JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a widely-used, lightweight data format for representing structured data.
- Used Extensively : Used in APIs, configuration files, and data exchange between servers and clients.
- Text-based: JSON is a simple text format, making it lightweight and easy to transmit.
- Human-readable: It uses key-value pairs, making the structure easy to understand.
- Language-independent: While it is derived from JavaScript, JSON is supported by many programming languages including Python, Java, PHP, and more.
- Supported Data structures: Represents data as objects, arrays, strings, numbers, booleans, and null.
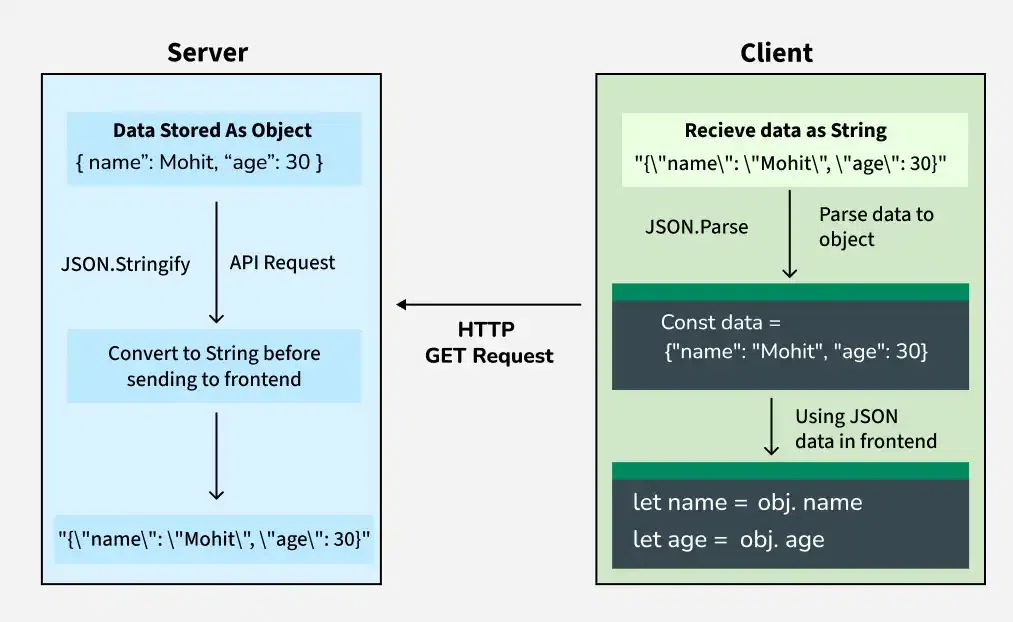
JSON Data Flow: From Server to Client
JSON vs XML
When it comes to data formats, JSON and XML are the two most common choices. JSON is generally preferred for web applications due to its smaller size, ease of use, and better performance. Here's a quick comparison:
| Feature | JSON | XML |
|---|---|---|
| Readability | Human-readable | Human-readable but more verbose |
| Data Size | Smaller and more compact | Larger due to extra markup |
| Parsing | Easier to parse in most languages | More complex parsing |
| Support | Broad support across languages | Initially JavaScript, but now widely supported |
| Use Cases | Web APIs, configuration files, data transfer | Data storage, document formatting |
How JSON Data Flow Works in Web Applications
In a typical web application, JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is used to transfer data between the server and the client (frontend). JSON is language-independent, which makes it ideal for communication between different technologies.
Server Side
- Data is stored as an object (for example, a dictionary or class instance).
- Before sending the data over the network, it is converted into a JSON string.
- This JSON string is sent to the client through an API response (such as an HTTP GET request).
Client Side
- The client receives the data as a JSON string.
- The JSON string is parsed back into a native object depending on the programming language used.
- Once parsed, individual values can be accessed and used in the application.
Example JSON String Received from Server
{"name":"Mohit", "age":30}
This JSON data contains:
- name: "Mohit"
- age: 30
Parsing JSON in Different Programming Languages
Although the JSON data is the same, each language uses its own method or library to parse it.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp>
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json;
int main() {
string json_s = R"({"name": "Mohit", "age": 30})";
json obj = json::parse(json_s);
string name = obj["name"];
int age = obj["age"];
cout << "Name: " << name << ", Age: " << age << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <jansson.h>
int main() {
const char *json_s = "{\"name\": \"Mohit\", \"age\": 30}";
json_error_t error;
json_t *root = json_loads(json_s, 0, &error);
if (!root) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: on line %d: %s\n", error.line, error.text);
return 1;
}
const char *name = json_string(json_object_get(root, "name"));
int age = json_integer_value(json_object_get(root, "age"));
printf("Name: %s, Age: %d\n", name, age);
json_decref(root);
return 0;
}
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String json_s = "{\"name\": \"Mohit\", \"age\": 30}";
JSONObject obj = new JSONObject(json_s);
String name = obj.getString("name");
int age = obj.getInt("age");
System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Age: " + age);
}
}
import json
json_s = '{"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}'
obj = json.loads(json_s)
name = obj["name"]
age = obj["age"]
print(f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}")
using System;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
public class Program {
public static void Main() {
string json_s = "{\"name\": \"Mohit\", \"age\": 30}";
dynamic obj = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(json_s);
string name = obj.name;
int age = obj.age;
Console.WriteLine("Name: " + name + ", Age: " + age);
}
}
const json_s = '{"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json_s);
const name = obj.name;
const age = obj.age;
console.log(`Name: ${name}, Age: ${age}`);
Output
Name: Mohit, Age: 30
JSON Structure
The basic structure of JSON consists of two primary components:
- Objects: These are enclosed in curly braces {} and contain key-value pairs.
- Arrays: Arrays are ordered lists enclosed in square brackets [].
Objects in JSON
A JSON object is a collection of key-value pairs enclosed in curly braces {}. The key is always a string, and the value can be a variety of data types, including strings, numbers,arrays and even other objects.
Example:
{ "name": "Mohit Kumar",
"age": 30,
"isStudent": false }
In this example, name, age, and isStudent are keys, and "John Doe", 30, and false are their respective values.
Arrays in JSON
A JSON array is an ordered collection of values enclosed in square brackets []. These values can be of any type, including objects, arrays, or primitive data types.
Example:
{ "fruits": ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] }
Here, fruits is a key, and the value is an array containing the elements "apple", "banana", and "cherry".
Key JSON Data Types
JSON supports the following data types:
- String: A sequence of characters, e.g., "hello".
- Number: Integer or floating-point numbers, e.g., 10, 3.14.
- Boolean: A value representing true or false.
- Array: An ordered list of values.
- Object: A collection of key-value pairs.
- Null: A null value indicating the absence of any value.
Working with JSON in JavaScript
In JavaScript, we can easily parse JSON data into a JavaScript object and vice versa using built-in methods like JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify().
Parse JSON to Object
To parse a JSON string into a JavaScript object, use JSON.parse().
let jsonS = '{"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}';
let jsonObj = JSON.parse(jsonS);
console.log(jsonObj.name);
Output
Mohit
Convert Object to JSON
To convert a Javascript object into a JSON string, use JSON.stringify()
let obj = {name: "Mohit", age: 30};
let jsonS= JSON.stringify(obj);
console.log(jsonS);
Output
{"name":"Mohit","age":30}
Working with JSON in Python
Python provides a built-in json module to work with JSON data. We can use the json.loads() method to convert a JSON string to a dictionary and json.dumps() to convert a dictionary to a JSON string.
Parse JSON to Dictionary
In Python, a JSON string can be converted into a dictionary using the built-in json module using json.loads().
import json
json_str = '{"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}'
data = json.loads(json_str)
print(data["name"])
Output
Mohit
Convert Dictionary to JSON
In Python, a dictionary can be converted into a JSON string using the json.dumps() method.
import json
data = {"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}
json_str = json.dumps(data)
print(json_str)
Output
{"name": "Mohit", "age": 30}
Applications of JSON
- APIs: JSON is the most commonly used format for API responses due to its lightweight nature.
- Configuration Files: Many software systems use JSON files for storing configuration data.
- Databases: Some NoSQL databases, like MongoDB, store data in JSON-like formats.
- Data Transfer: JSON is widely used for transferring data between servers and clients, especially in web development.
JSON Basics
JSON SetUp
- How to Format JSON in VSCode
- Json-Server Setup And Introduction
- What is the correct JSON content type ?
JSON Python
JSON Java
Differences
- JSON vs JavaScript Object
- Difference between JSON and XML
- What is the difference between YAML and JSON?
- Difference Between JSON and BSON
- Difference Between JSON and AJAX
JSON Methods
Miscellaneous
- JSON Web Token (JWT)
- Python JSON
- What is JSON-Java (org.json)?
- JSON Schema
- JSON Interview Questions
- JavaScript JSON Complete Reference
Important Questions
- How to Convert Map to JSON in JavaScript ?
- How to Convert JSON Object to CSV in JavaScript ?
- How to Convert Blob Data to JSON in JavaScript ?
- How to Convert Excel to JSON in JavaScript ?