Displaying the Current Working Directory in Linux | pwd Command
Last Updated :
01 Nov, 2025
The pwd command in Linux displays the full path of your current working directory from the root directory.
- It helps users identify their present location within the filesystem.
- pwd can be a shell built-in command (pwd) or an external binary (/bin/pwd).
- The $PWD environment variable stores the current directory path.
- The command supports two common options: -L (logical) and -P (physical).
It helps users identify their exact location within the Linux file system hierarchy.
Displaying the Current Working Directory
To print the current working directory, simply enter:
pwd
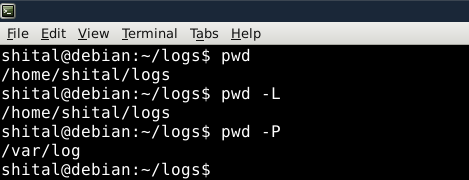 Display the Current Working Directory
Display the Current Working Directory - The output will be the absolute path of your current location in the file system.
- In the given example the directory /home/shital/logs/ is a symbolic link for a target directory /var/logs/
Syntax
The basic syntax of the 'pwd' command is
pwd [OPTIONS]
This command doesn't have any arguments or options, but it can accept flags for specific behavior.
1. Displaying the Current Working Directory Using Binary pwd (/bin/pwd):
The binary /bin/pwd displays the absolute path of the current working directory directly from the system’s executable, ensuring accurate results even in complex environments.
Syntax:
/bin/pwd
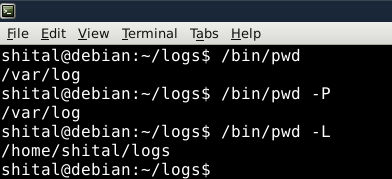 Display the Current Working Directory
Display the Current Working Directory - The default behavior of Built-in pwd is the same as pwd -L. Using "pwd -L" to obtain the symbolic path of a directory containing a symbolic link.
- The default behavior of /bin/pwd is the same as pwd -P. Utilizing "pwd -P" to display the actual path, ignoring symbolic links.
2. The $PWD Environment variable.
The $PWD environment variable is a dynamic variable that stores the path of the current working directory. It holds the same value as 'pwd -L' – representing the symbolic path.
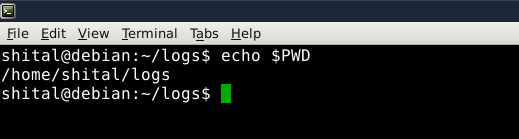 $PWD
$PWDExecuting this command prints the symbolic path stored in the $PWD environment variable
Flags For Specific behavior in `pwd` command in Linux.
- The "-L" flag resolves symbolic links and prints the path of the target directory.
- The default behavior of the shell built-in "pwd" is equivalent to using "pwd -L".
- Mention the "-P" flag, which displays the actual path without resolving symbolic links.
- The default behavior of the binary "/bin/pwd" is the same as using "pwd -P"
pwd -L: Prints the symbolic path.
pwd -P: Prints the actual path.
What is the core purpose of the pwd command in Linux?
-
-
To show the current working directory path
-
-
To display user permissions
Explanation:
pwd outputs the exact filesystem location you are currently in.
Which option of pwd shows the real physical path without resolving symbolic links?
Explanation:
pwd -P prints the actual path on disk and ignores symlink redirection.
If a directory /home/user/logs is a symlink to /var/logs, which command shows /home/user/logs?
Explanation:
pwd -L displays the symbolic path exactly as it appears, even if it points elsewhere.
What value does the $PWD environment variable store?
-
-
-
Symbolic current directory path
-
Home directory path always
Explanation:
$PWD holds the logical (symbolic) representation of your current working directory.
Which version of pwd behaves by default like pwd -P?
-
-
pwd executed inside terminal emulator
-
-
Explanation:
/bin/pwd uses physical resolution, matching the behavior of pwd -P by default.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Linux Administrator System