ExpressJS express.json() Function
Last Updated :
20 Sep, 2025
The express.json() is a built-in middleware in Express. It helps your app read JSON data sent from the client (like in POST or PUT requests) and makes it available in req.body. Without it, Express cannot understand JSON data in requests.
Use Cases:
- APIs: Parse JSON data in RESTful APIs.
- POST Requests: Handle form or client data in JSON format.
- Complex Data: Easily manage structured JSON data.
Syntax:
ExpressJSon( [options] )
In the above syntax:
- Parameters: The options parameter has various properties like inflate, limit, type, etc.
- Return Value: It returns an Object.
How express.json() Works?
- Middleware Function: express.json() is a built-in middleware in Express.
- Reads Request Body: It looks at the body of incoming HTTP requests.
- Parses JSON Data: If the body contains JSON, it converts it into a JavaScript object.
- Stores in req.body: The parsed object is placed inside req.body.
- Easier Access: You can directly use req.body in your routes to access the client’s data.
Steps To Use ExpressJSon() Function
Step 1: Create a Node.js application using the following command.
mkdir nodejs
cd nodejs
npm init -y
Step 2: Install the required dependencies.
npm install express
Step 3: Create the required files and start the server.
node index.js
Handling JSON Data in ExpressJS
JavaScript
// Filename - index.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/', function (req, res) {
console.log(req.body.name);
res.end();
});
app.listen(PORT, function (err) {
if (err) console.log(err);
console.log("Server listening on PORT", PORT);
});
Output
When a POST request is made to http://localhost:3000/ with the header Content-Type: application/json and the body {"name":"GeeksforGeeks"}, the following output is displayed on the console:
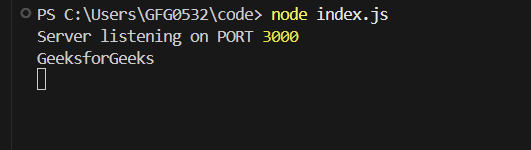
In this example
- The ExpressJSon() middleware is applied to parse incoming JSON request bodies, making the data accessible via req.body.
- A POST route is defined at the root (/) to handle requests, logging the name property from the JSON payload to the console.
Without Using ExpressJSON()
JavaScript
// Filename - index.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
// Without this middleware
// app.use(express.json());
app.post('/', function (req, res) {
console.log(req.body.name);
res.end();
});
app.listen(PORT, function (err) {
if (err) console.log(err);
console.log("Server listening on PORT", PORT);
});
Output:
When a POST request is made to http://localhost:3000/ with the header Content-Type: application/json and the body {"name":"GeeksforGeeks"}, the following output is displayed on the console:
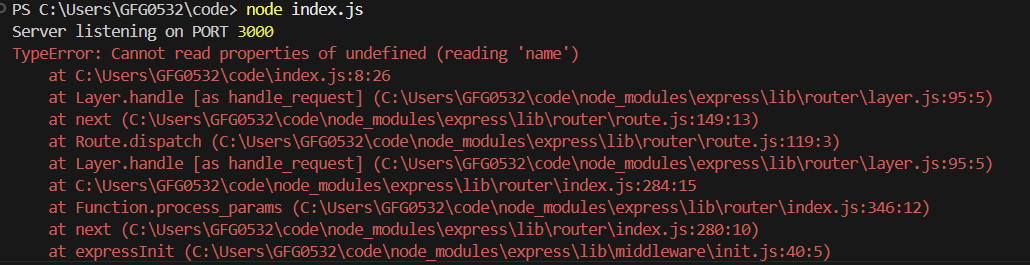
In this example
- It creates an Express server on port 3000.
- A POST / route logs req.body.name and ends the response.
- Without app.use(express.json()), the server cannot parse JSON request bodies, so req.body will be undefined.
What is the main purpose of using express.json() in an Express application?
-
-
To parse URL query parameters
-
To parse incoming JSON request bodies
-
Explanation:
express.json() is a built-in middleware that reads incoming request bodies containing JSON data and converts them into JavaScript objects, making them available in req.body.
What happens if express.json() middleware is NOT used while handling a JSON POST request?
-
The server crashes immediately
-
JSON data is automatically parsed by Express
-
req.body will be undefined
-
The request is rejected with a 404 error
Explanation:
Without app.use(express.json()), Express cannot parse JSON request bodies, so req.body remains undefined, even if valid JSON data is sent by the client.
Which of the following correctly describes how express.json() works?
-
It converts JavaScript objects into JSON responses
-
It reads request headers only
-
It parses JSON request bodies and stores them in req.body
-
It validates JSON schema automatically
Explanation:
express.json() reads the request body, checks if it contains JSON, parses it into a JavaScript object, and stores it in req.body for easy access inside route handlers.
Which condition must be met for express.json() to correctly parse incoming data?
-
Request method must be GET
-
The request must include Content-Type: application/json
-
Data must be sent as URL parameters
-
express.json() must be used after route definitions
Explanation:
For express.json() to parse the body, the client must send the request with the header
Content-Type: application/json, indicating that the request body contains JSON data.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/4
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/4
1/4
< Previous
Next >
Explore
HTML & CSS Tutorials
JS Tutorial
Frontend
Backend
Database