The json.dump() function in Python is used to convert (serialize) a Python object into JSON format and write it directly to a file.
Example: This example shows how to write a Python dictionary into a JSON file using json.dump().
import json
data = {"name": "Joe", "age": 25}
with open("data.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f)
Output
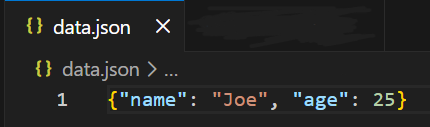
Explanation:
- json.dump(data, f) converts the dictionary data into JSON format.
- The JSON output is written directly into the file data.json.
Syntax
json.dump(obj, file, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, indent=None, separators=None)
Parameters:
- obj: Python object to convert (dict, list, etc.)
- file: File object where JSON data is written
- skipkeys: Ignores non-serializable keys if True
- ensure_ascii: Escapes non-ASCII characters if True
- allow_nan: Allows NaN and Infinity values
- indent: Adds indentation for readable output
- separators: Custom separators for formatting
Examples
Example 1: This example writes dictionary data into a JSON file with indentation to make it easy to read.
import json
d = {"id": 1, "name": "Lisa", "salary": 50000}
with open("emp.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(d, f, indent=4)
Output
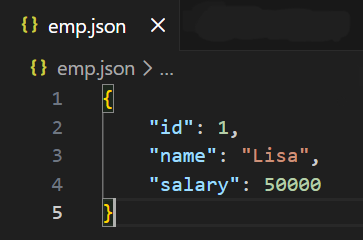
Explanation:
- indent=4 formats the JSON file with proper spacing.
- The dictionary d is written in a readable JSON structure.
Example 2: This example shows how skipkeys=True avoids errors when keys are not JSON-compatible.
import json
d = {("x", "y"): 10, "z": 20}
with open("data.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(d, f, skipkeys=True)
Output
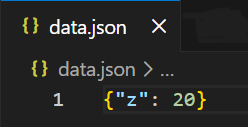
Explanation:
- Tuple keys like ("x", "y") are not supported in JSON.
- skipkeys=True ignores such entries instead of raising an error.
Example 3: This example preserves non-ASCII characters in the JSON file.
import json
d = {"msg": "¡Hola Mundo!"}
with open("text.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(d, f, ensure_ascii=False)
Output
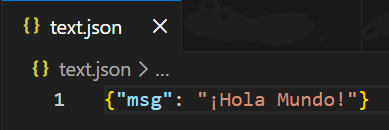
Explanation:
- ensure_ascii=False keeps special characters unchanged.
- Useful for multilingual text and Unicode data.
dump() vs dumps()
Both json.dump() and json.dumps() are used to convert Python objects into JSON, but they differ in where the JSON output goes a file or a string.
| dump() | dumps() |
|---|---|
| Used when Python objects need to be written directly to a JSON file | Used when Python objects need to be converted into a JSON-formatted string |
| Requires a file object as an argument | Does not require a file, returns a string |
| Writes JSON directly to disk | Stores JSON in memory as a string |
| Commonly used for saving data to files | Commonly used for printing, logging, or API responses |
| Generally faster for file writing | Slightly slower due to string creation |