How to make Reusable React Components ?
Last Updated :
13 Aug, 2025
React components are modular pieces of UI that take data via props to render dynamic and complex interfaces. They encapsulate both structure and logic, allowing developers to reuse and maintain code efficiently. In fact, reusing components can reduce code duplication by up to 60%, making your applications more scalable and maintainable.
When creating reusable React components, it's important to keep in mind two key factors:
1. Avoid side effects:
It is not recommended to include logic that interacts with external data, such as making API calls, directly inside a reusable component. Instead, you should pass this logic as props to the component.
For example, if a button not only has a visual function but also fetches data from the internet, it may not be reusable in other contexts.
In this case, we have a reusable button component that lacks best practices. In the example section, I will demonstrate why this is the case.
// It is a Reusable ButtonReusable component and this is a bad practices
const ButtonReusable = () => {
return (
<button> Click Me </button>
);
}
2. Use Props:
Props are parameters passed to a component to customize its behavior and appearance, making it reusable for different purposes.
// It is a buttonReusable component that can change its color
const ButtonReusable = ({ color }) => {
return (
<button style={{ backgroundColor: blue }}> Click Here </button>
);
}
This is considered bad practice because the label on the button is fixed as "Click Here". If you wish to change the text on your button to, for example, "Sign Up", you would have to go back to the button component and make that change. This means that every time you want to use a different text, you would have to edit the code again. In other words, the button would no longer be reusable.
To optimize performance in reusable React components, you can use memoization to avoid unnecessary re-renders. React's React.memo and useMemo hooks allow you to cache the result of a component or calculation, ensuring that the component only re-renders when necessary. For more details, check out this memoization guide.
Steps to Create a React Application:
Step 1: Create a React application using the following command:
npx create-react-app gfg
Step 2: After creating your project folder(i.e. gfg), move to it by using the following command:
cd gfg
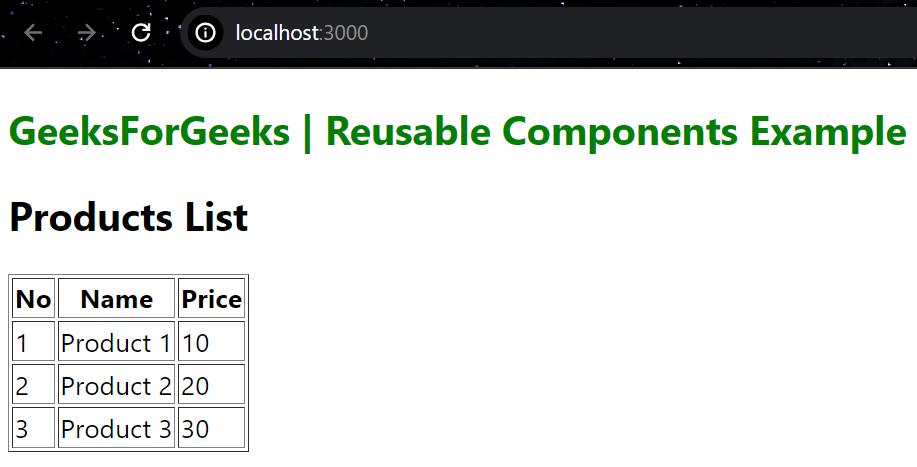
Example: This below example demonstrate the Reusable React Components.
In this example, You can see ProductList and ProductItem component can be composed together and accept props for customization and are reusable with different data sets.
App.js
//File path: src/App.js
import React from 'react';
import ProductList from './ProductList.js';
const App = () => {
const products = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Product 1', price: 10 },
{ id: 2, name: 'Product 2', price: 20 },
{ id: 3, name: 'Product 3', price: 30 },
];
return (
<div style={{ margin: '5px' }}>
<h2 style={{ color: 'green' }}>
GeeksForGeeks | Reusable Components Example
</h2>
<ProductList products={products} />
</div>
);
};
export default App;
//File path: src/ProductList.js
import React from 'react';
import ProductItem from './ProductItem.js';
const ProductList = ({ products }) => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Products List</h2>
<table border={1}>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>No</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{products.map((product) => (
<ProductItem key={product.id}
product={product} />
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
);
};
export default ProductList;
//File path: src/ProductItem.js
import React from 'react';
const ProductItem = ({ product }) => {
return (
<tr>
<td>{product.id}</td>
<td>{product.name}</td>
<td>{product.price}</td>
</tr>
);
};
export default ProductItem;
To run the application use the following command:
npm run start
Output: Now go to http://localhost:3000 in your browser
What is the primary benefit of using reusable components in React?
-
-
-
Helps avoid code duplication and improves maintainability
-
Makes components difficult to test
Explanation:
Reusable components reduce code duplication (up to 60% as given) and make applications more scalable, maintainable, and efficient.
Which of the following is considered a bad practice in reusable components?
-
Using props for customization
-
Hardcoding button text inside the component
-
Passing functions to components
-
Using React.memo for optimization
Explanation:
Hardcoding text or styles reduces reusability. Props should be used to customize content like label, color, etc.
What is the recommended way to handle external data logic (like API calls) in reusable components?
-
Write API logic inside the reusable component
-
-
Pass the required logic as props from the parent
-
Use only class components
Explanation:
Reusable components should avoid side effects. Instead of writing API logic inside them, we pass functions/data using props to keep them flexible.
Which tool helps avoid unnecessary re-rendering in reusable React components?
Explanation:
React.memo and useMemo help in memoization, preventing components from re-rendering unless necessary, improving performance.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/4
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/4
1/4
< Previous
Next >
Explore
React Fundamentals
Components in React
React Hooks
Routing in React
Advanced React Concepts
React Projects