An ip2 network provides the foundational data layer for modern digital operations, offering deep insights into the origin, characteristics, and potential risks associated with any IP address. Understanding how to leverage this intelligence is no longer a luxury but a necessity for cybersecurity, marketing, and compliance. This guide delves into the core components of an ip2 network, its critical business applications, and how to choose a provider that delivers the speed and accuracy your operations demand. The quality of your IP intelligence directly impacts your ability to prevent fraud, personalize user experiences, and maintain a competitive edge in a data-driven world.
The Core Components of an IP2 Network
A comprehensive ip2 network is built upon several pillars of data, each providing a unique lens through which to analyze internet traffic. These components work together to create a detailed profile of every connection, enabling businesses to make informed, real-time decisions. From identifying a user’s geographical location to understanding the infrastructure they are using, this data is invaluable. A robust ip2 network provider synthesizes these elements into an easily accessible format, typically via an API, allowing for seamless integration into existing workflows and applications.
IP Geolocation Data: Pinpointing User Location
IP geolocation is arguably the most recognized feature of an ip2 network. It involves mapping an IP address to its real-world geographic location, such as country, state, city, and even postal code. This data is essential for a wide range of applications, including content localization, targeted advertising, and enforcing geographic restrictions. For example, an e-commerce platform can use this data to display prices in the local currency, while a streaming service can ensure it only shows content licensed for a specific region. The accuracy of this data is paramount; even minor inaccuracies can lead to poor user experiences and compliance issues. High-quality ip2 network services use a blend of network routing data, direct partnerships, and advanced algorithms to provide precise location information.
Proxy and VPN Detection: Ensuring Data Integrity
In an era of increasing privacy concerns and sophisticated fraud schemes, identifying anonymized traffic is critical. An essential function of a powerful ip2 network is its ability to detect whether a user is connecting through a proxy, VPN, or Tor node. This capability is vital for fraud prevention, as malicious actors frequently use these services to mask their true identity and location. By flagging anonymized connections, businesses can apply additional security checks, block suspicious transactions, or prevent access to sensitive systems. This technology analyzes various IP characteristics, such as its hosting provider, known usage patterns, and port configurations, to identify non-direct connections. This component is crucial for maintaining the integrity of user data and protecting digital assets.
ASN and Carrier Information: Understanding Network Origins
Every IP address is part of a larger network block assigned to an Autonomous System (AS). An Autonomous System Number (ASN) uniquely identifies this network, which is typically an Internet Service Provider (ISP), a large enterprise, or a university. An ip2 network provides detailed ASN and carrier information, revealing the owner of the IP block and the type of network it belongs to (e.g., residential, mobile, or business). This information is incredibly useful for analytics, cybersecurity, and traffic routing. For instance, knowing if a user is on a mobile carrier network versus a university network can inform content delivery strategies. Security teams use this data to identify traffic originating from known malicious networks or data centers associated with bot activity.
WHOIS Data: Uncovering Domain and IP Ownership
WHOIS data provides registration information for IP addresses and domain names. While traditionally used for network administration, it offers valuable context within an ip2 network framework. It can reveal the organization that owns a specific IP block, along with contact details and registration dates. This information can be used to verify the legitimacy of a business partner, investigate the source of a cyberattack, or perform due diligence. When integrated with other IP intelligence, WHOIS data adds another layer of verification, helping to paint a complete picture of an IP address’s background and affiliations.
Section Summary:
- Geolocation: Pinpoints the user’s physical location (country, city, ZIP).
- Proxy Detection: Identifies traffic from VPNs, proxies, and Tor to flag masked users.
- ASN/Carrier Data: Reveals the network owner (e.g., ISP, mobile carrier) of the IP address.
- WHOIS Information: Provides registration details about the IP block owner.

Why Accurate IP2 Network Data is Crucial for Business
The quality of data from an ip2 network directly translates into business performance and security. Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to blocked legitimate customers, failed marketing campaigns, and security vulnerabilities. Conversely, precise, real-time IP intelligence empowers organizations to operate more efficiently, securely, and profitably. Making decisions based on reliable data from a premier ip2 network minimizes risk and maximizes opportunity across various departments, from marketing to IT security. The investment in a high-quality IP intelligence solution offers a substantial return by protecting revenue and enhancing customer trust.
Enhancing Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention
The primary driver for adopting ip2 network solutions is often cybersecurity. Financial institutions, e-commerce sites, and online services are constant targets for fraudulent activities like account takeover, credential stuffing, and payment fraud. IP intelligence provides the first line of defense. By analyzing the IP address of every login attempt or transaction, security systems can flag high-risk indicators. For example, a login attempt from a country where the user has never been, or from an IP address known to be part of a botnet, can be automatically blocked or challenged with multi-factor authentication. An effective ip2 network can differentiate between a legitimate user traveling abroad and a fraudster using a proxy, a critical distinction that prevents financial loss and protects brand reputation.
Personalizing Content and Advertising
Personalization is key to customer engagement. IP geolocation data from an ip2 network enables businesses to tailor website content, product recommendations, and advertising to a user’s location. This creates a more relevant and seamless experience. An online retailer can feature winter clothing for a user in a cold climate and swimwear for someone in a tropical region. Similarly, ad campaigns can be geo-targeted to specific cities or regions, maximizing ad spend and increasing conversion rates. Without accurate data, personalization efforts can backfire, such as showing ads for a New York-based event to a user in California, resulting in wasted resources and a poor user experience.
Enforcing Digital Rights and Compliance
Many businesses, particularly in the media and gaming industries, are bound by licensing agreements that restrict content distribution to specific geographical areas. An ip2 network is essential for enforcing these digital rights management (DRM) policies. Streaming services use IP geolocation to ensure that users can only access content available in their country. This is also critical for compliance with international regulations like GDPR or local gambling laws, which often have location-based requirements. Failure to enforce these restrictions can lead to severe legal and financial penalties. The reliability of the ip2 network data is therefore a cornerstone of a company’s legal and compliance framework.
Improving Network Performance and Analytics
Beyond security and marketing, ip2 network data is instrumental in network management and business intelligence. By analyzing the geographic distribution and network types of their users, companies can optimize their infrastructure. For instance, they might decide to place content delivery network (CDN) servers closer to a growing user base in a new region to reduce latency. Web analytics are also enriched with this data, providing deeper insights into user behavior. Marketers can analyze campaign performance by region, and product teams can identify where their user base is growing fastest, informing strategic business decisions and infrastructure investments.
Section Summary:
- Security: Block fraudulent transactions and account takeovers by identifying high-risk IPs.
- Personalization: Increase engagement and sales by tailoring content and ads to user location.
- Compliance: Enforce geo-restrictions for content licensing and adhere to regional regulations.
- Analytics: Optimize network infrastructure and gain deeper business insights from user data.
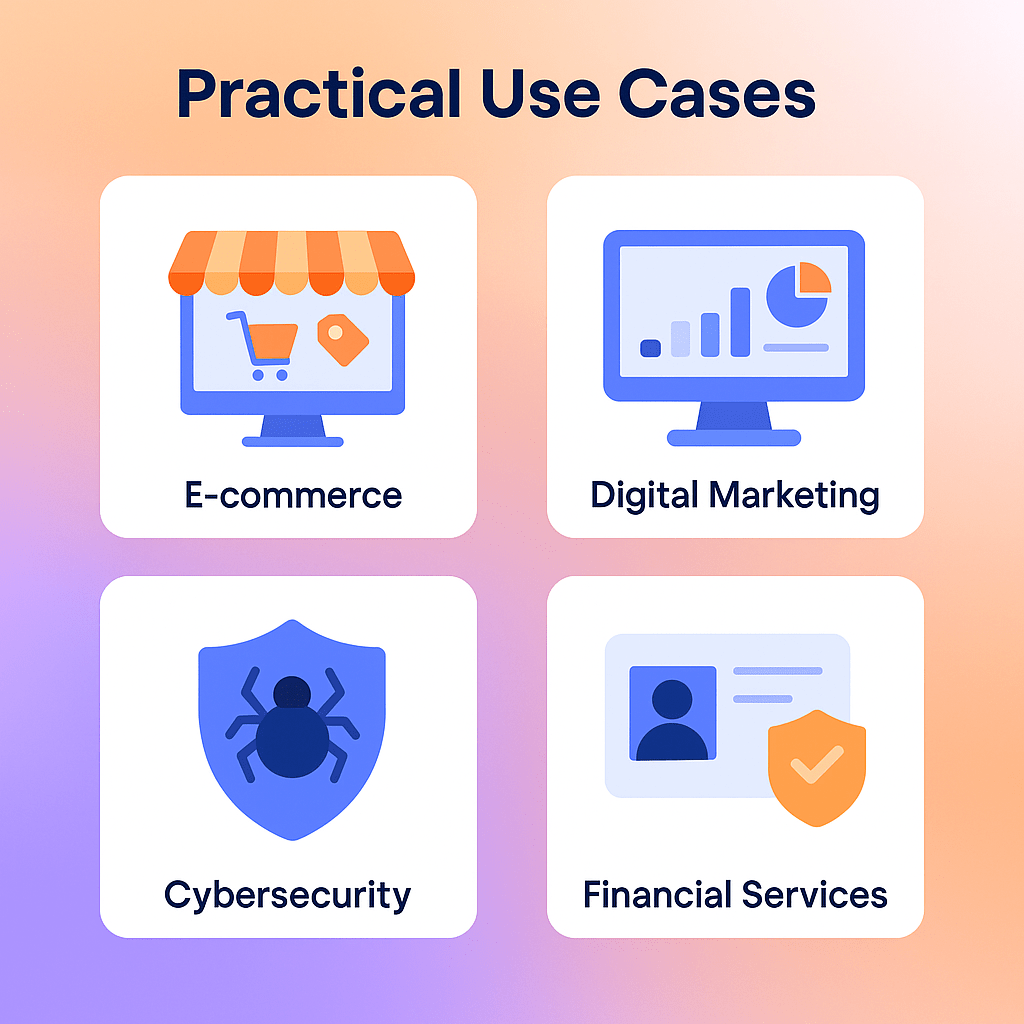
Leveraging IP Intelligence: Practical Use Cases
The theoretical benefits of an ip2 network come to life in its practical applications across various industries. Businesses integrate this data into their core processes to automate decisions, mitigate risks, and uncover new growth opportunities. From preventing a fraudulent purchase to delivering a perfectly timed local promotion, the use cases are both diverse and impactful. A flexible and fast ip2 network allows this intelligence to be applied in real-time, where it can provide the most value.
E-commerce: Geo-targeting and Price Optimization
For e-commerce platforms, an ip2 network is a multi-purpose tool. It’s used to automatically calculate shipping costs and taxes based on the user’s location, simplifying the checkout process. Retailers also use it for dynamic pricing, adjusting prices based on regional market conditions, competitor pricing, and local demand. Most importantly, it serves as a powerful fraud detection mechanism. By cross-referencing the IP location with the shipping and billing addresses, platforms can flag orders with significant discrepancies, a common indicator of stolen credit card usage. This single use of an ip2 network can save businesses millions in chargebacks and lost goods.
Digital Marketing: Campaign Analytics and Audience Segmentation
Digital marketers rely on ip2 network data to refine their strategies and measure campaign effectiveness. By enriching lead forms with geolocation data, sales teams can assign leads to the correct regional representatives automatically. In analytics, marketers can segment website traffic by country, state, or city to understand which regions are responding best to their messaging. This allows them to allocate marketing budgets more effectively, focusing resources on high-performing areas. Furthermore, identifying the ISP and connection type (e.g., business vs. residential) helps in B2B marketing to differentiate between traffic from target companies and general consumer traffic.
Cybersecurity: Threat Intelligence and Anomaly Detection
In the cybersecurity domain, an ip2 network is a core component of threat intelligence platforms. Security analysts use IP data to investigate alerts and trace the origins of attacks. By identifying the ASN and hosting provider of a malicious IP, they can block entire network ranges associated with bad actors. Anomaly detection systems continuously monitor for unusual patterns, such as a user account being accessed from multiple countries in a short period. This kind of real-time intelligence, powered by a fast ip2 network API, is crucial for responding to threats before they escalate into major security breaches. For more information on security use cases, explore our solutions for preventing online fraud.
Financial Services: Risk Assessment and Compliance Checks
Financial institutions operate under strict regulatory requirements, including Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws. An ip2 network plays a vital role in these compliance processes. During online account opening or loan applications, the user’s IP address is analyzed to ensure it aligns with the provided physical address. The system also checks if the IP originates from a sanctioned country or is a known proxy used for illicit activities. This helps financial firms assess risk and prevent fraudulent account openings, ensuring they remain compliant with global financial regulations.
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Key Benefit |
| E-commerce | Fraud Detection & Geo-Targeting | Reduced chargebacks, increased sales |
| Digital Marketing | Audience Segmentation & Analytics | Higher ROI on ad spend, better leads |
| Cybersecurity | Threat Intelligence & Blocking | Proactive threat mitigation, breach prevention |
| Financial Services | Risk Assessment & Compliance | Reduced fraud, adherence to AML/KYC laws |
The Technology Behind a High-Performance IP2 Network
Not all ip2 network providers are created equal. The quality, speed, and accuracy of the data depend entirely on the underlying technology and infrastructure. A top-tier provider invests heavily in sophisticated data collection methods, a robust global network, and real-time processing capabilities. Understanding these technical differentiators is key to selecting a service that can meet the demands of real-time applications where milliseconds matter. The architecture of the ip2 network directly impacts its ability to deliver actionable intelligence without introducing latency.
Data Collection and Aggregation Methods
The foundation of any ip2 network is its data. Leading providers use a multi-faceted approach to collect and verify information. This includes analyzing BGP routing data from across the internet, establishing partnerships with ISPs worldwide, and using proprietary algorithms to correlate different data points. Some providers also deploy a global network of probes to actively test and map IP address spaces. This constant process of collection, cross-referencing, and verification ensures the data remains accurate and up-to-date, reflecting the dynamic nature of the internet where IP address assignments can change frequently.
The Role of Residential and ISP Proxies in Data Accuracy
For the highest level of accuracy, especially in distinguishing between different types of connections, leveraging a diverse proxy network is essential. By routing traffic through real-world residential and ISP proxies, an ip2 network provider can gather ground-truth data on how specific IP blocks are being used. This method is far more reliable than relying solely on passive database analysis. NetNut’s network, for example, utilizes direct connectivity with ISPs, providing exceptionally clean and accurate data on residential IPs. This allows for more precise geolocation and more reliable identification of IP types (e.g., residential vs. data center), which is crucial for sensitive use cases like fraud detection.
Real-time Data vs. Static Databases
A significant differentiator in the ip2 network market is the freshness of the data. Some providers rely on downloadable static databases that are updated periodically (e.g., weekly or monthly). While suitable for some offline analysis, this approach is inadequate for real-time applications. A modern, high-performance ip2 network operates on a real-time model, where data is continuously updated. This is achieved through a cloud-based API that queries a constantly refreshed central database. For applications like transaction fraud screening or real-time ad bidding, access to the latest IP intelligence is non-negotiable, as using even slightly outdated data could mean approving a fraudulent transaction or wasting ad spend.
API Integration for Seamless Access
The primary method for accessing an ip2 network is through an Application Programming Interface (API). A well-designed API is crucial for easy integration and high performance. It should be fast, reliable, and scalable to handle millions of queries per day. Leading providers offer RESTful APIs that return data in standard formats like JSON, making it easy for developers to incorporate IP intelligence into any application. The API’s response time is a critical performance metric; a low-latency API ensures that IP lookups do not become a bottleneck in user-facing processes like website loading or checkout flows.
Section Summary:
- Data Collection: Uses diverse sources like BGP data and ISP partnerships for comprehensive coverage.
- Proxy Networks: Leverages residential proxies to gather highly accurate, ground-truth data.
- Real-time vs. Static: Superior services offer real-time APIs over periodically updated static databases.
- API Access: Provides fast, scalable, and easy-to-integrate APIs for seamless implementation.
Choosing the Right IP Intelligence Provider
Selecting the right ip2 network provider is a critical decision that impacts security, user experience, and operational efficiency. With various vendors in the market, it’s essential to look beyond marketing claims and evaluate providers based on concrete performance metrics and features. The ideal partner will offer a solution that is not only accurate and fast but also scalable and easy to integrate into your existing technology stack. A thorough evaluation process will ensure you choose an ip2 network that serves as a strategic asset for your business.
Key Factors to Consider: Accuracy, Speed, and Scalability
These three factors form the trifecta of a high-quality ip2 network service.
- Accuracy: How correct is the data? This is especially crucial for geolocation and proxy detection. Ask for accuracy statistics, particularly for the regions that matter most to your business.
- Speed: How quickly does the API respond? Low latency is vital for any real-time application. A delay of even 100 milliseconds can impact user experience and conversion rates.
- Scalability: Can the service handle your query volume, both now and in the future? Ensure the provider’s infrastructure is built to handle spikes in traffic without performance degradation. A provider should be able to process billions of queries per day without issue.
Evaluating Data Freshness and Update Frequency
The internet is constantly changing, with IP addresses being reassigned and new proxies emerging daily. A provider’s commitment to data freshness is a key indicator of quality. Inquire about their update frequency. A top-tier ip2 network will have a continuous update cycle, ensuring the data you receive is a reflection of the internet as it is right now, not as it was last week. This is particularly important for proxy detection, as malicious actors are constantly rotating the IP addresses they use.
Understanding Different Data Formats (API vs. Database)
Consider how you plan to use the data. For real-time, online applications (like e-commerce checkout or ad serving), a cloud-based API is the only viable option. It provides the most current data and requires no local infrastructure management. For offline, large-scale data analysis projects, a downloadable database file might be an option. However, most modern use cases demand the real-time capabilities that only an API-first ip2 network can provide. Evaluate the clarity and completeness of the API documentation and the level of support offered to developers.
The NetNut Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Reliability
NetNut provides a leading ip2 network solution built on a unique infrastructure. By partnering directly with ISPs around the world, NetNut accesses IP data directly from the source, bypassing the inconsistencies of public or peer-to-peer networks. This results in an exceptionally fast, stable, and accurate data feed. Our network is optimized for performance, delivering some of the lowest latencies in the industry, making it ideal for the most demanding real-time applications. Whether for cybersecurity, ad-tech, or market research, NetNut offers a premium ip2 network designed for businesses that cannot compromise on data quality or speed.
Provider Selection Checklist:
- [ ] Does the provider offer verifiable accuracy statistics?
- [ ] Is the API latency low enough for my real-time needs?
- [ ] Can the infrastructure scale to support my peak query volume?
- [ ] Is the data updated in real-time or on a periodic schedule?
- [ ] Does the provider have direct relationships with ISPs for higher-quality data?
- [ ] Is the API well-documented and easy to integrate?
Future Trends in IP Network Intelligence
The field of IP intelligence is continuously evolving in response to new technologies, regulations, and threat landscapes. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for any business that relies on an ip2 network for its operations. The future will see IP data becoming even more granular, integrated with other data sources, and powered by advanced analytics. Providers who innovate in these areas will deliver the most value, helping businesses navigate an increasingly complex digital world. A forward-thinking ip2 network strategy is essential for long-term success.
The Impact of IPv6 Adoption
As the world slowly transitions from IPv4 to IPv6, the landscape of IP intelligence will change significantly. The vast address space of IPv6 presents new challenges and opportunities for an ip2 network. Geolocation for IPv6 is currently less precise than for IPv4, as the allocation and usage patterns are still developing. Leading providers are actively working on improving their IPv6 mapping capabilities. Businesses must ensure their chosen ip2 network provider has a clear roadmap for IPv6 to avoid being left with a data gap as adoption accelerates.
AI and Machine Learning in Anomaly Detection
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) are set to revolutionize the ip2 network space. AI/ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets of IP behavior to identify subtle patterns and anomalies that would be invisible to rule-based systems. For example, an ML model could learn the typical access patterns for a user account and flag a login from a new IP type or ASN as suspicious, even if the location is plausible. This proactive approach to threat detection will make IP intelligence a more powerful tool for preventing sophisticated fraud and cyberattacks. For further reading, consult authoritative sources like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
Growing Importance of Mobile IP Data
With the majority of internet traffic now coming from mobile devices, the accuracy of mobile IP data is more important than ever. Mobile IPs are often more dynamic than fixed-line broadband IPs, making them harder to geolocate accurately. A top-tier ip2 network needs to excel at identifying mobile carriers and providing precise location data for mobile users. This is critical for mobile advertising, location-based services, and fraud detection on mobile apps. Providers with strong partnerships with mobile network operators will have a distinct advantage in this area.
Ultimately, the power of an ip2 network lies in its ability to provide clear, actionable intelligence from a single data point: the IP address. As digital interactions become more complex, the insights derived from a high-quality ip2 network will only grow in importance, serving as a cornerstone of modern digital strategy.