Descripción
Limita el acceso a tu sitio a los visitantes que hayan iniciado sesión o que acceden al sitio desde un conjunto de direcciones IP especificadas. Envía visitantes restringidos a la página de inicio de sesión, redirigirlos o mostrar un mensaje o página. Una gran solución para Extranets, Intranets alojadas públicamente o sitios paralelos de desarrollo / pruebas.
Añade varias opciones de configuración nuevas al panel de configuración de lectura, así como al panel de configuración de red en multisitio. Desde estos paneles puedes:
- Activar o desactivar la restricción del sitio
- Cambiar el comportamiento de restricción: enviar a iniciar sesión, redirigir, mostrar un mensaje, mostrar una página
- Añadir direcciones IP a una lista no restringida, incluidos rangos
- Añade rápidamente tu IP actual a la lista de no restringidos
- Personaliza la ubicación de redireccionamiento, incluida una opción para enviarlos a la misma ruta solicitada y establecer el código de respuesta HTTP para la optimización de SEO.
- Define un mensaje simple para mostrar los visitantes restringidos, o selecciona una página para mostrarles. ¡Genial por los avances de «próximamente»!
Capturas
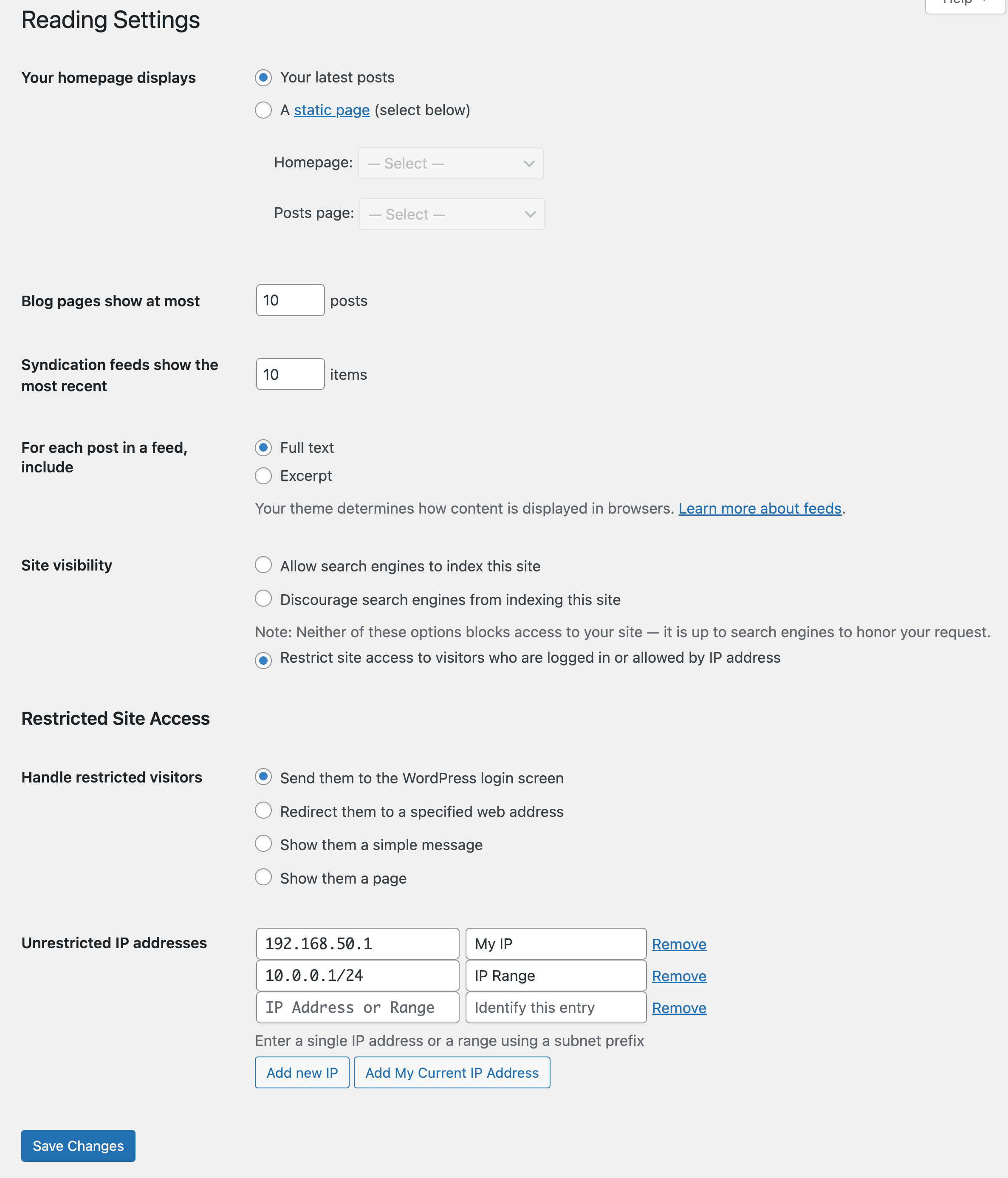
Captura de pantalla del panel de configuraciones con la opción de acceso restringido al sitio (enviar a la página de inicio de sesión). 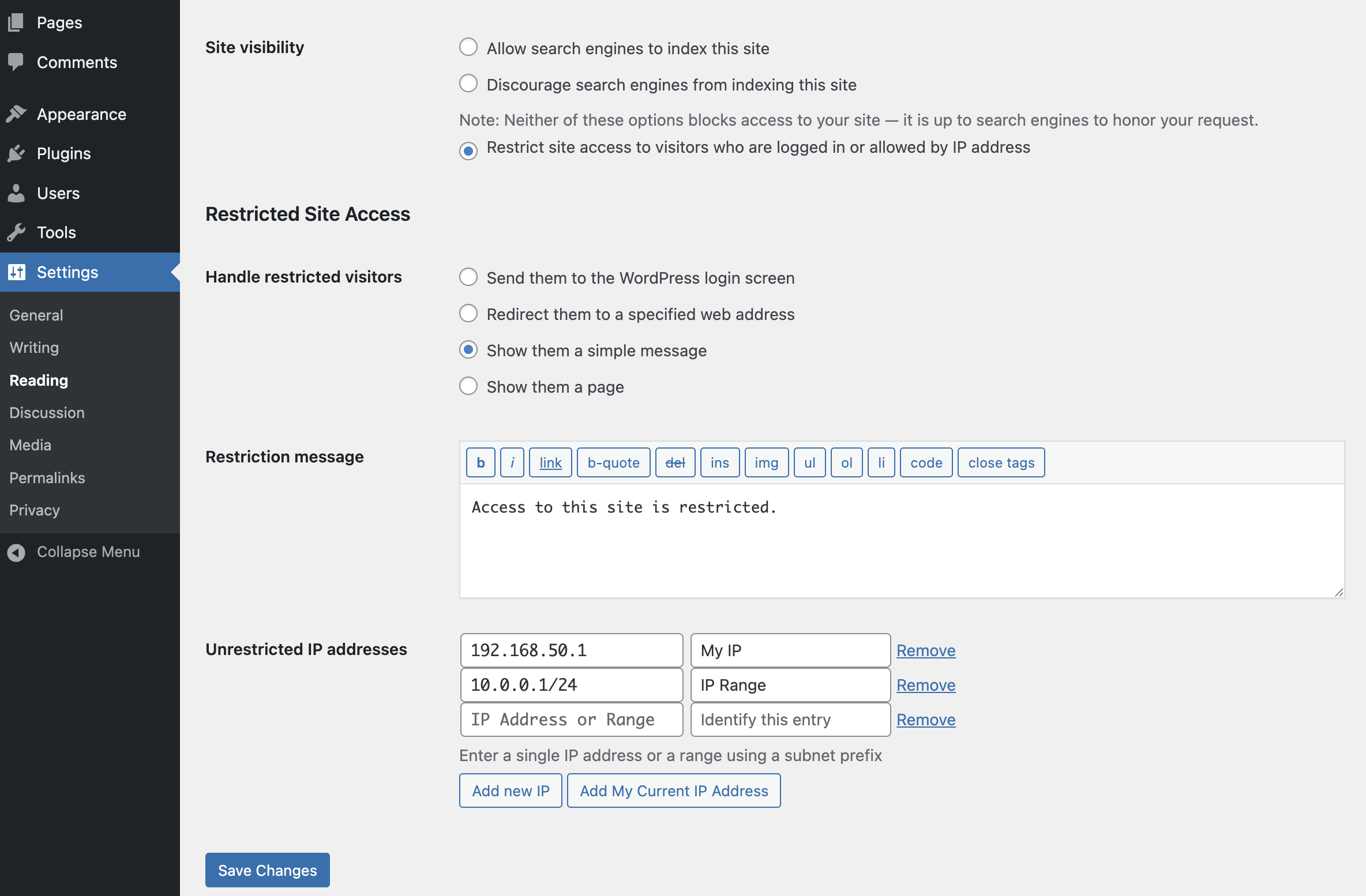
Captura de pantalla del panel de configuración con la opción de mensaje de restricción habilitada 
¡Mucha ayuda en línea! Se muestra y se comporta como la ayuda nativa de WordPress.
Instalación
- Instálalo fácilmente con el panel de control de plugins de WordPress o descarga el plugin manualmente y sube la carpeta extraída al directorio
/wp-content/plugin/. - Activa el plugin a través del menú «Plugins» en WordPress.
- Configura el plugin yendo al menú «Lectura» (WP3.5+) o «Privacidad» (versiones anteriores) en «Ajustes».
FAQ
-
¿Dónde cambio los ajustes de las restricciones?
-
Los ajustes de Restricted Site Access se añaden a la página de Lectura, con las opciones nativas de WordPress de privacidad. (Fue movido aquí desde una página independiente de ajustes de Privacidad en la versión 3.5.)
-
¡No funciona! ¡Mi sitio es totalmente accesible!
-
Normalmente, Restricted Site Access no es compatible con algunas soluciones de caché de páginas. Si bien el plugin se engancha lo antes posible para verificar los permisos de los visitantes, es importante entender que algunos plugins de caché de páginas generan resultados estáticos que evitan que los plugins, como Restricted Site Access, puedan comprobar los visitantes individuales.
En la medida en que los sitios bloqueados por este plugin no deberían preocuparse por el alto rendimiento en en la parte pública, recomendamos encarecidamente deshabilitar las soluciones de almacenamiento en caché de páginas mientras se restringe el acceso a tu sitio. Ten en cuenta que de todos modos la mayoría de los complementos de caché de páginas no almacenan en caché las opciones de «conectado». También ten en cuenta que el plugin es totalmente compatible con otras capas de almacenamiento en caché, como la memoria caché de objetos de WordPress.
-
¿Cómo permito el acceso a páginas específicas o partes de mi sitio?
-
Los desarrolladores pueden usar el filtro
restricted_site_access_is_restrictedpara anular el comportamiento de restricción normal. Ten en cuenta que las comprobaciones de restricción suceden antes de que WordPress ejecute cualquier consulta; pasa la solicitud de consulta de la variable global$wppara que los desarrolladores puedan investigar qué está intentando cargar el visitante.Por ejemplo, para desbloquear una feed RSS, coloca el siguiente código PHP en el archivo functions.php del tema o en un simple plugin:
add_filter( 'restricted_site_access_is_restricted', 'my_rsa_feed_override', 10, 2 ); function my_rsa_feed_override( $is_restricted, $wp ) { // check query variables to see if this is the feed if ( ! empty( $wp->query_vars['feed'] ) ) { $is_restricted = false; } return $is_restricted; } -
¿Cómo de seguro es este plugin?
-
Los visitantes que no están conectados o permitidos por una dirección IP no podrán navegar por tu sitio (pero ten cuidado con las incompatibilidades de los plugins del almacenamiento en caché de página, mencionados anteriormente). Restricted Site Access no bloquea el acceso a, enlaces directos a los archivos en la carpeta de medios y cargas (por ejemplo). También es importante recordar que las direcciones IP pueden ser falsificadas. Debido a que Restricted Site Access se ejecuta como un plugin, está sujeto a cualquier otra vulnerabilidad presente en tu sitio.
Restricted Site Access no está destinado a ser una caja fuerte de datos secretos, sino simplemente una forma confiable y conveniente de manejar visitantes no deseados.
In 7.3.2, two new filters were added that can be utilized to help prevent IP spoofing attacks. The first filter allows you to set up a list of approved proxy IP addresses and the second allows you to set up a list of approved HTTP headers. For any sites that were using Restricted Site Access prior to version 7.5.0, a handful of HTTP headers are trusted by default. To change this, utilize the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to modify the HTTP headers you want to trust. If your site is not running behind a proxy, we recommend doing the following:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_headers', '__return_empty_array' );This will then only use the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header to determine the IP address of the visitor. This header can’t be spoofed, so this will increase security. Note that this is now the default for all new installs since version 7.5.0.If your site is running behind a proxy (like a CDN), you usually can’t rely on the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header, as this will contain the IP address of the proxy, not the user. If your proxy uses static IP addresses, we recommend using thersa_trusted_proxiesfilter to set those trusted IP addresses:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_proxies', 'my_rsa_trusted_proxies' ); function my_rsa_trusted_proxies( $trusted_proxies = array() ) { // Set one or more trusted proxy IP addresses. $proxy_ips = array( '10.0.0.0/24', '10.0.0.0/32', ); $trusted_proxies = array_merge( $trusted_proxies, $proxy_ips ); return array_unique( $trusted_proxies ); }And then use the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to set which HTTP headers you want to trust. Consult with your proxy provider to determine which header(s) they use to hold the original client IP:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_headers', 'my_rsa_trusted_headers' ); function my_rsa_trusted_headers( $trusted_headers = array() ) { // Set one or more trusted HTTP headers. $headers = array( 'HTTP_X_FORWARDED', 'HTTP_FORWARDED', ); return $headers; }If your proxy does not use static IP addresses, you can still utilize the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to change which HTTP headers you want to trust. -
He recibido una advertencia sobre la caché de página. ¿Qué significa?
-
As of version 7.6.0, RSA attempts to prevent full page caching on sites with an IP address allow list. This is to prevent the page content from being stored at the caching level and displayed to unauthorized visitors.
Page caching plugins often hook into WordPress to quickly serve the last cached output of a page before we can check to see if a visitor’s access should be restricted. Not all page caching plugins behave the same way, but several solutions – including external solutions we might not detect – can ignore the no-caching headers set by WordPress and show cached content to unauthorized users.
-
Why can’t logged-in users see all the sites on my multisite instance?
-
In 6.2.0, the behavior in a multisite install changed from allowing any logged-in user to see a site to checking their role for that specific site. This is a safer default given the varying ways multisite is used; however, if you would prefer to rely on the previous behavior rather than explicitly adding users to each site, place the following PHP code in the theme’s functions.php file or in a simple plug-in:
add_filter( 'restricted_site_access_user_can_access', 'my_rsa_user_can_access' ); function my_rsa_user_can_access( $access ) { if ( is_user_logged_in() ) { return true; } return $access; } -
Is there a way to configure this with [WP-CLI](https://make.wordpress.org/cli/)?
-
As of version 7.0.0, CLI integration has been added. To see the available commands, type the following in your WordPress directory:
$ wp rsa -
How can I programatically define whitelisted IPs?
-
In 7.0.0, the capacity to define a pipe delimited array of whitelisted IP addresses via constant was introduced.
In your
wp-config.phpfile, you can define the following:define( 'RSA_IP_WHITELIST', '192.0.0.1|192.0.0.10' );In 7.1.1, the capacity to programmatically add / remove / set access IPs programmatically was introduced.
The following are valid statements:
Set IPs, ignoring all stored values (but not the constant defined values), if you’re going to use the approach with array indices rather than mixing the two.
Restricted_Site_Access::set_ips( array( '192.168.0.1', '192.168.0.2', '192.168.0.3' ) ); Restricted_Site_Access::set_ips( array( 'labelfoo' => '192.168.0.1', 'labelbar' => 192.168.0.2', 'labelbaz' => 192.168.0.3' ) );Add IPs, if they’re not already added.
Restricted_Site_Access::append_ips( array( '192.168.1.5' => 'five', '192.168.1.6' => 'six' ) );Remove IPs, if they are in the list.
Restricted_Site_Access::remove_ips( array( '192.168.1.2','192.168.1.5','192.168.1.6', ) ); -
Is there a constant I can set to ensure my site is (or is not) restricted?
-
As of version 7.1.0, two constants were introduced that give you the ability to specify if the site should be in restricted mode.
You can force the plugin to be in restricted mode by adding the following to your
wp-config.phpfile:define( 'RSA_FORCE_RESTRICTION', true );Or to ensure your site won’t be in restricted mode:
define( 'RSA_FORBID_RESTRICTION', true );Make sure you add it before the
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy blogging. */line.Please note that setting
RSA_FORCE_RESTRICTIONwill overrideRSA_FORBID_RESTRICTIONif both are set. -
What does ‘Discourage search engines from indexing this site’ do?
-
When the ‘Discourage search engines from indexing this site’ option is enabled, it prevents search engines from indexing the site while still permitting access to regular visitors.
-
What does ‘Restrict site access to visitors who are logged in or allowed by IP address’ do?
-
When this option is activated, it serves as a barrier to all visitors except those who are authenticated (logged in) or whose IP addresses are included in the ‘Unrestricted IP addresses’ setting. This restriction applies universally, even to automated crawlers such as search engines.
Reseñas
Colaboradores y desarrolladores
«Restricted Site Access» es un software de código abierto. Las siguientes personas han colaborado con este plugin.
Colaboradores«Restricted Site Access» está traducido en 6 idiomas. Gracias a los traductores por sus contribuciones.
Traduce «Restricted Site Access» a tu idioma.
¿Interesado en el desarrollo?
Revisa el código , echa un vistazo al repositorio SVN o suscríbete al registro de desarrollo por RSS.
Registro de cambios
7.6.1 – 2025-10-29
- Fixed: Ensure field data is set properly before we use it. Resolves a fatal error with Elementor (props @ktorktor, Vishal Patel, fatjester, @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc via #371).
7.6.0 – 2025-10-27
- Added: New setting allowing you to hide the WordPress admin bar on the frontend for specific user roles (props @sanketio, @fabiankaegy, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #362).
- Added: New
RSA_NETWORK_MODEconstant to define default setting for network mode for multisite (props @sanketio, @claytoncollie, @dkotter via #363). - Added: More details on how caching may impact the plugin (props @peterwilsoncc, @jakemgold, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via GHSA-jfqv-gvp2-qq5f).
- Fixed: Ensure IP addresses can be saved properly at the network level (props @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc via #367).
- Security: Prevent caching of page content when using an IP allow list (props @peterwilsoncc, @fabiankaegy, @joemcgill, @jakemgold, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via GHSA-jfqv-gvp2-qq5f).
- Security: Bump
cross-spawnfrom 7.0.3 to 7.0.6,@wordpress/scriptsfrom 29.0.0 to 30.16.0 andhttp-proxy-middlewarefrom 2.0.6 to 2.0.9 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #355). - Security: Bump
tar-fsfrom 3.0.8 to 3.0.9 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #359). - Security: Bump
brace-expansionfrom 1.1.11 to 1.1.12,on-headersfrom 1.0.2 to 1.1.0 andcompressionfrom 1.7.4 to 1.8.1 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #361).
7.5.3 – 2025-05-19
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 6.5 to 6.6.
- Changed: Bump WordPress «tested up to» version 6.8 (props @kmgalanakis, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #349, #352).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 6.5 to 6.6 (props @jeffpaul via #351, #352).
- Fixed: PHP Notice that the function
_load_textdomain_just_in_timewas called incorrectly (props @kmgalanakis, @dkotter via #350). - Security: Bump
axiosfrom 1.7.4 to 1.8.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #346).
7.5.2 – 2025-02-05
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 6.4 to 6.5.
- Changed: Bump WordPress «tested up to» version 6.7 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @mehidi258 via #335, #336).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 6.4 to 6.5 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @mehidi258 via #335, #336).
- Fixed: Add missing textdomain to a few strings (props @NekoJonez, @dkotter via #338).
- Security: Bump
axiosfrom 1.6.7 to 1.7.4 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #326). - Security: Bump
webpackfrom 5.90.0 to 5.94.0 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #327). - Security: Bump
wsfrom 7.5.10 to 8.18.0 and@wordpress/scriptsfrom 27.1.0 to 29.0.0 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #328). - Security: Bump
expressfrom 4.19.2 to 4.21.2,sendfrom 0.18.0 to 0.19.0 andserve-staticfrom 1.15.0 to 1.16.2 (props @dependabot, @peterwilsoncc via #340). - Security: Bump
@wordpress/e2e-test-utils-playwrightfrom 1.7.0 to 1.16.0,nanoidfrom 3.3.7 to 3.3.8,mochafrom 10.2.0 to 11.0.1 and removescookie(props @dependabot, @peterwilsoncc via #341).
7.5.1 – 2024-07-09
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 5.7 to 6.4.
- Changed: Bump WordPress «tested up to» version 6.6 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #313, #318).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 5.7 to 6.4 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #313, #318).
- Security: Bump
tj-actions/changed-filesfrom 32 to 41 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #297). - Security: Bump
expressfrom 4.18.2 to 4.19.2 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
follow-redirectsfrom 1.15.5 to 1.15.6 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
webpack-dev-middlewarefrom 5.3.3 to 5.3.4 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
bracesfrom 3.0.2 to 3.0.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
pac-resolverfrom 7.0.0 to 7.0.1 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
socksfrom 2.7.1 to 2.8.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
wsfrom 7.5.9 to 7.5.10 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319).
7.5.0 – 2023-12-14
Note: this release changes the default behavior for new installs in regards to IP detection. This shouldn’t impact existing installs but there are two filters that can be used to change this behavior. See the readme for full details.
- Fixed: Update code snippet in the readme (props @dkotter, @jeffpaul via #291).
- Security: For new installs, ensure we only trust the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header by default. Existing installs will still utilize the old list of approved headers but can modify this (and are recommended to) by using thersa_trusted_headersfilter (props @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc, @dustinrue, @mikhail-net, Darius Sveikauskas via #290). - Security: Bump
axiosfrom 0.25.0 to 1.6.2 and@wordpress/scriptsfrom 23.7.2 to 26.19.0 (props @dependabot, @dkotter via #293).
