Explore the key steps involved in PHP Form Handling with examples. Gain understanding of PHP Form Validation and its various types, to protect your script from malicious code:
In this tutorial, you will learn PHP forms, PHP form validation, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to form handling.
Please note that we have used PHP version 7 in all examples.
Prerequisite: For a better understanding of this tutorial, you need to have a good understanding of HTML form handling.
Let’s begin!
Table of Contents:
Form Handling and Validation in PHP

PHP Form Handling
PHP forms are similar to HTML forms. In PHP, we can create HTML forms using the <form> tag as shown below.
<?php
//php code
?>
<form method="post" action="#">
Email:
<input type="text" name="email">
<br><br>
Password:
<input type="password" name="pwd">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="send" value="Send">
</form>
<?php
//php code
?>
Similar to an HTML form, the PHP form action specifies the location for transferring the submitted form data. The form method can be GET or POST.
PHP Form Validation
What & Why Form Validation?
Form validation is the technical process of finding out the validity of user-entered data in a form. Validation plays a key role in any system, as it helps to protect data and the system from malicious users.
Types of Validation
There are two types of validation in PHP. They are,
- Client-side validation
- Server-side validation
Client-side validation is performed on the client or the web browser using client-side languages like HTML5, JavaScript, etc. In contrast, server-side validation is performed on the server using server-side languages such as PHP.
It is recommended to have both types of validation for a stronger validation.
The following table shows the differences between the two validation types:
| Parameter | Client-side Validation | Server-side Validation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Performs on | The validation process performs on the client (web browser). | The validation process performs on the server. |
| 2 | Visibility | The code can be accessed by the user. | The code cannot be accessed by the user. |
| 3 | Security | Less secure. | More secure. |
| 4 | Speed | Faster (because data don’t send to the server). | Slower (because data send to the server). |
| 5 | Languages | Client-side validation is performed using HTML5, JavaScript, etc. | Server-side validation is performed using programming languages like PHP, etc. |
Example of PHP Form Validation
Note: In this example, we have only shown server-side validation and purposely omitted the client-side validation to demonstrate the server-side validation.
Imagine that you want to create a student registration form, and the following requirements were given:
| Field | Mandatory/Optional | Validation Rules | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Title | Mandatory | Selectable field. |
| 2 | Name | Mandatory | Only letters and whitespaces. |
| 3 | Gender | Mandatory | Selectable field. |
| 4 | Birth Date | Mandatory | Date picker. |
| 5 | Address | Mandatory | Should be able to type an address. |
| 6 | Phone Number | Mandatory | Only 10 numbers. |
| 7 | Mandatory | A valid email. | |
| 8 | Website | Optional | A valid URL. |
| 9 | Terms and conditions | Mandatory | The user must agree to the terms and conditions to submit the form. |
Let’s design the form.
For the above fields, the following HTML form elements are recommended:
| Field | HTML Form Element | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Title | |
| 2 | Name | |
| 3 | Gender | |
| 4 | Birth date | |
| 5 | Address | |
| 6 | Phone number | |
| 7 | ||
| 8 | Website | |
| 9 | Terms and conditions |
You can practice this example by running the following programming code:
<?php
$error = $title = $name = $gender = $bday = $address = $phone = $email = $website = $terms = NULL;
//check if the form submitted method is POST
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST") {
$title = clean($_POST['title']);
//check if the title is empty
if (empty($title)) {
//error message is assgined to $error
$error['title'] = "Please select title.";
}
$name = clean($_POST['name']);
if (empty($name)) {
$error['name'] = "Please enter name.";
} else {
$name = $_POST['name'];
// Check if the name only contains letters and whitespaces.
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name)) {
$error['name'] = "The name can only contain letters and whitespaces.";
}
}
$gender = @clean($_POST['gender']); //@ is used to error free
if (empty($gender)) {
$error['gender'] = "Please select gender.";
}
$bday = clean($_POST['bday']);
if (empty($bday)) {
$error['bday'] = "Please select birth date.";
}
$address = clean($_POST['address']);
if (empty($address)) {
$error['address'] = "Please enter address.";
}
$phone = clean($_POST['phone']);
if (empty($phone)) {
$error['phone'] = "Please enter phone number.";
} else {
$phone = $_POST['phone'];
// check if the phone number contains 10 numbers
if (!preg_match ("/^[0-9]*$/", $phone) || (strlen ($phone) != 10)) {
$error['phone'] = "Invalid phone number.";
}
}
$email = clean($_POST['email']);
if (empty($email)) {
$error['email'] = "Please enter email.";
} else {
$email = $_POST['email'];
// check the format of the email
if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) {
$error['email'] = "Invalid email.";
}
}
$website = clean($_POST['website']);
if (!empty($website)) {
// check the format of the website
if (!filter_var($website, FILTER_VALIDATE_URL)) {
$error['website'] = "Invalid URL.";
}
}
$terms = @clean($_POST['terms']);
if (empty($terms)) {
$error['terms'] = "You must agree to the terms and conditions.";
}
//check if there are any errors
if (empty($error)) {
$success = "You have successfully registered.";
}
}
function clean($data) {
// remove spaces
$data = trim($data);
// remove special characters
$data = stripslashes($data);
//remove html codes
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>Student Registration Form</h2>
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
Title *:
<select name="title">
<option value="">--Select--</option>
<option value="Mr">Mr</option>
<option value="Mrs">Mrs</option>
<option value="Miss">Miss</option>
</select>
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['title']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Name *:
<input type="text" name="name">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['name']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Gender *:
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="Male") echo "checked";?> value="male">Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="Female") echo "checked";?> value="female">Female
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['gender']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Birth Date *:
<input type="date" name="bday">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['bday']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Address *:
<textarea name="address" rows="4" cols="50"></textarea>
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['address']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Phone Number *:
<input type="text" name="phone">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['phone']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Email *:
<input type="text" name="email">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['email']; ?></span>
<br><br>
Website (URL):
<input type="text" name="website">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['website']; ?></span>
<br><br>
I agree to the terms and conditions. *
<input type="checkbox" name="terms">
<span style="color:red;"><?php echo @$error['terms']; ?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="send" value="Send">
<br><br>
<span style="color:green;"><?php echo @$success; ?></span>
</form>
<?php
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST") {
if (empty($error)) {
echo "<h3>Your Information:</h3>";
echo "<b>Title:</b> ".$title;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Name:</b> ".$name;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Gender:</b> ".$gender;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Birth Date:</b> ".$bday;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Address:</b> ".$address;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Phone Number:</b> ".$phone;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Email:</b> ".$email;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>Website:</b> ".$website;
echo "<br>";
echo "<b>I've agreed to the terms and conditions.</b>";
}
}
?>
Let’s play around with this form.
Enter different combinations of valid and/or invalid values and submit the form to see how the validation works.
When you fill the form with invalid values and submit it, you will get server-side validation errors. If you fill the form correctly and submit it, then you will get a success message while displaying the submitted data below the form.
The following screenshots show the browser output of the above programming code in below cases:
- When the page loads:

- After submitting the form without entering any data:
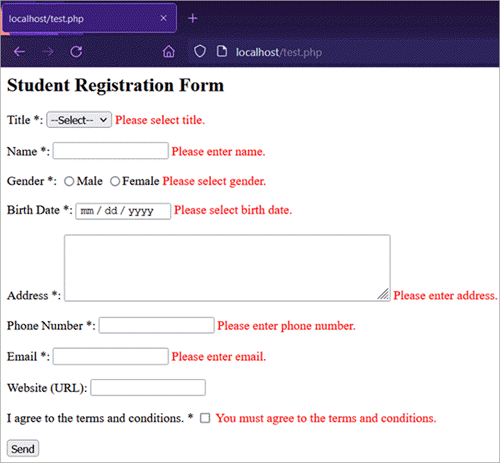
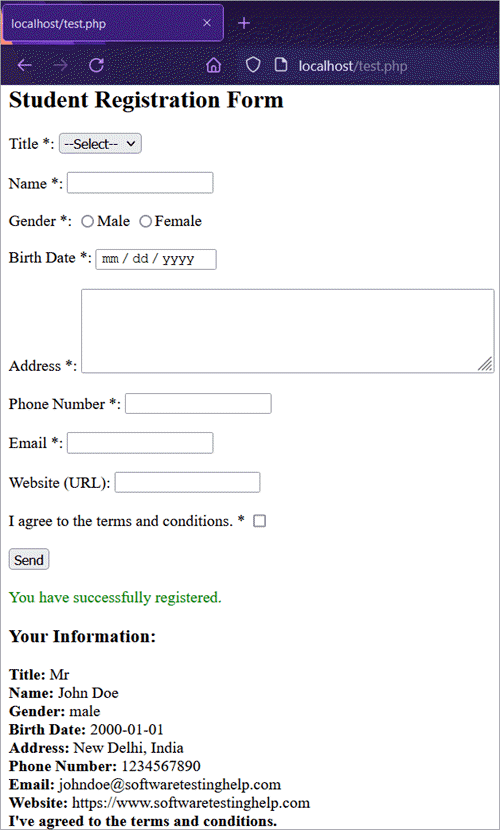
- After entering (valid) data and submitting the form:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can you create a form in PHP?
Yes, you can create an HTML form using the <form> tag in PHP.
2. What is PHP form action?
It specifies the location for transferring the submitted form data.
3. What is meant by form validation?
Form validation is the technical process of determining the validity of user data in a form.
4. Why do we need to validate PHP forms?
We need to validate PHP forms to protect data from malicious users.
5. How many types of validation are there in PHP?
There are two validation types in PHP. They are client-side validation and server-side validation.
6. What is the main advantage of client-side validation?
The main advantage of client-side validation is that the user receives feedback quickly because the data doesn’t send to the server.
Conclusion
Validation is the technical process of finding out the validity of user data.
The two types of validation in PHP are client-side validation and server-side validation. We need to add both types of validation for stronger validation.








