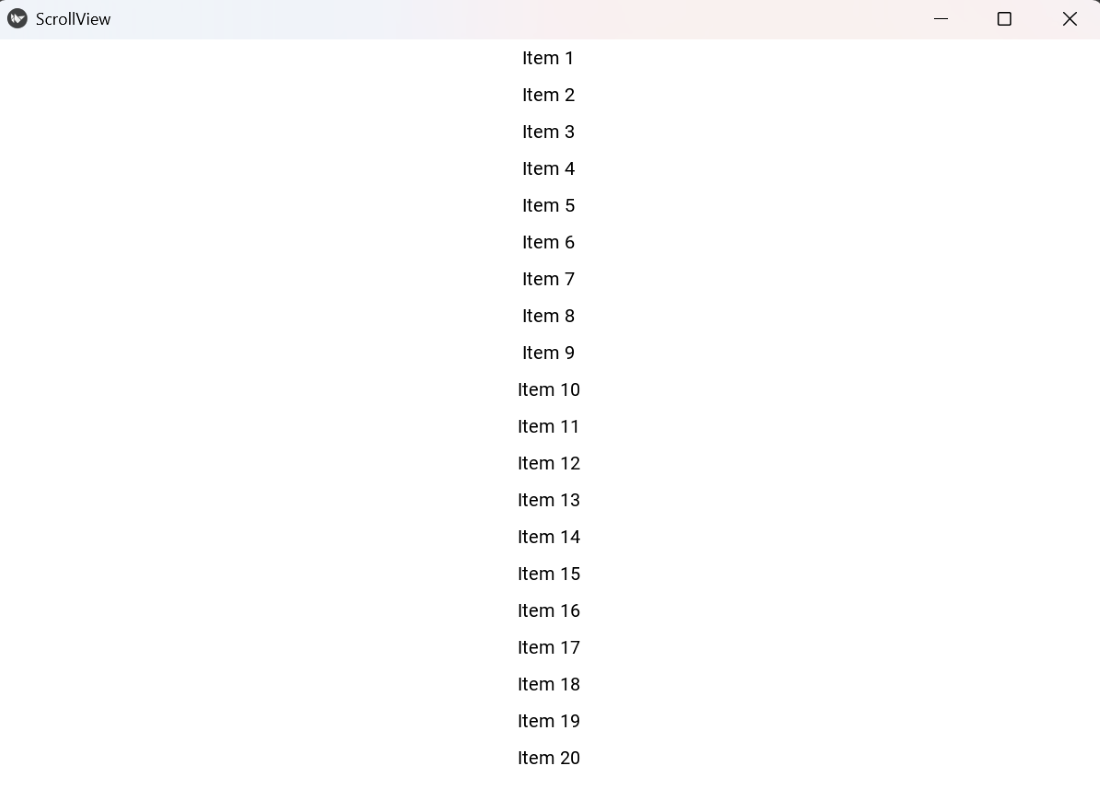
Explanation:
- BoxLayout arranges labels vertically.
- size_hint_y=None and layout.bind(minimum_height=layout.setter('height')) ensure layout height fits all labels.
- Each Label has a fixed height and is added to the layout.
- ScrollView allows vertical scrolling.
Example 2: This program demonstrates customizing the scroll bar color and width while scrolling through multiple labels.
Python
Window.clearcolor = (0.95, 0.95, 0.95, 1)
class ScrollBarCustom(ScrollView):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.bar_color = [0, 0, 1, 1]
self.bar_width = 12
layout = BoxLayout(orientation='vertical', size_hint_y=None)
layout.bind(minimum_height=layout.setter('height'))
for i in range(15):
lbl = Label(text=f"Label {i+1}", size_hint_y=None, height=80, font_size=24, color=(0,0,0,1))
layout.add_widget(lbl)
self.add_widget(layout)
class ScrollViewApp(App):
def build(self):
return ScrollBarCustom()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ScrollViewApp().run()
Output
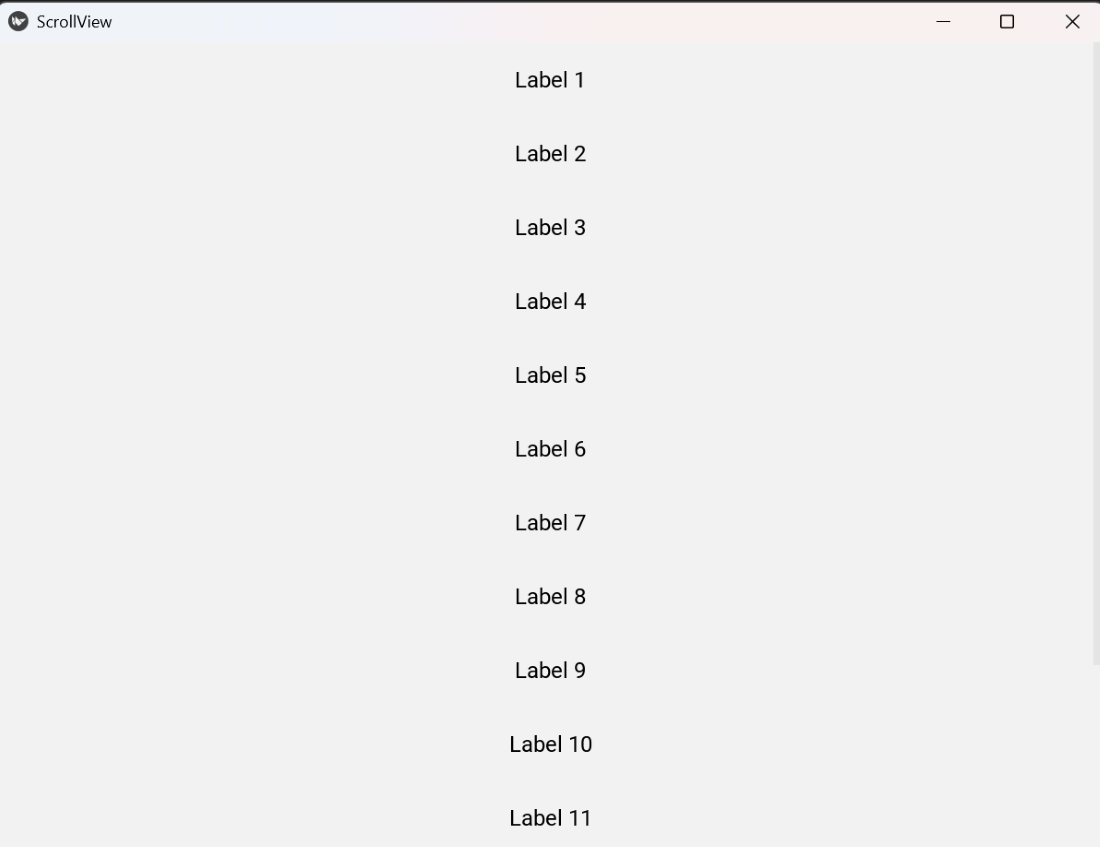
Explanation:
- self.bar_color sets the scrollbar color.
- self.bar_width sets the scrollbar width.
- BoxLayout organizes labels vertically.
- Each Label has size_hint_y=None for fixed height.
- ScrollView scrolls through the layout vertically.
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice