Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to show all views in a MySQL database using the SHOW FULL TABLE statement or by querying information from the data dictionary.
The SHOW FULL TABLES returns a list of views in a specified database. If you want to display the statement that creates the view, check out the SHOW CREATE VIEW statement tutorial.
MySQL Show View – Using SHOW FULL TABLES statement
MySQL treats the views as tables with the type 'VIEW'. Therefore, you can use the SHOW FULL TABLES statement to display all views in the current database as follows:
SHOW FULL TABLES
WHERE table_type = 'VIEW';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because the SHOW FULL TABLES statement returns both tables and views, we need to add a WHERE clause to obtain views only.
If you want to show all views in a specific database, you can use the FROM or IN clause in the SHOW FULL TABLES statement:
SHOW FULL TABLES
[{FROM | IN } database_name]
WHERE table_type = 'VIEW';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, you specify a database name from which you want to obtain the views after the FROM or IN clause.
For example, the following statement shows all views from the sys database:
SHOW FULL TABLES IN sys
WHERE table_type='VIEW';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)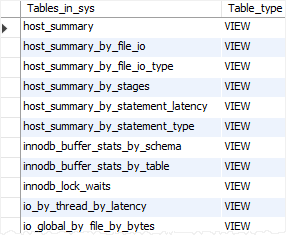
If you want to find views that match a pattern, you can use the LIKE clause as follows:
SHOW FULL TABLES
[{FROM | IN } database_name]
LIKE pattern;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, the following statement uses the LIKE clause to find all views from the sys database, whose names start with the waits:
SHOW FULL TABLES
FROM sys
LIKE 'waits%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
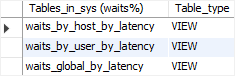
Note that the SHOW TABLES statement returns only the views that you have the privilege to access.
MySQL Show View – Using INFORMATION_SCHEMA database
The information_schema database provides access to MySQL database metadata such as databases, tables, data types of columns, or privileges. The information schema is also known as a database dictionary or system catalog.
To show the views of a database, you use the tables table from the information_schema database:
SELECT *
FROM information_schema.tables;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here’s the partial output:
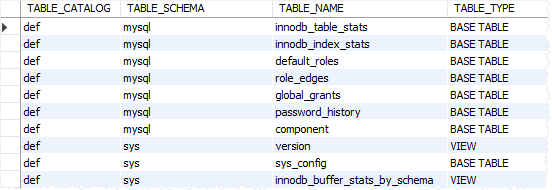
The columns that are relevant to the views are:
- The
table_schemacolumn stores the schema or database of the view (or table). - The
table_namecolumn stores the name of the view (or table). - The
table_typecolumn stores the type of tables:BASE TABLEfor a table,VIEWfor a view, orSYSTEM VIEWfor anINFORMATION_SCHEMAtable.
For example, this query returns all views from the classicmodels database:
SELECT
table_name view_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_type = 'VIEW' AND
table_schema = 'classicmodels';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To find the views that match a pattern, you use the table_name column. For example, this query finds all views whose names start with customer:
SELECT
table_name view_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_type = 'VIEW' AND
table_schema = 'classicmodels' AND
table_name LIKE 'customer%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary
- Use the
SHOW FULL TABLEwith thetype_typeVIEWto return all views from the current database. - Use the
SHOW FULL TABLE FROM(orIN) statement to get all views in a specified database. - Add the
LIKEclause to theSHOW FULL TABLEstatement to get the views that match a pattern. - Query data from the table
information_schema.tablesto get the views in a database.