Serializers - Django REST Framework
Last Updated :
20 Nov, 2025
In Django REST Framework (DRF), serializers convert complex data such as model instances or querysets into formats like JSON or XML for API responses.
- Transform database objects into JSON or other supported formats.
- Convert incoming JSON data back into Python types.
- Validate the input data before saving it to the database.
- Provide a clean way to control what data is exposed through an API.
Creating a Basic Serializer
To create a basic serializer, import serializers from rest_framework and define the fields to expose, similar to defining a Django form or model.
Python
from rest_framework import serializers
# create a serializer
class CommentSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
# initialize fields
email = serializers.EmailField()
content = serializers.CharField(max_length = 200)
created = serializers.DateTimeField()
Serializer can be declared for any entity or object based on the required fields.
Using Serializer to serialize data
A serializer such as CommentSerializer can be used to serialize a single comment or a list of comments. Using the Serializer class is similar to working with Django Forms.
Create a Comment class to represent a comment object that the serializer can process:
Python
from datetime import datetime
# create a class
class Comment(object):
def __init__(self, email, content, created = None):
self.email = email
self.content = content
self.created = created or datetime.now()
# create a object
comment = Comment(email ='[email protected]', content ='foo bar')
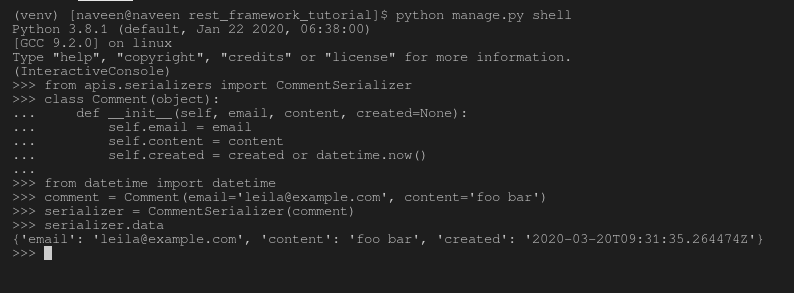
After the object is created, open the Python shell and serialize the comment:
Python manage.py shell
Run the following code:
>>> from apis.serializers import CommentSerializer
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> class Comment(object):
... def __init__(self, email, content, created=None):
... self.email = email
... self.content = content
... self.created = created or datetime.now()
...
>>> comment = Comment(email='[email protected]', content='foo bar')
>>> serializer = CommentSerializer(comment)
>>> serializer.data
Output:
ModelSerializer
A ModelSerializer n DRF provides a shortcut that automatically generates a serializer class based on a Django model.
It behaves like a regular Serializer but provides additional features such as:
- Automatic field generation from the model.
- Model-based validators like unique_together.
- Default implementations of .create() and .update() methods.
Syntax:
class SerializerName(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = ModelName
fields = List of Fields
Example: Models.py
Python
from django.db import models
class Account(models.Model):
user_id = model.IntegerField()
account_name = model.CharField(max_lenght=50)
user = model.CharField(max_length=100)
created = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
Serializer:
Python
class AccountSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Account
fields = ['user_id', 'account_name', 'user', 'created']
By default, all model fields are automatically mapped to corresponding serializer fields.
HyperlinkedModelSerializer
The HyperlinkedModelSerializer works similarly to ModelSerializer but represents relationships using hyperlinks instead of primary keys. Each object includes a url field that represents its unique endpoint, allowing easier navigation between related resources.
Syntax:
class SerializerName(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = ModelName
fields = List of Fields
Example:
Python
class AccountSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Account
fields = ['id', 'account_name', 'users', 'created']
This approach makes the API responses more RESTful by using hyperlinks to connect related data.
Serializer Fields
Each field in a serializer works similarly to a Django form field, it handles validation, default values, error messages, and data representation.
Commonly Used Serializer Fields:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|
| BooleanField | A boolean field used to wrap True or False values. |
| CharField | CharField is used to store text representation. |
| EmailField | EmailField is also a text representation and it validates the text to be a valid e-mail address. |
| RegexField | As the name defines, RegexField matches the string to a particular regex, else raises an error. |
| URLField | URLField is basically a RegexField that validates the input against a URL matching pattern. |
| SlugField | SlugField is a RegexField that validates the input against the pattern [a-zA-Z0-9_-]+. |
| IPAddressField | IPAddressField is a field that ensures the input is a valid IPv4 or IPv6 string. |
| IntegerField | IntegerField is basically a integer field that validates the input against Python’s int instance. |
| FloatField | FloatField is basically a float field that validates the input against Python’s float instance. |
| DecimalField | DecimalField is basically a decimal field that validates the input against Python’s decimal instance. |
| DateTimeField | DateTimeField is a serializer field used for date and time representation. |
| DateField | DateField is a serializer field used for date representation. |
| TimeField | Timefield is a serializer field used for time representation. |
| DurationField | DurationField is a serializer field used for duration representation. |
| ChoiceField | ChoiceField is basically a CharField that validates the input against a value out of a limited set of choices. |
| MultipleChoiceField | MultipleChoiceField is basically a CharField that validates the input against a set of zero, one or many values, chosen from a limited set of choices. |
| FileField | FileField is basically a file representation. It performs Django’s standard FileField validation. |
| ImageField | ImageField is an image representation.It validates the uploaded file content as matching a known image format. |
| ListField | ListField is basically a list field that validates the input against a list of objects. |
| JSONField | JSONField is basically a field class that validates that the incoming data structure consists of valid JSON primitives. |
| HiddenField | HiddenField is a field class that does not take a value based on user input, but instead takes its value from a default value or callable. |
| DictField | DictField is basically a dictionary field that validates the input against a dictionary of objects. |
Note: NullBooleanField (a boolean field that allowed True, False, or NULL) is deprecated. Use BooleanField(null=True, blank=True) instead.
Core arguments in serializer fields
Each field in a Django REST Framework (DRF) serializer accepts a set of core arguments that control validation, default values, and data behavior.
These arguments allow developers to define how a field should behave during serialization (output) and deserialization (input).
| Argument | Description |
|---|
| read_only | Set this to True to ensure that the field is used when serializing a representation, but is not used when creating or updating an instance during deserialization |
| write_only | Set this to True to ensure that the field may be used when updating or creating an instance, but is not included when serializing the representation. |
| required | Setting this to False also allows the object attribute or dictionary key to be omitted from output when serializing the instance. |
| default | If set, this gives the default value that will be used for the field if no input value is supplied. |
| allow_null | Normally an error will be raised if None is passed to a serializer field. Set this keyword argument to True if None should be considered a valid value. |
| source | The name of the attribute that will be used to populate the field. |
| validators | A list of validator functions which should be applied to the incoming field input, and which either raise a validation error or simply return. |
| error_messages | A dictionary of error codes to error messages. |
| label | A short text string that may be used as the name of the field in HTML form fields or other descriptive elements. |
| help_text | A text string that may be used as a description of the field in HTML form fields or other descriptive elements. |
| initial | A value that should be used for pre-populating the value of HTML form fields. |
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice