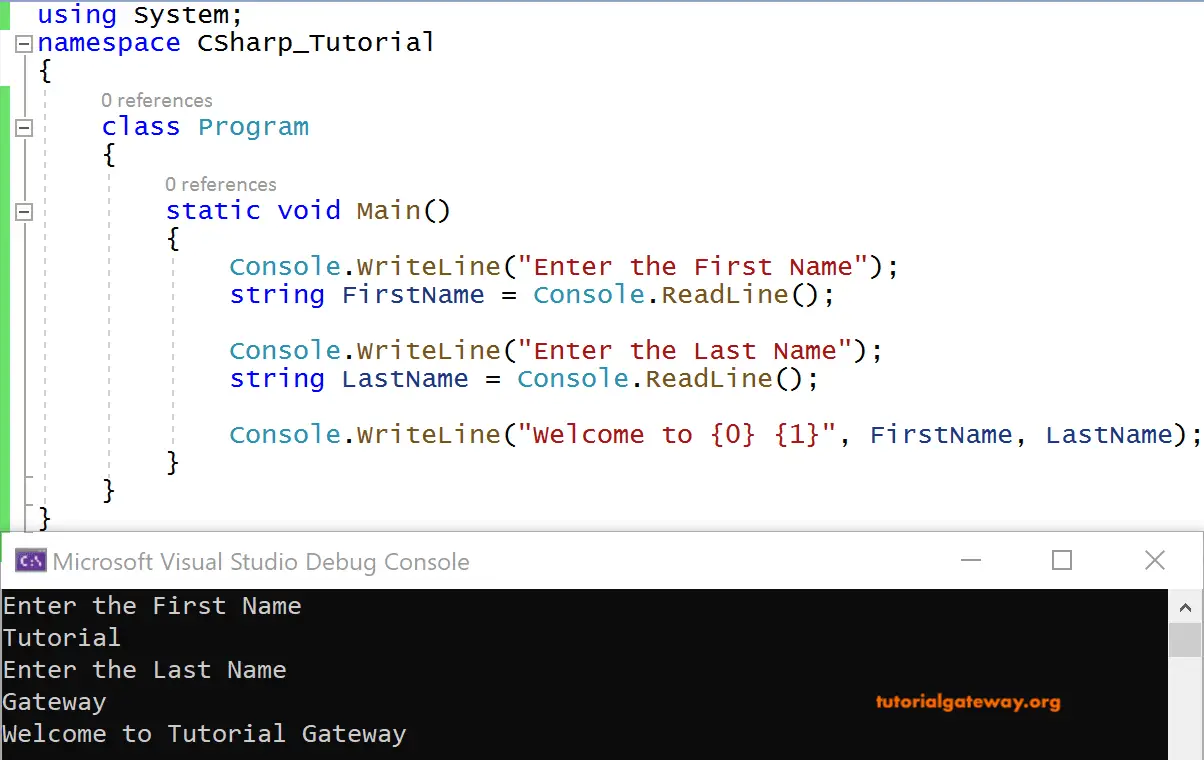
This section shows the C# basic program example and explains the program structure line by line. Before we get into the complete tutorial, let us understand the basic structure of the program example.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string PrintMessage = "First C# Program";
Console.WriteLine(PrintMessage);
}
}
The above C# example program belongs to a basic or simple Console application. Here, I want to print a simple message “First C# Program” on a command prompt window.
Console.WriteLine() —This is the print statement in this language.
Here, Console is a class derived from the System Namespace, whereas WriteLine() is a method in the Console class.
The System is the Namespace, which is a collection of various things like classes, enums, structs, interfaces, delegates, etc. Even a Namespace can contain other Namespaces.
Instead of using namespaces, we can even use fully qualified names in the declaration. i.e., System.Console.WriteLine();
Program is a Class Name in which we are writing the code.
What we have done in this Basic Example Program is take a string (Data type) variable PrintMessage and stored a message in it. And finally printed that message through that variable on the Console.
Here is our output showing on the Console.
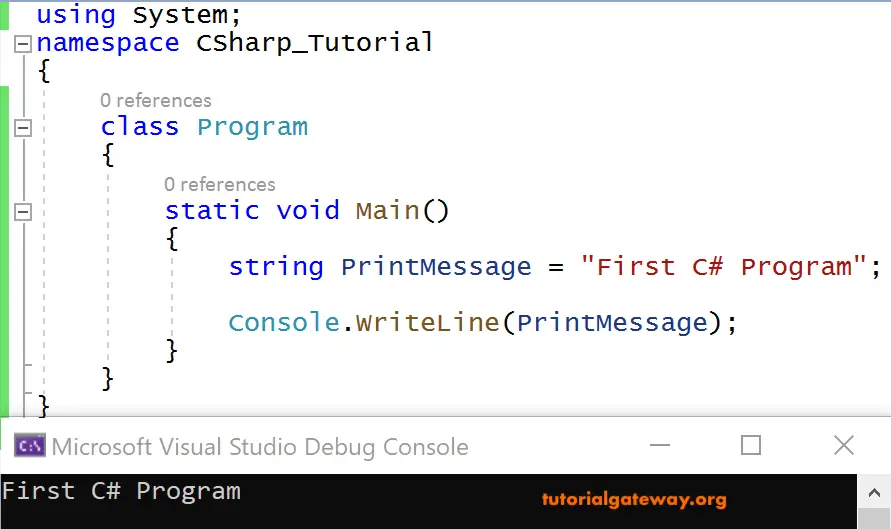
There are two ways to write onto a C# Console and we show both of them in the coming examples.
C# Basic Example Program using Concatenation
We write a C# program asking the user to enter the course name. And then printing a message to the Console after reading the course name from the Console.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter the Course Name");
string Course = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to " + Course);
}
}
OUTPUT
Here Console.ReadLine() reads the course name from the user, i.e., C# Programming Tutorial. Next, we are storing that text in a string variable, course, for printing purposes.
We are concatenating the string “Welcome to” with the text taken from the user. i.e., C# Programming Tutorial using ‘+’(the concatenating or arithmetic plus operator).
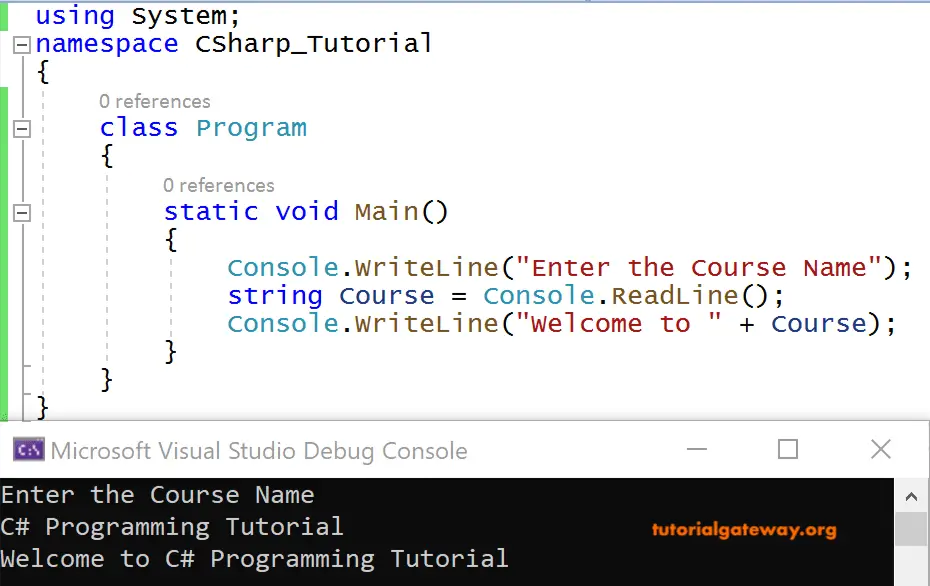
C# Basic Example Program using Place holder syntax
Instead of concatenating them, we can use placeholder syntax for printing the string as the output.
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to {0} ", course);
Here, the text read from the string variable course will get substituted in the place ‘{0}’.
In the real-time environment, mostly placeholder syntax is preferred for printing onto the Console programs.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter the First Name");
string FirstName = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Enter the Last Name");
string LastName = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to {0} {1}", FirstName, LastName);
}
}
OUTPUT