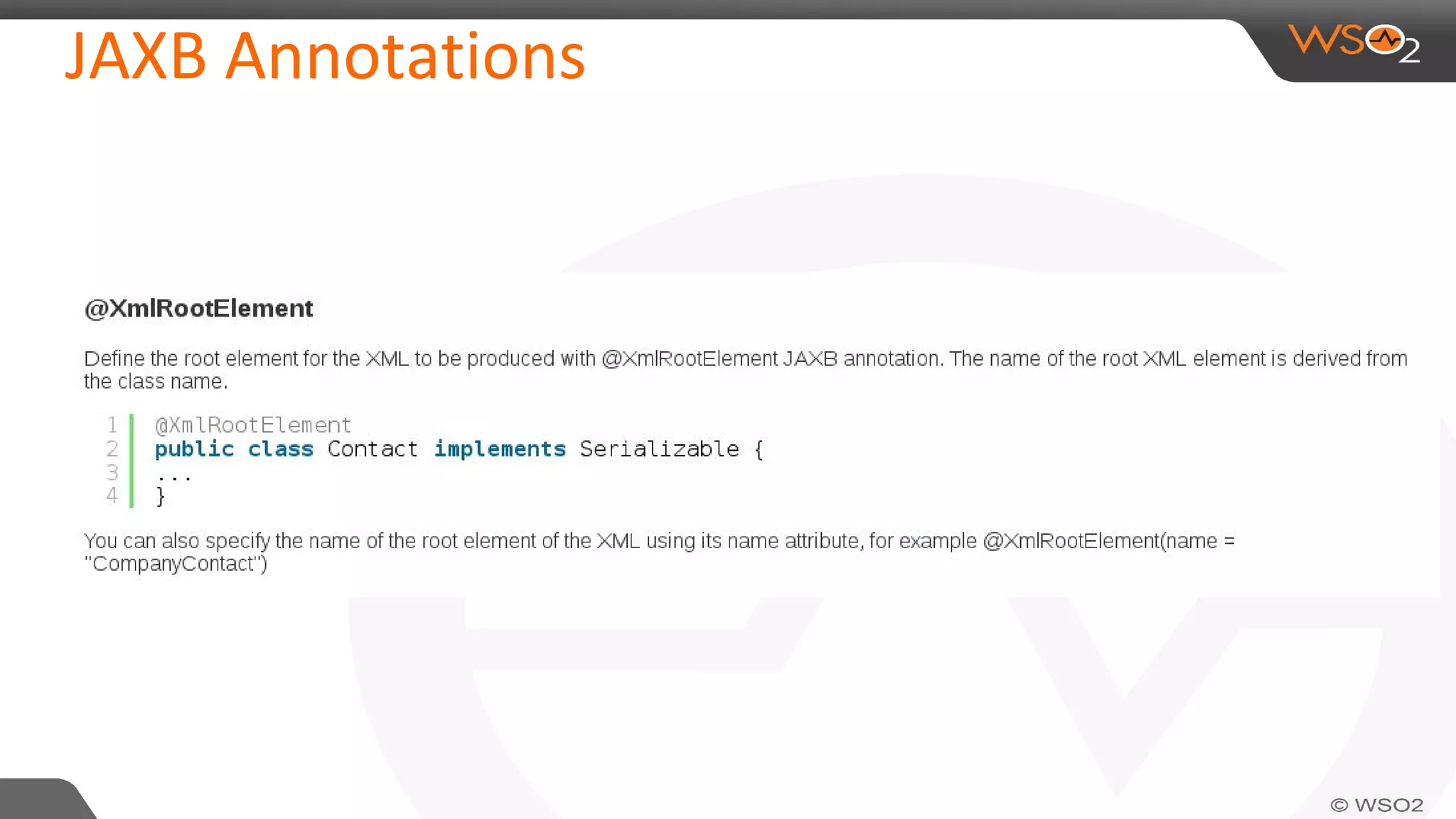
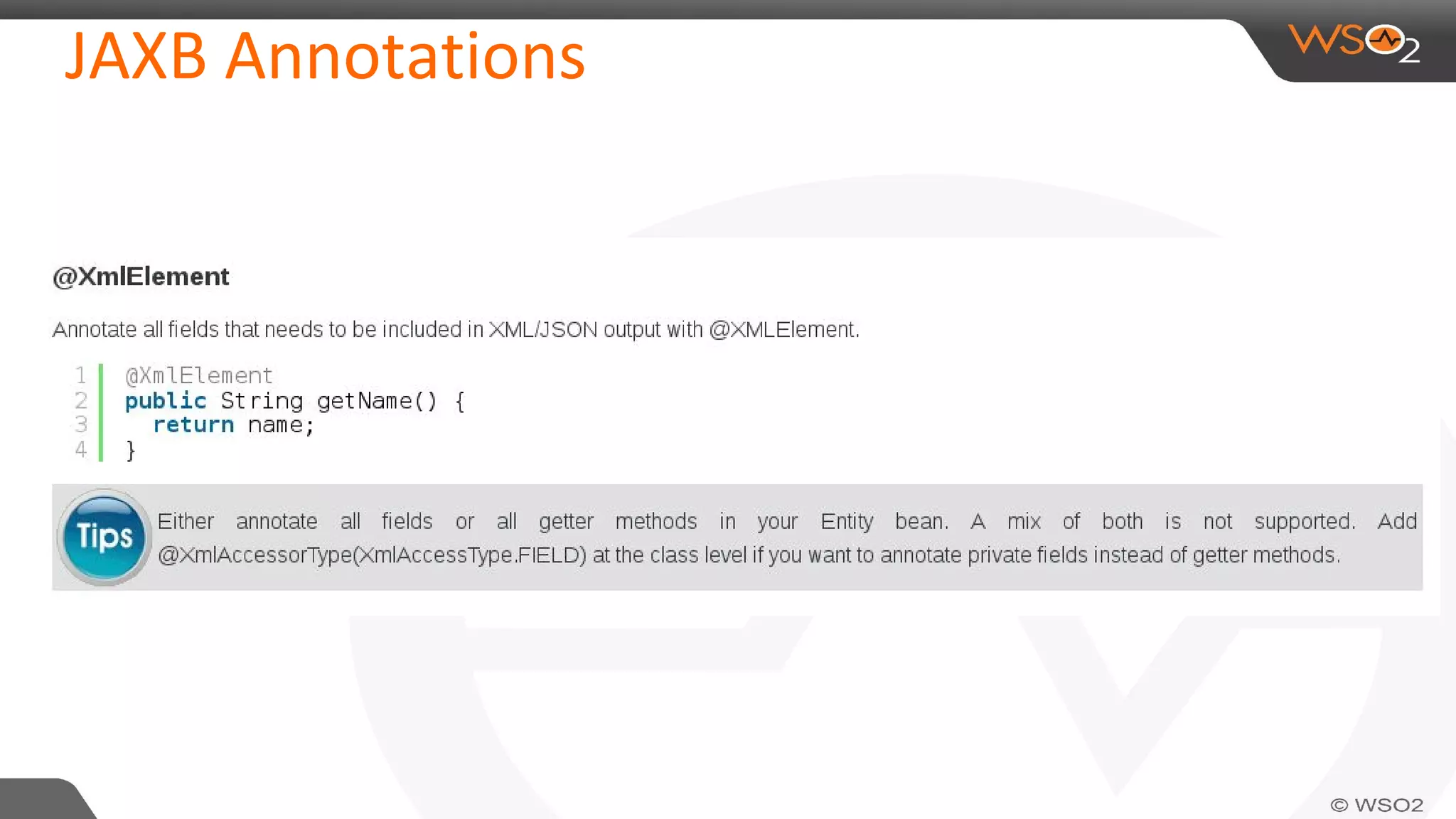
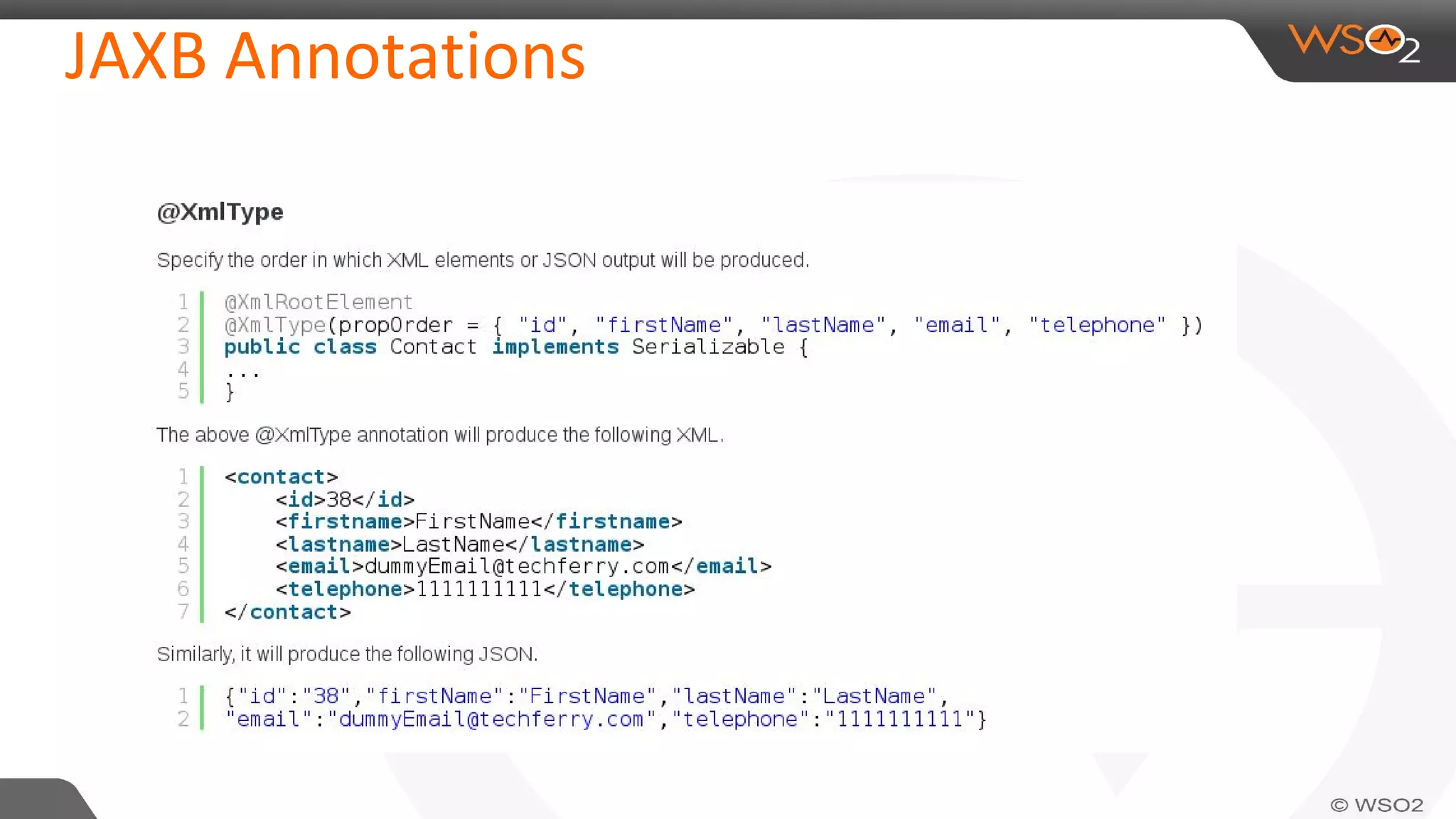
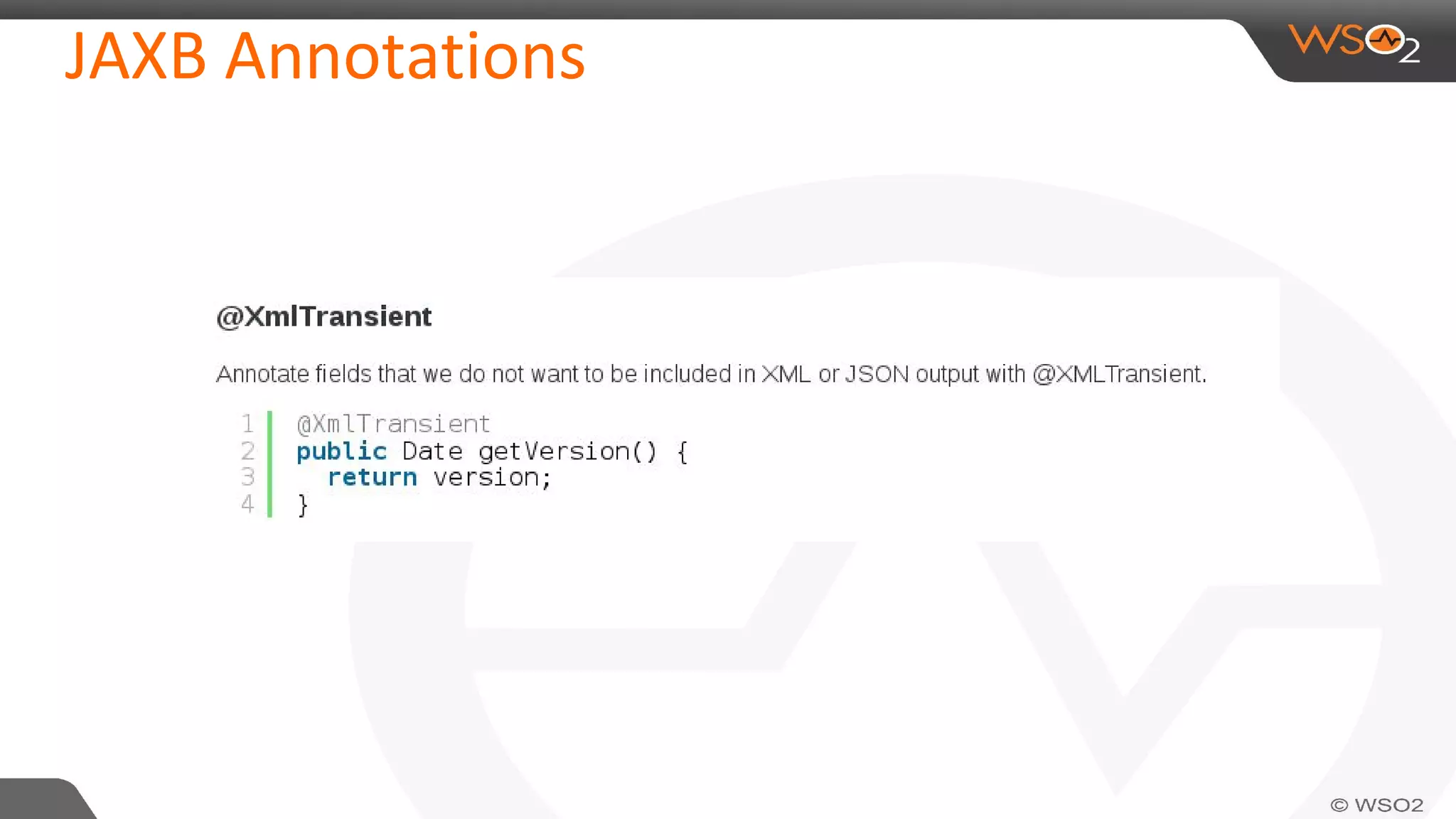
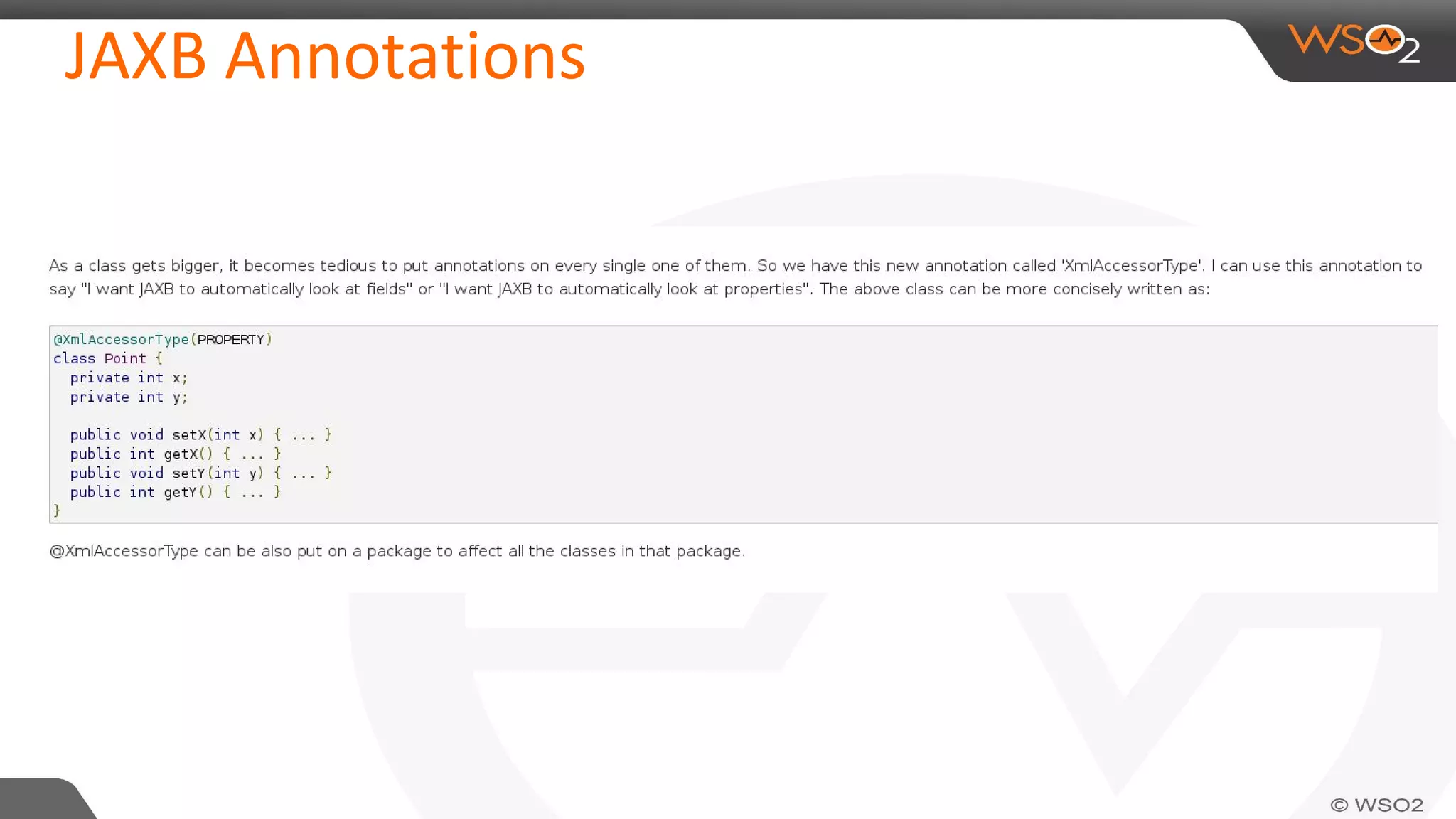
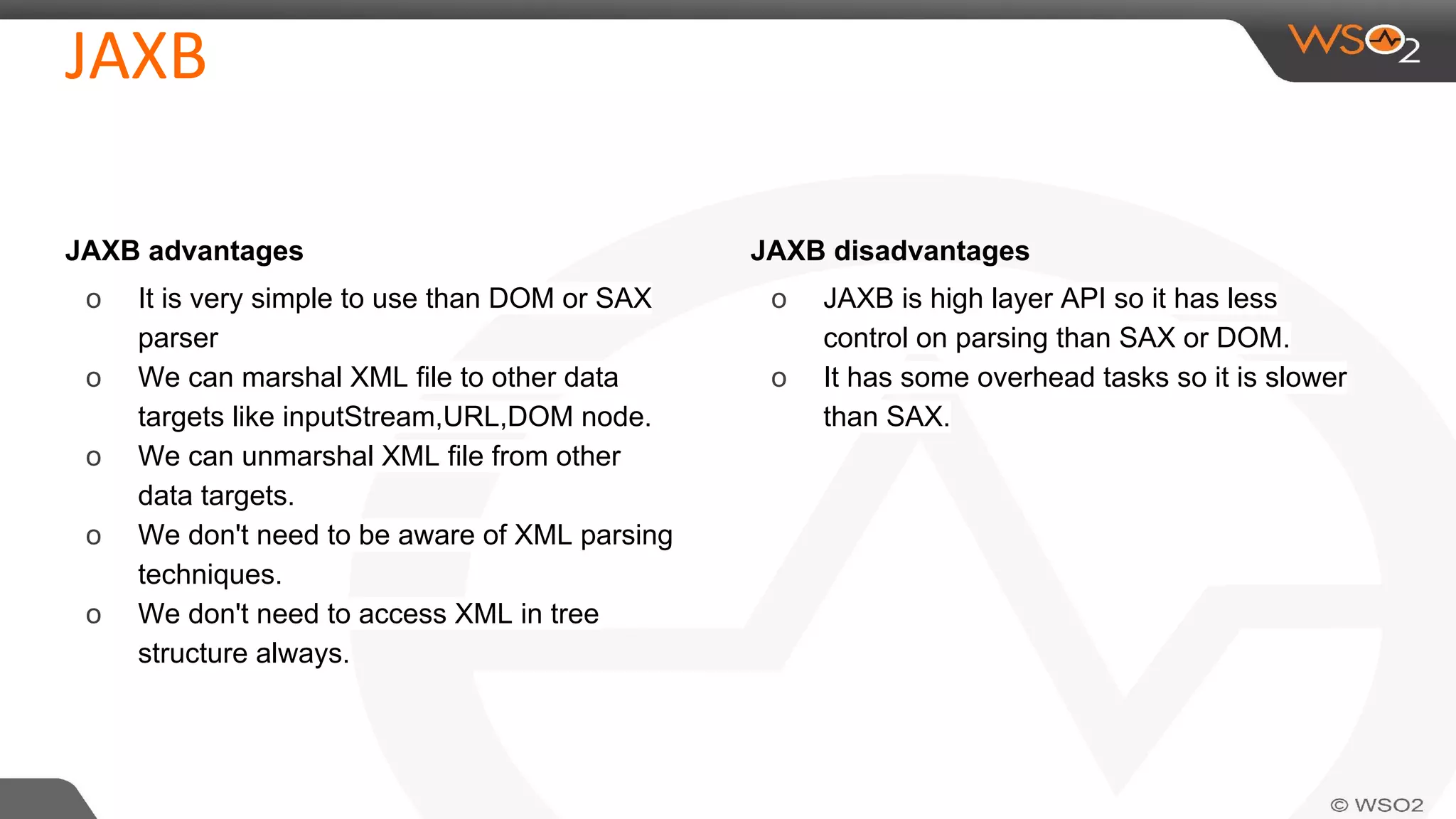
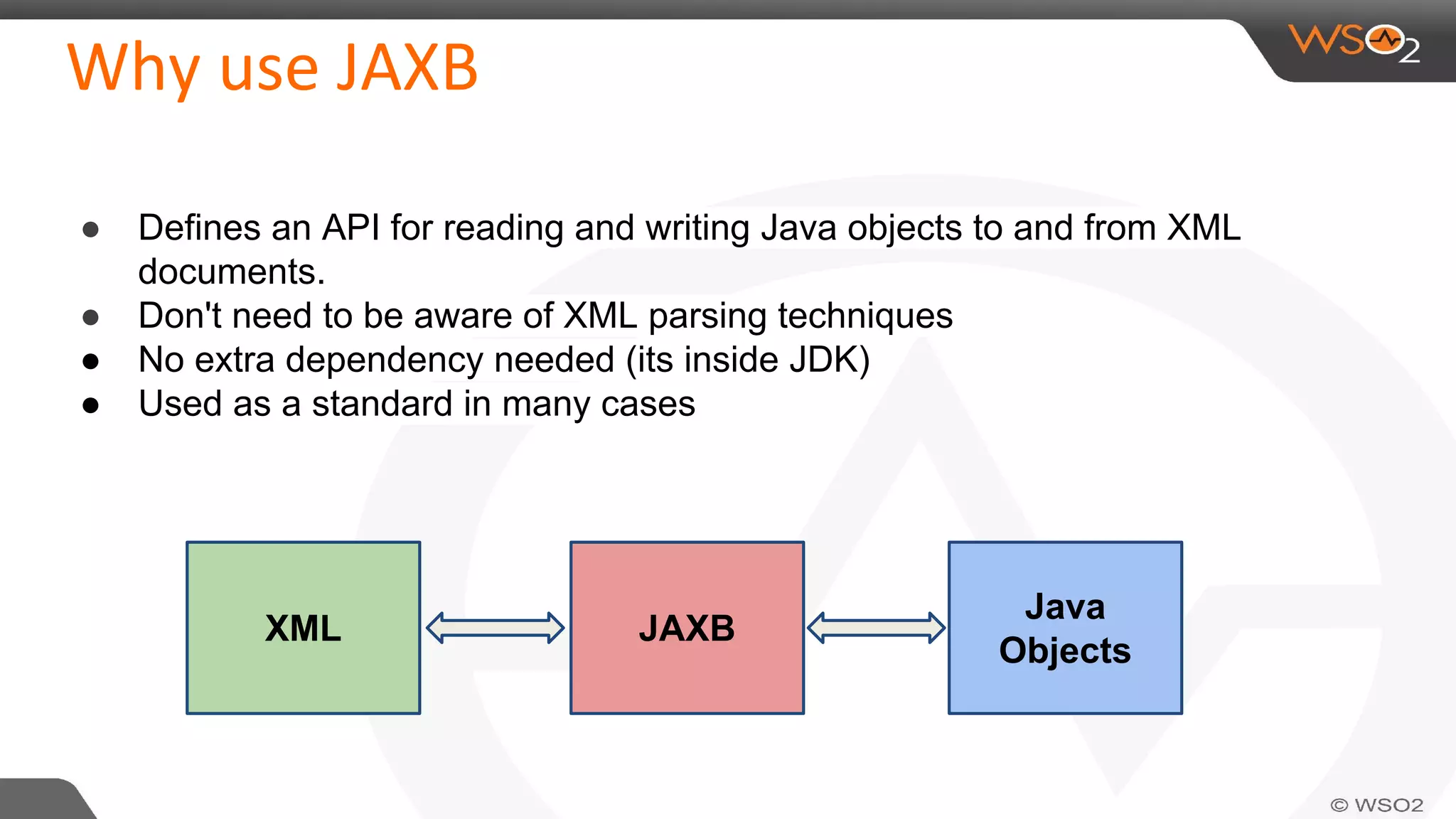
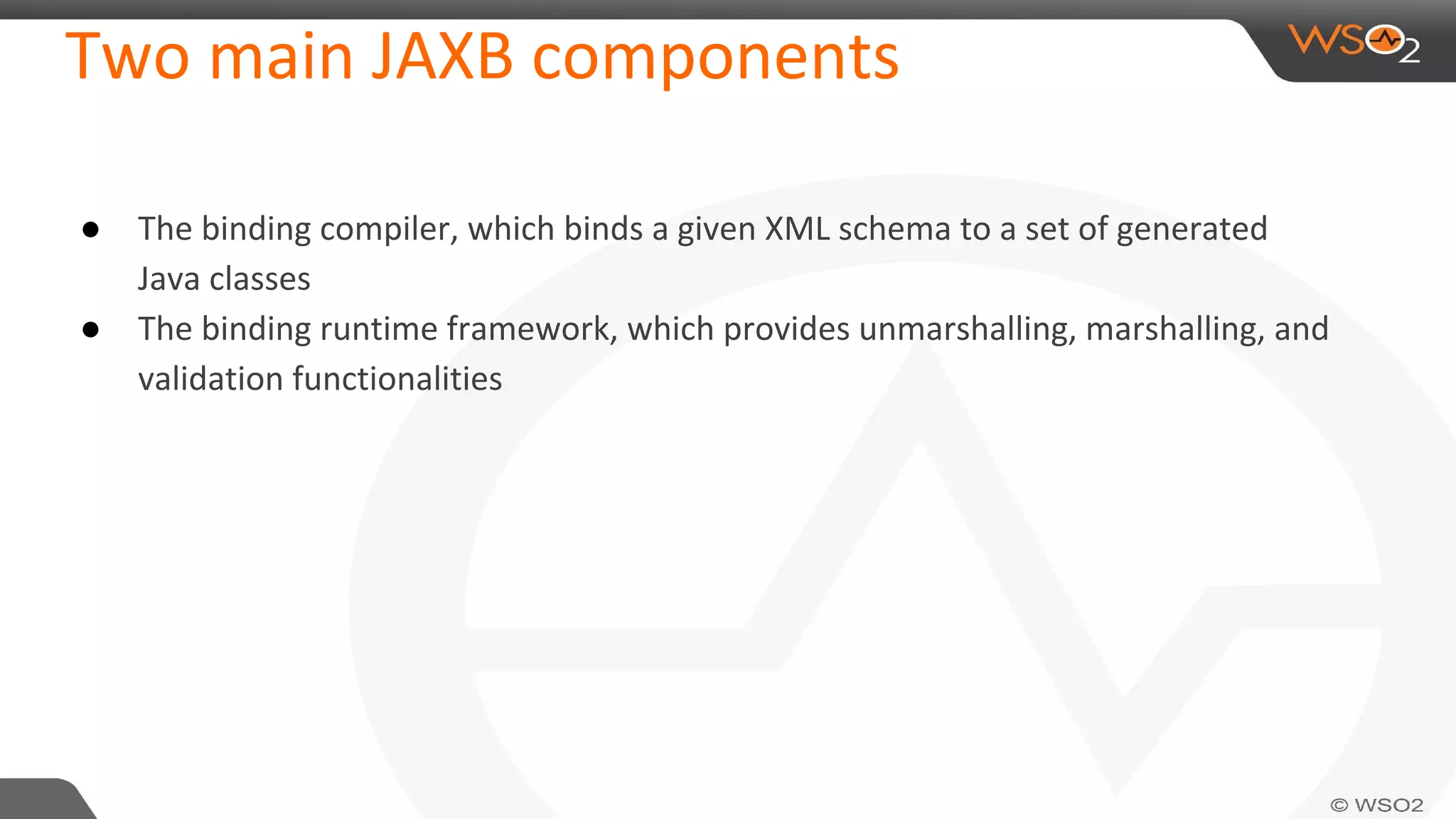
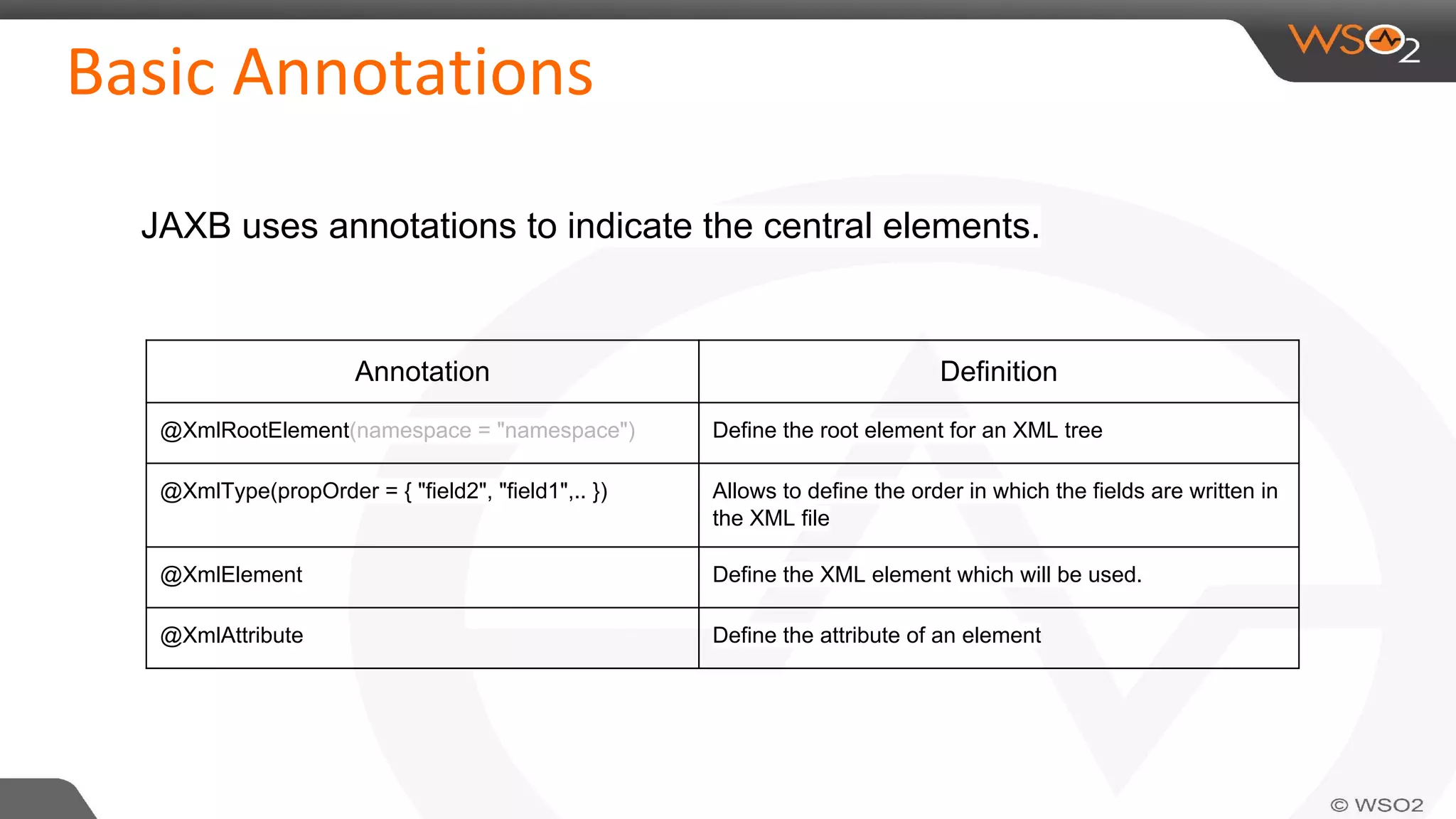
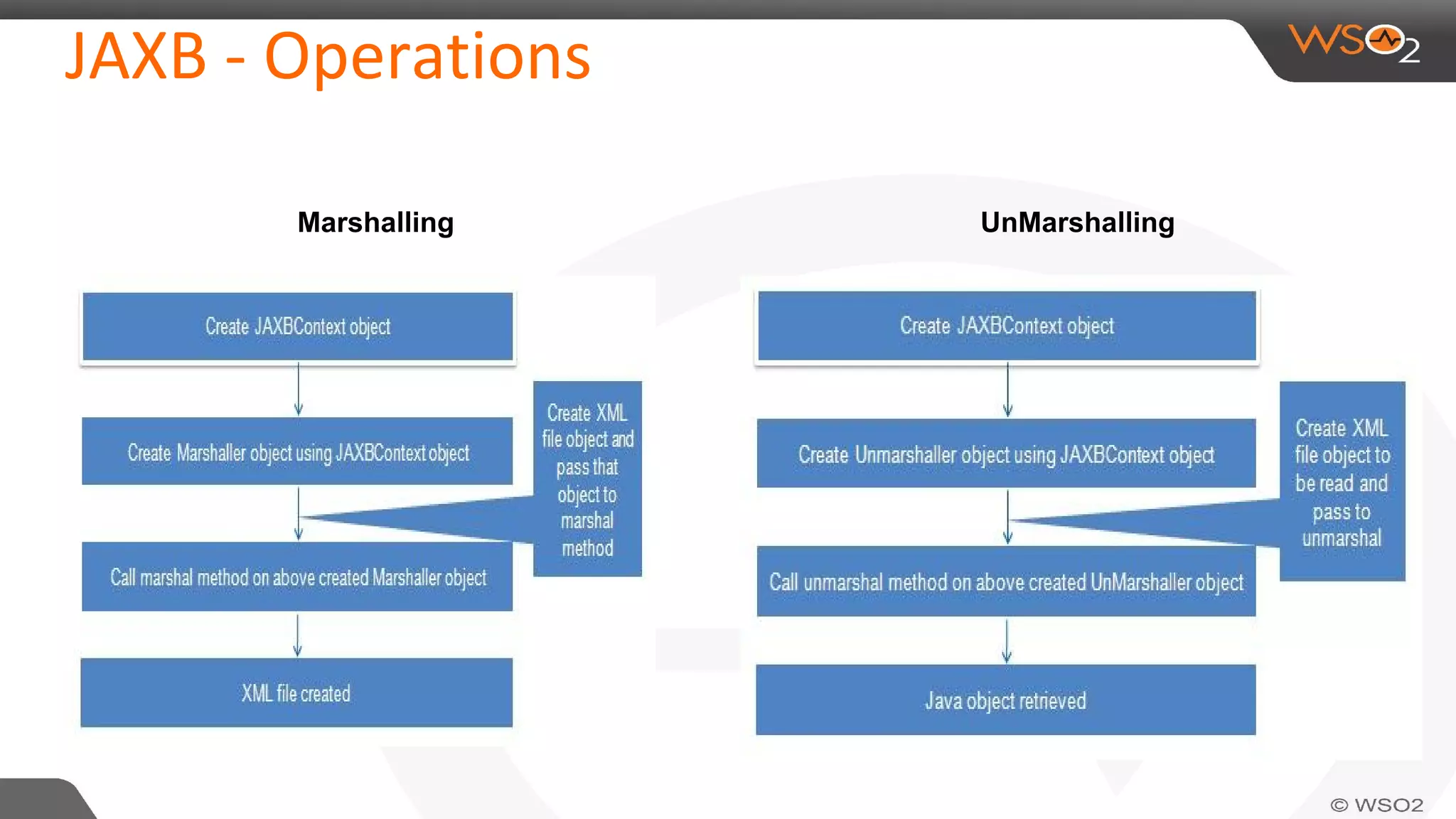
JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding) defines an API for reading and writing Java objects to and from XML documents. It uses annotations to map XML elements and attributes to Java objects. This allows Java objects to be automatically marshalled to XML and XML to be unmarshalled to Java objects without needing to understand XML parsing techniques. JAXB comes bundled with the JDK so there are no extra dependencies. It provides a simpler model than DOM or SAX for working with XML in Java applications.






![run the following command:
$xjc course-booking.xsd -p org.wso2.jaxb.training -d src/generated
● -d <dir>: Place the generated files into this directory.
● -p <package>: Place the generated files in this package.
● -nv: Don't perform strict validation of the input schema.
● -httpproxy <proxy>: Use this if you are behind a proxy. Takes the format [user[:password]@]proxyHost[:proxyPort].
● -classpath <arg>: Specify the classpath, if necessary.
● -readOnly: Generates read-only source code files, if your OS supports this.
There is also an equivalent ant task, which makes it quite easy to integrate into an Ant or Maven-based build process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmlparsingusingjaxbslides-151013065346-lva1-app6892/75/XML-parsing-using-jaxb-11-2048.jpg)