Explore the core concept of PHP Syntax and PHP comments with simple examples. Understand the exact process to write Single-Line Comments and Multi-line Comments in minutes:
In this tutorial, you will learn basic PHP syntax, the relationship between PHP and HTML, case sensitivity, space sensitivity, PHP comments, and frequently asked questions.
Please note that we have used PHP version 7 in all examples.
Let’s begin!
=> In-Depth PHP Tutorials for Beginners
Table of Contents:
Understanding PHP Syntax & Comments

Basic PHP Syntax
Basic syntax defines the fundamental rules or structure of a computer language. You must follow the syntax or the syntax rules when coding.
The following list shows the basic syntax rules of PHP:
- Start with <?php and end with ?>.
- Every statement ends with a semicolon (;).
- Variables are case-sensitive.
PHP with HTML
A PHP code can be embedded into an HTML document. A PHP file must have the .php file extension, not the .html file extension.
Further Reading => PHP Vs HTML: Explore the Differences
The below programming code shows an example. You can try this example by running the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> </title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
?>
</body>
</html>
Note: When you are coding, don’t forget to use proper spacing and indentation, as it improves the code readability. Usually, we use 2-space or 4-space indentation.
The below screenshot shows the browser output of the above programming code:
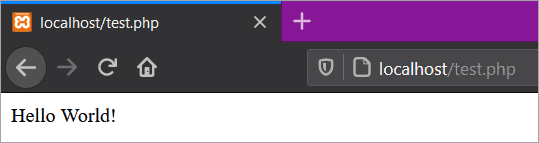
However, there is no requirement to embed PHP code into an HTML document. It simply can be like this (without HTML):
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
?>
Both provide the same output.
Case Sensitivity
In PHP, all variables (variable names) are case-sensitive. However, classes, functions, user-defined functions, and keywords are not case-sensitive. This can be illustrated better with two examples explained below.
Example 1:
The keyword true, can be written in different cases like TRUE, true, True, etc. as keywords are not case sensitive.
Example 2:
$animal, $ANIMAL, and $aNIMAL are three different variables, as variable names are case-sensitive.
Note: You may not be fully familiar with the above examples as we have not covered the concepts of variables, classes, functions, user-defined functions, and keywords yet. In later tutorials, we will dive deeply into those topics. Therefore, keep in touch with our upcoming tutorials.
White Space Sensitivity
Whitespace is any character or a series of characters that are rendered as space.
It can be:
- A space character
- A tab character
- A new line character, etc.
PHP ignores (extra) whitespace. In other words, PHP is whitespace-insensitive.
The following programming codes show an example. You can try this example by running the following code:
Code A:
<?php
$name = "Jane Doe";
echo $name;
?>
Code B:
<?php
$name = "Jane Doe";
echo $name;
?>
Code A does not contain any extra white space. In Code B, there are some extra white spaces (between the variable and the = mark, and between the echo keyword and the variable). However, both outputs produce the same result as PHP ignores those whitespaces.
The below screenshot shows the browser output of the above programming code:
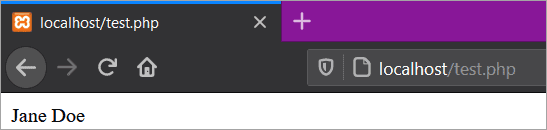
Comments in PHP
What is a Comment?
A comment is an additional text put by the programmer while coding, for future reference purposes. They do not execute as part of the program.
There are two main types of comments: single-line and multiline comments.
Single-Line Comments
As the name suggests, a single-line comment only spans a single line. There are two types of single-line comments, called C++ style and shell-style comments.
Please refer to the code snippet below for syntax.
// This is a c++ style single line comment.
# This is a shell-style single line comment.
Multi-line Comments
As the name suggests, a multiline comment spans multiple lines (more than one line).
Please refer to the code snippet below for the syntax:
/* This is a
Multi-line
Comment.
*/
Example: The following code shows an example. You can try this example by running the following code:
<?php
echo "Some text 1 <br/>"; // This is a example.
echo "Some text 2 <br/>"; # This is another example.
/* This is also
an
example.
*/
echo "Some text 3";
?>
The below screenshot shows the browser output of the above programming code:
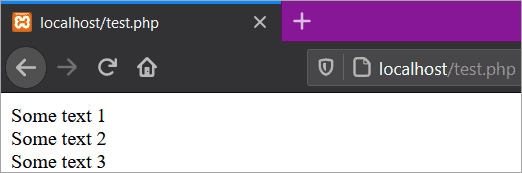
As we learned, comments didn’t execute as a part of the program, hence not visible to the user (in the browser output).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is PHP whitespace sensitive?
No, it ignores (extra) whitespace.
2. Is PHP case-sensitive?
It can be considered as a case-sensitive language, as variables are case-sensitive. However, classes, functions, user-defined functions, and keywords are case-insensitive.
3. Should you close PHP tags?
It is optional. However, it is a good programming practice to use close tags.
4. How do you write Hello World in PHP?
Below is the code to write Hello World:
<?php
echo “Hello World”;
?>
5. What are PHP comments?
It is a piece of information about the code that is added by the developer for future reference, and it is not part of the executable code.
6. What is a single-line comment in PHP? Explain with syntax?
It is a comment that only spans a single line. The common syntax of single-line comments is shown below.
// This is a single-line comment.
Also Read => PHP Laravel Framework
Conclusion
PHP is a case-sensitive and space-insensitive language. It may also contain HTML.
You can comment out PHP code to prevent execution of that code as part of the program. There are two types of comments, named single-line and multi-line comments.








