In Python, math module contains a number of mathematical operations, which can be performed with ease using the module.
Python3 1==
Code #2:
Python3 1==
math.tan() function returns the tangent of value passed as argument. The value passed in this function should be in radians.
Syntax: math.tan(x) Parameter: x : value to be passed to tan() Returns: Returns the tangent of value passed as argumentCode #1:
# Python code to demonstrate the working of tan()
# importing "math" for mathematical operations
import math
a = math.pi / 6
# returning the value of tangent of pi / 6
print ("The value of tangent of pi / 6 is : ", end ="")
print (math.tan(a))
# Python program showing
# Graphical representation of
# tan() function
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
in_array = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 10)
out_array = []
for i in range(len(in_array)):
out_array.append(math.tan(in_array[i]))
i += 1
print("in_array : ", in_array)
print("\nout_array : ", out_array)
# red for numpy.sin()
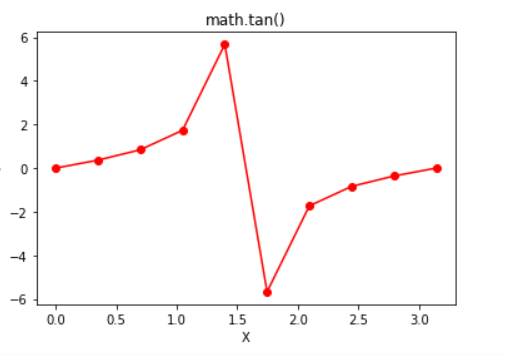
plt.plot(in_array, out_array, color = 'red', marker = "o")
plt.title("math.tan()")
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.show()
Output:
in_array : [0. 0.34906585 0.6981317 1.04719755 1.3962634 1.74532925 2.0943951 2.44346095 2.7925268 3.14159265] out_array : [0.0, 0.36397023426620234, 0.8390996311772799, 1.7320508075688767, 5.671281819617707, -5.671281819617711, -1.7320508075688783, -0.8390996311772804, -0.36397023426620256, -1.2246467991473532e-16]