Read, write, delete & modify files effortlessly with built-in file handling functions. Learn all the techniques of PHP File Handling and streamline your file manipulation process:
In this tutorial, you will learn file manipulation in PHP with related functions like PHP fopen, PHP file uploading, and some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to PHP file handling.
Please note that we have used PHP version 7 in all examples.
Let’s begin!
=> In-Depth PHP Tutorials for Beginners
Table of Contents:
File Handling in PHP: Simple Guide

PHP File Manipulation
Sometimes, we have to work with external files when developing software. It may read data from an external file or writing data into an external file, etc. PHP facilitates users to manipulate files by writing a few code lines.
PHP has several built-in functions for file manipulation.
Some of the important file manipulation functions are shown in the list below:
- Create a file – fopen()
- Output a file – readfile()
- Open a file – fopen()
- Read a file – fread()
- Close a file – fclose()
- Write a file – fwrite()
- Append a file – fwrite()
- Delete a file – unlink()
=>> Visit this link to find the full list
Note: It may be a little confusing, as some functions are used for multiple purposes. For example, the fopen() function is used to open a file as well as to create a file.
Create a File – fopen()
PHP fopen() function is used to create a file. It has two mandatory parameters:
- 1st parameter – the name of the file to be created
- 2nd parameter – file open mode
There are six file open modes available to create a file. These are listed in the table below:
| Mode | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | w | Create a file for write only. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. |
| 2 | a | Create a file for write only. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. |
| 3 | x | Create a new file for write only. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning. |
| 4 | w+ | Create a file for read/write. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. |
| 5 | a+ | Create a file for read/write. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. |
| 6 | x+ | Create a new file for read/write. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning. |
An example is shown below. You can practice this example by running the following programming code:
<?php
fopen("new.txt","w");
?>
Output:
It will create a file called new.txt in your project folder.
Note: In this example, we use the file mode, w. Therefore, if there is already a file called new.txt in your project folder, it will be deleted, and a new file with the same file name will be created. You may practice this example using other file modes as well.
Output a File – readfile()
The readfile() function is used to output a file. If the function is successfully executed, it returns the number of bytes read from the file. Otherwise, it returns false.
To read a file, it must be created.
An example is shown below. You can practice this example by running the following programming code.
First, you need to create a file called sample.txt with the following content in your project folder.
Hello World
You may use any file name, type (text file or HTML file), and/or content.
Create another file with the following code and run it.
<?php
echo readfile("sample.txt");
?>
Output:
Hello World11
In the above output, 11 is the number of bytes reads from the file, sample.txt.
Open, Read and Close a File – fopen(), fread() & fclose()
The fopen() function is used to open a file (or a URL).
It has two mandatory parameters:
- 1st parameter – file name to be opened
- 2nd parameter – file open mode
There are eight file open modes available to open a file. They are listed in table below:
| Mode | Description | File Pointer Position | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | r | Opens a file for read only. | The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file. |
| 2 | w | Opens a file for write only. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. | The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file. |
| 3 | a | Opens a file for write only. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. | The position of the file pointer is at the end of the file. |
| 4 | x | Creates a new file for write only. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning. | – |
| 5 | r+ | Opens a file for read/write. | The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file. |
| 6 | w+ | Opens a file for read/write. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. | The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file. |
| 7 | a+ | Opens a file for read/write. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. | The position of the file pointer is at the end of the file. |
| 8 | x+ | Creates a new file for read/write. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning. | – |
The fread() function is used to read a file. It is also known as binary-safe file read. To read a file, it must be opened. The fread() function has two mandatory parameters.
- 1st parameter – stream/source
- 2nd parameter – number of bytes to be read
The fclose() function is used to close the file.
An example is shown below. You can practice this example by running the following programming code.
You need to have a file called sample.txt with the following content in your project folder.
Hello World
Create another file with the following code and run it.
<?php
$f = fopen("sample.txt","r");
echo fread($f,5);
fclose($f);
?>
Output:
Hello
Five bytes have been read from the file sample.txt.
Write and Append a File – fwrite()
The fwrite() function is used to write/append a file.
To write/append a file, it must be opened.
A few examples are shown below. You can practice these examples by running the following programming codes.
Example 1: Write a file – When there is no existing file called sample.html in your project folder
<?php
$f = fopen("sample.html","w");
fwrite($f, "John Doe");
fclose($f);
?>
Output:
It will create a file called sample.html with the following content in your project folder.
John Doe
Example 2: Write a file – When there is an existing file called sample.txt in your project folder
You need to have a file called sample.txt with the following content in your project folder.
Hello World
Create another file with the following code and run it.
<?php
$f = fopen("sample.txt","w");
fwrite($f, "Welcome to Software Testing Help!");
fclose($f);
?>
Output:
It will delete the existing sample.txt file and create a new file with the same name with the following content.
Welcome to Software Testing Help!
Example 3: Append a file – When there is an existing file called welcome.html in your project folder
First, create a file called welcome.html with the following content in your project folder.
Welcome,
Create another file with the following code and run it.
<?php
$f = fopen("welcome.html","a");
fwrite($f, " John Doe!");
fclose($f);
?>
Output:
It will append the content, John Doe!, to the welcome.html file as shown below.
Welcome, John Doe!
Delete a File – unlink()
The unlink() function is used to delete a file. If the file is successfully deleted, outputs 1 (only if you use the echo statement) and if the file is not found, outputs a warning.
A few examples are shown below. You can practice these examples by running the following programming codes.
Example 1: Delete an existing file
Note: You should have a file called sample.txt in your project folder.
<?php
echo unlink("sample.txt");
?>
Output:
1
sample.txt will be deleted from your project folder.
Example 2: Trying to delete a non-existing file
Note: newsample.txt is non-existing.
<?php
echo unlink("newsample.txt");
?>
Output:
Warning: unlink(newsample.txt): No such file or directory in C:\laragon\www\index.php on line 3
PHP File Upload
PHP allows users to upload files to the system.
Let’s understand it with an example.
In this example, you have to create two files and a folder to upload the attachments (like images, etc.). The two files are named index.php and upload.php, and the folder is named uploads.
Index.php contains the following programming code:
<form method="post" action="upload.php" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Attachment:
<br>
<input type="file" name="myfile">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Upload.php contains the following programming code:
<?php
$upload_path = "uploads/";
$upload_path = $upload_path.basename( $_FILES['myfile']['name']);
if(move_uploaded_file($_FILES['myfile']['tmp_name'], $upload_path)) {
echo "File uploaded successfully.";
} else{
echo "An error occurred. Please try again.";
}
?>
Now run the index.php file.
Output:
- When the page loads:
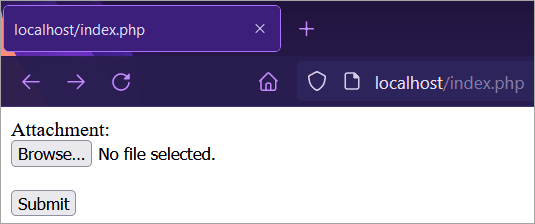
- After uploading a file and submitting it:
If the file is successfully uploaded, it will generate a success message, as shown in the image below. Otherwise, an error message will be displayed. Visit the uploads folder that you have created to see the uploaded file.

Furthermore, PHP $_FILES are file upload variables. We can use the file_get_contents() function that reads a file into a string.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why file system is used in PHP?
It is used to create, open, read, output, write, append, close, and delete files.
2. What are the main functions used in PHP for file manipulation?
The main functions include:
Create a file – fopen()
Output a file – readfile()
Open a file – fopen()
Read a file – fread()
Close a file – fclose()
Write a file – fwrite()
Append a file – fwrite()
Delete a file – unlink()
3. What does PHP fopen do?
It is a function used to open a file or a URL.
4. What are the modes used with PHP fopen()?
The modes are listed below:
“r” – Opens a file for read-only. The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file.
“w” – Opens a file for write-only. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file.
“a” – Opens a file for write-only. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. The position of the file pointer is at the end of the file.
“x” – Creates a new file for write-only. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning.
“r+” – Opens a file for read/write. The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file.
“w+” – Opens a file for read/write. If an existing file is found, it will be deleted, and a new file will be created with the same name. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. The position of the file pointer is at the start of the file.
“a+” – Opens a file for read/write. If the existing file has previous content, it will be kept. A new file will be created if there is no existing file. The position of the file pointer is at the end of the file.
“x+” – Creates a new file for read/write. If the file is existing, it will generate a warning.
5. Which function is used to delete a file?
The unlink() function is used to delete a file.
6. What is PHP file get_contents?
It reads a file into a string.
7. Why does PHP file_get_contents return false?
One possible reason is that your server prevents you from opening the located file using file_get_contents().
Conclusion
PHP has several built-in functions for file manipulation. Commonly used file manipulation functions are PHP fopen(), fread(), fclose(), fwrite(), readfile() and unlink(). Furthermore, PHP allows users to upload files to the system.








