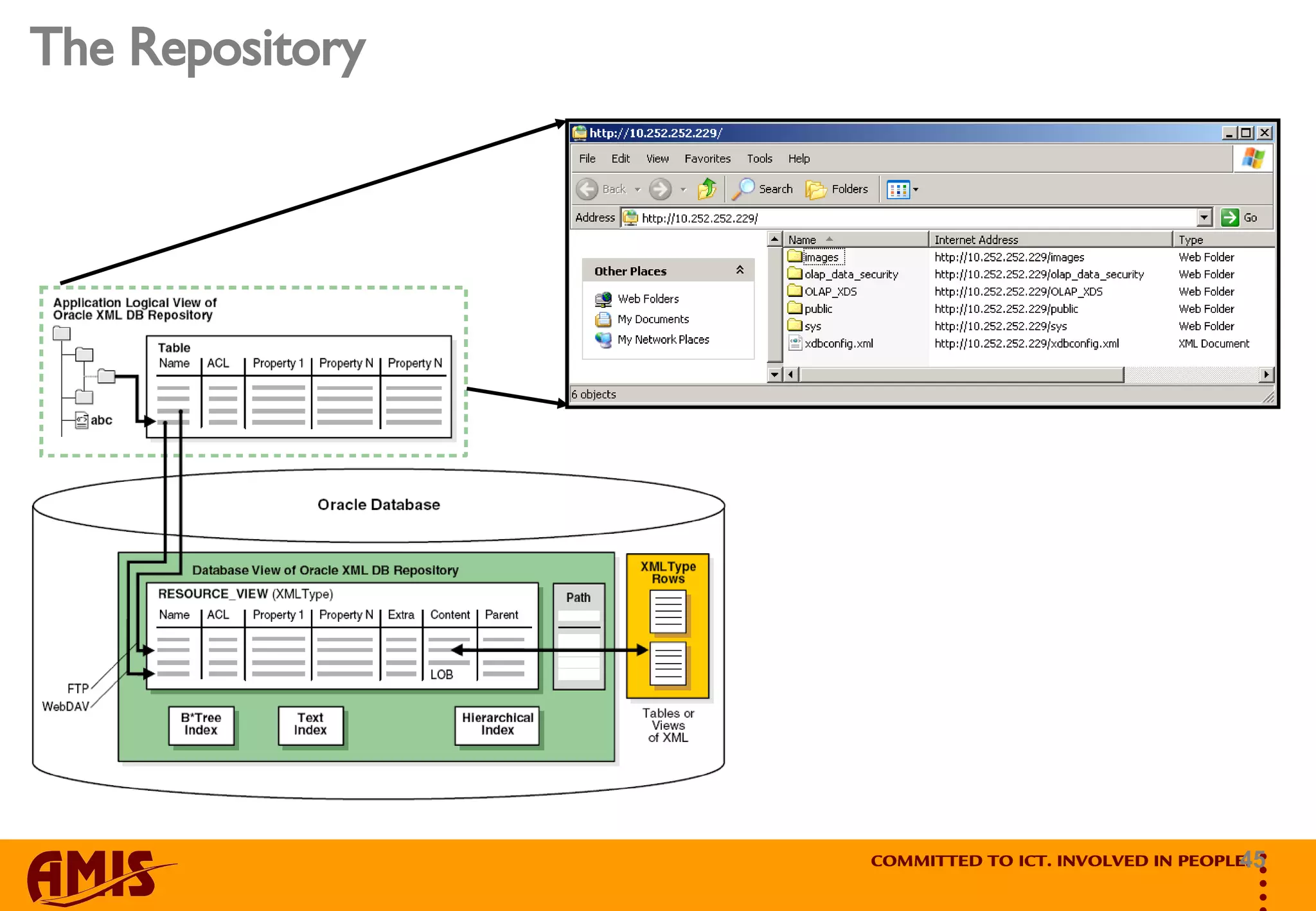
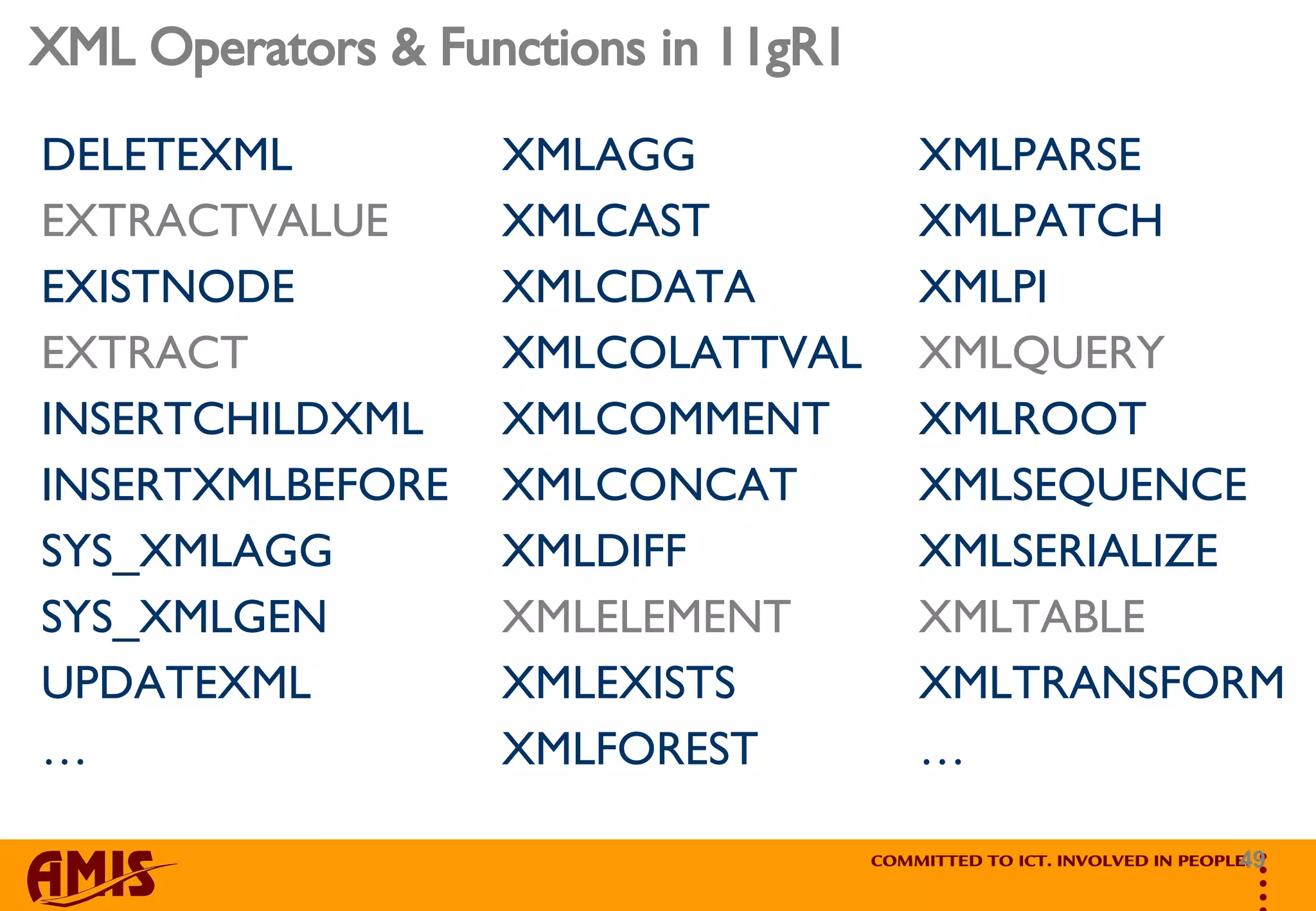
The document discusses the speaker's experience with Oracle XML Database 11g and provides an overview of key topics. It covers that XML is not relational, how to set up and configure the XML database, XML handling and storage options, the protocol server, using the repository, and data handling functions. The speaker aims to discuss encountered issues and provide tips based on their experience with the XML database.


















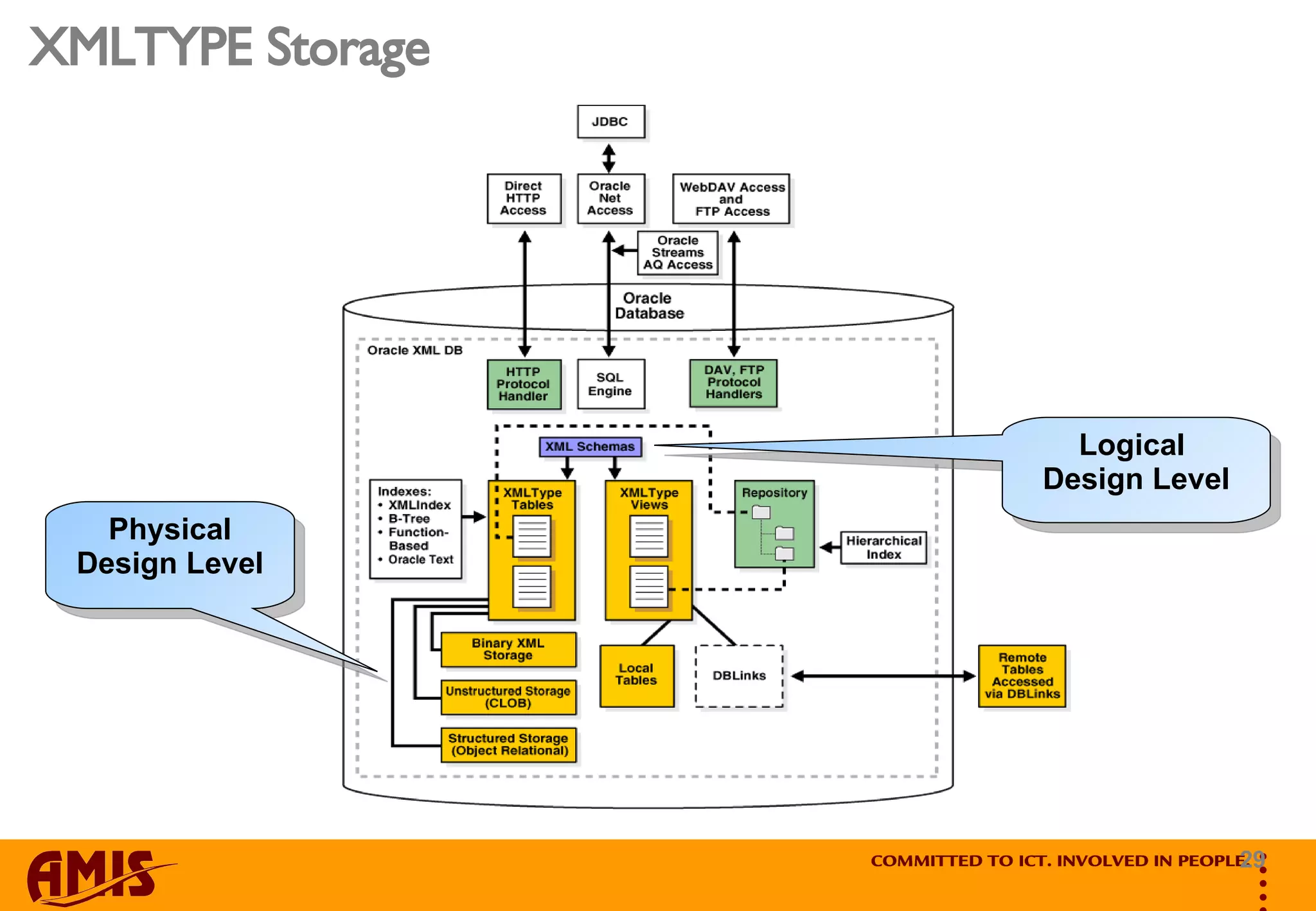

![CLOB, Object Relational, Binary XML XMLType (Tables) XMLType Views XMLDB Data Storage (Object) Relational Objects Relational Tables Relational World XMLDB World Binary XML Structured Mixed complex[y] BINARY XSD [y/n] XMLIndex Content complex[n] OR XSD [y] BTree, IOT Hybrid Content complex[n] Mixed XSD [y] BTree, IOT Unstructured Document na CLOB XSD [n] XMLIndex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marco-gralike-amis-real-world-experience-with-oracle-xml-database-11g-an-oracle-aces-perspective-oow-2k8-1223212872185689-8/75/Real-World-Experience-With-Oracle-Xml-Database-11g-An-Oracle-Ace-s-Perspective-Oracle-Open-World-2008-Marco-Gralike-33-2048.jpg)










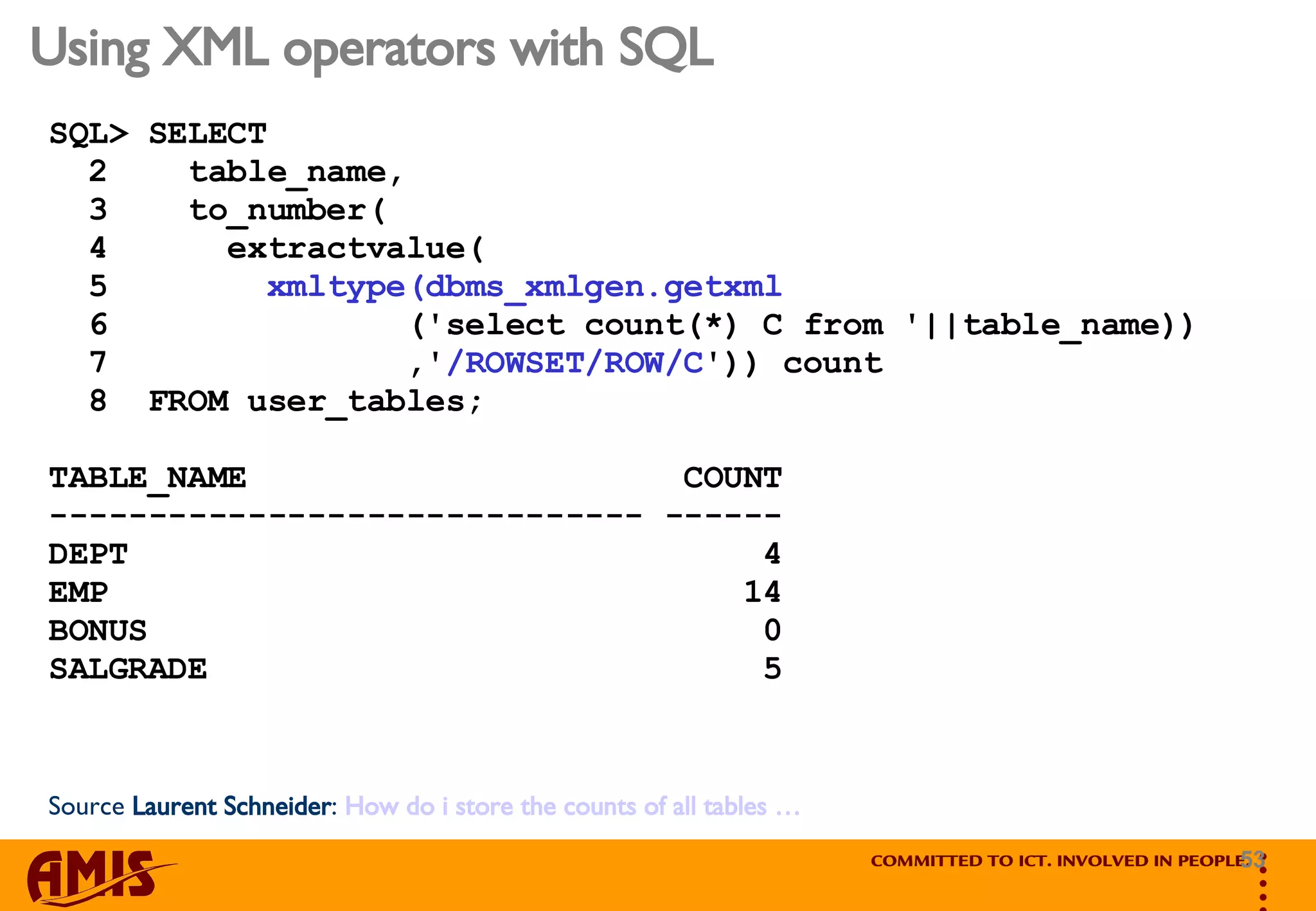

![Accessing the outside World TITLE LINK PUBLICATION_DATE CREATOR ----------------------------------------------------------------- DESCRIPTION CATEGORY ----------------------------------------------------------------- Quering RSS Feeds The XMLDB Way http://feeds.feedburner.com/~r/Bloggralikecom/~3/3 Wed, 25 Jun 2008 16:47:19 +0000 Marco Gralike Actually this IS old stuff (2006), but it got lost IN a… < ![CDATA[11g]]>< ![CDATA[Howto]]>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marco-gralike-amis-real-world-experience-with-oracle-xml-database-11g-an-oracle-aces-perspective-oow-2k8-1223212872185689-8/75/Real-World-Experience-With-Oracle-Xml-Database-11g-An-Oracle-Ace-s-Perspective-Oracle-Open-World-2008-Marco-Gralike-55-2048.jpg)









![Questions? [email_address] http://www.amis.nl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marco-gralike-amis-real-world-experience-with-oracle-xml-database-11g-an-oracle-aces-perspective-oow-2k8-1223212872185689-8/75/Real-World-Experience-With-Oracle-Xml-Database-11g-An-Oracle-Ace-s-Perspective-Oracle-Open-World-2008-Marco-Gralike-66-2048.jpg)