In Python, Using the input() function, we take input from a user, and using the print() function, we display output on the screen. Using the input() function, users can give any information to the application in the strings or numbers format.
After reading this article, you will learn:
- Input and output in Python
- How to get input from the user, files, and display output on the screen, console, or write it into the file.
- Take integer, float, character, and string input from a user.
- Convert the user input to a different data type.
- Command-line input
- How to format output.
Table of contents
Python Input() function
In Python 3, we have the following two built-in functions to handle input from a user and system.
input(prompt): To accept input from a user.print(): To display output on the console/screen.
In Python 2,we can use the following two functions:
input([prompt])raw_input([prompt])
The input() function reads a line entered on a console or screen by an input device such as a keyboard, converts it into a string. As a new developer, It is essential to understand what is input in Python.
What is the input?
The input is a value provided by the system or user. For example, suppose you want to calculate the addition of two numbers on the calculator, you need to provide two numbers to the calculator. In that case, those two number is nothing but an input provided by the user to a calculator program.
There are different types of input devices we can use to provide data to application. For example: –
- Stems from the keyboard: User entered some value using a keyboard.
- Using mouse click or movement: The user clicked on the radio button or some drop-down list and chosen an option from it using mouse.
In Python, there are various ways for reading input from the user from the command line environment or through the user interface. In both cases, the user is sending information using the keyboard or mouse.
Python Example to Accept Input From a User
Let’s see how to accept employee information from a user.
- First, ask employee name, salary, and company name from the user
- Next, we will assign the input provided by the user to the variables
- Finally, we will use the
print()function to display those variables on the screen.
Output:
Enter Employee Name: Jessa Enter salary: 8000 Enter Company name: Google Printing Employee Details Name Salary Company Jessa 8000 Google
How input() Function Works
syntax
input([prompt])Code language: Python (python)- The
promptargument is optional. Thepromptargument is used to display a message to the user. For example, the prompt is, “Please enter your name.” - When the
input()function executes, the program waits until a user enters some value. - Next, the user enters some value on the screen using a keyboard.
- Finally, The
input()function reads a value from the screen, converts it into a string, and returns it to the calling program.
Note: If you enter an integer or float number, still, it will convert it into a string. If you want to number input or input in other data types, you need to perform type conversion on the input value.
Let’s understand this with an example.
Example to check data type of input value
Output:
Enter roll number 22 Enter age Jessa Roll number: 22 Name: Jessa Printing type of a input values type of number <class 'str'> type of name <class 'str'>
As you know whatever you enter as input, the input() function always converts it into a string.
Read How to check if user input is a number or string.
Take an Integer Number as input from User
Let’s see how to accept an integer value from a user in Python. We need to convert an input string value into an integer using an int() function.
Example:
Output:
Enter first number 28 Enter second number 12 First Number: 28 Second Number: 12 Addition of two number is: 40
Note: As you can see, we explicitly added a cast of an integer type to an input function to convert an input value to the integer type.
Now if you print the type of first_number you should get integer type. type(first_number ) will return <class 'int'>
Take Float Number as a Input from User
Same as integer, we need to convert user input to the float number using the float() function
Output:
Enter marks 74.65 Student marks is: 74.65 type is: <class 'float'>
Practice Problem
Accept one integer and one float number from the user and calculate the multiplication of both the numbers.
Show Solution
Get Multiple inputs From a User in One Line
In Python, It is possible to get multiple values from the user in one line. We can accept two or three values from the user.
For example, in a single execution of the input() function, we can ask the user his/her name, age, and phone number and store it in three different variables.
Let’ see how to do this.
- Take each input separated by space
- Split input string using
split()get the value of individual input
Output:
Enter your name, Age, Percentage separated by space Jessa 18 72.50 User Details: Jessa 18 72.50
Also, you can take the list as input from the user to get and store multiple values at a time.
Read: How to take a list as an input from a user.
Accept Multiline input From a User
As you know, the input() function does not allow the user to provide values separated by a new line.
If the user tries to enter multiline input, it reads only the first line. Because whenever the user presses the enter key, the input function reads information provided by the user and stops execution.
Let’s see how to gets multiple line input.
We can use a loop. In each iteration of the loop, we can get input strings from the user and join them. You can also concatenate each input string using the + operator separated by newline (\n).
Example:
Output:
Tell me about yourself My Name is Jessa I am a software engineer Final text input My Name is Jessa I am a software engineer
Python Input() vs raw_input()
- The
input()function works differently between Python 3 and Python 2. - In Python 2, we can use both the
input()andraw_input()function to accept user input. - In Python 3, the
raw_input()function of Python 2 is renamed toinput()and the originalinput()function is removed.
The difference between the input() and raw_input() functions is relevant only when using Python 2.
- The main difference between those two functions is
input()function automatically converts user input to the appropriate type. i.e., If a user-entered string input() function converts it into a string, and if a user entered a number, it converts to an integer. - The
raw_input()convert every user input to a string.
Let’s see how to use raw_input() in Python 2.
Example 1: Python 2 raw_input() function to take input from a user
Output:
Enter your name Jessa Student Name is: Jessa <type 'str'> Enter your age 18 Student age is: 18 <type 'str'>
Note: As you can see, raw_input() converted all user values to string type.
Example 2: Python 2 input() function to take input from a user
Output:
Enter your Name Jessa Student Name is: Jessa <type 'str'> Enter your age 18 Student age is: 18 <type 'int'>
Note: As you can see, input() converted all user values to appropriate data type.
Note: To get the this behavior of input() in Python 3, use eval(input('Enter Value'))
Command Line input
A command line interface (CLI) is a command screen or text interface called a shell that allows users to interact with a program.
For example, On windows, we use the Command Prompt and Bash on Linux. command line or command-line interface is a text-based application for viewing, handling, and manipulating files on our computer. The command line also called cmd, CLI, prompt, console, or terminal.
On command-line, we execute program or command by providing input/arguments to it. Also, output and error are displayed A command line.
We can run Python programs on the command line. The command line input is an argument that we pass to the program at runtime.
Python provides following modules to work with command-line arguments.
sysmodulegetoptm oduleargsparsemodulefiremoduledocotpmodule
Python sys module
The Python sys module is the basic module that implements command-line arguments in a simple list structure named sys.argv.
sys.argv[0]: The first argument is always the program/script name.sys.argv: Returns the list of command line arguments.len(sys.argv): Count of command line arguments.
Steps:
Write the below code in a file and save it as a sample.py
Run the below command on the command line
python sample.py 20 30 40Code language: Python (python)Output
Total argument passed : 4
Here 10, 20, 30 are command-line arguments passed to the program. Each input represents a single argument.
- The first argument, i.e.,
sys.argv[0], always represents the Python program name (.py) file - The other list elements i.e.,
sys.argv[1]tosys.argv[n]are command-line arguments. Space is used to separate each argument.
Note: argv is not an array. It is a list. This is a straightforward way to read command-line arguments as a string. See the following example to check the type of argv
Example
Now let’s see another example where we display all command-line arguments passed to the program.
Example : To Display command line argumnets
Run the below command on the command line
python sample.py 20 30 40Code language: Python (python)Output
C:\Anaconda3>python sample.py 20 30 40 All command line inputs sample.py 20 30 40
Note : The space is separator between command line arguments.
In Python, by default, command-line arguments are available in string format. Based on our requirement, we can convert it into the corresponding type by using the typecasting method.
See the following example where we change the data type of arguments using the int() method.
Example
Output
C:\Anaconda3>python sample.py 20 30 Argument one: Argument Two: Addition is: 50
If we try to access arguments with out of the range index on the command line, we will get an error.
Output
C:\Anaconda3>python sample.py 20
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "sample.py", line 3, in <module>
print(argv[2])
IndexError: list index out of range
Output in Python
Python has a built-in print() function to display output to the standard output device like screen and console.
Example 1: Display output on screen
Output:
Enter Name: Jessa User Name: Jessa
Example 2: Display Output by separating each value
Output:
name = input('Enter Name ')
Enter Name Jessa
Enter zip code 412365
Enter street name abc street
Enter house number 234
Jessa-412365-abc street-234
Output Formatting
Most of the time, we need to format output instead of merely printing space-separated values. For example, we want to display the string left-justified or in the center. We want to show the number in various formats.
You can display output in various styles and formats using the following functions.
str.format()repr()str.rjust(),str.ljust(), andstr.center().str.zfill()- The
%operator can also use for output formatting
Now, Let see each one by one.
str.format() to format output
<code class="EnlighterJSRAW" data-enlighter-language="python">str.format(*args, **kwargs)</code>Code language: Python (python)- The
stris the string on which the format method is called. It can contain text or replacement fields delimited by braces {}. - Each replacement field contains either the numeric index of a positional argument present in the format method or the name of a keyword argument.
- The format method returns a formatted string as an output. Each replacement field gets replaced with the actual string value of the corresponding argument present in the format method. i.e., args.
Let see this with an example:
Note: Here {0} and {1} is the numeric index of a positional argument present in the format method. i.e., {0} = Ault and {1} = Kelly. Anything that not enclosed in braces {} is considered a plain literal text.
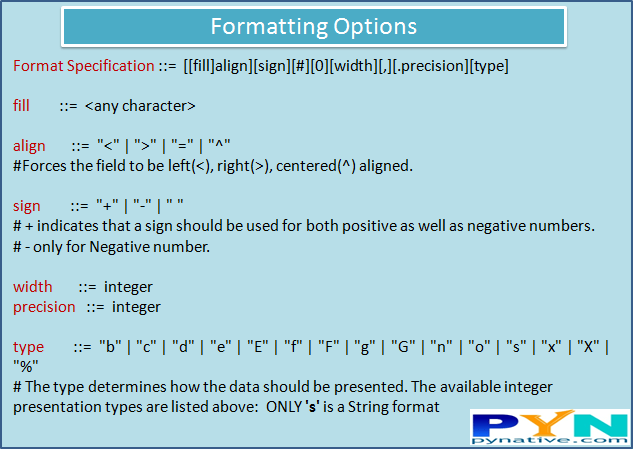
Let see different ways to display output using a format() method. You can find various Formatting options here.
Format Output String by its positions
Output:
Enter First Name Ault Enter Last Name Kelly Enter Organization Name Google Ault, Kelly works at Google Kelly, Ault works at Google FirstName Ault, LastName Kelly works at Google Ault, Kelly Ault, Kelly works at Google
Accessing Output String Arguments by name
Output:
Enter Name Jhon Enter marks 74 Student: Name: Jhon, Marks: 74%
Output Alignment by Specifying a Width
Output:
Enter text This is a sample text
This is a sample text
This is a sample text
This is a sample text
Specifying a Sign While Displaying Output Numbers
Output:
Enter Positive Number 25.25 Enter Negative Number -15.50 +25.250000; -15.500000 25.250000; -15.500000
Display Output Number in Various Format
Output:
Enter number 356 The number is:356 Output number in octal format : 544 Output number in binary format: 101100100 Output number in hexadecimal format: 164 Output number in HEXADECIMAL: 164
Display Numbers as a float type
Output:
Enter float Number 234.567 Output Number in The float type :234.567000 padding for output float number234.57 Output Exponent notation2.345670e+02 Output Exponent notation2.345670E+02
Output String Alignment
Let’s see how to use str.rjust(), str.ljust() and str.center() to justify text output on screen and console.
Output:
Enter String Jessa Left justification Jessa******************************************************* Right justification *******************************************************Jessa Center justification ***************************Jessa****************************
Next Steps
To practice what you learned in this article, I have created a Quiz and Exercise.
References:

How do I use “input()”, “if” and “else” in a class to call a specified output from the all?
for example, in this class (some names are meaningless) I want only ” f” is printed through a number or letter that I insert in an “input()” statement (by using if – else)
class Dog:
def __init__ (self, breed, shape, country):
self.breed= breed
self.shape= shape
self.country= country
def sort (q):
print(q.breed)
print(q.shape)
print(q.country)
d= Dog(‘york’, ‘big’,’British’)
f = Dog(‘penny’, ‘small’, ‘Egypt’)
d.sort()
f.sort()
What’s up friends, how is the whole thing, and what you desire to say on the topic of this paragraph,
in my view its actually amazing for me.
Feel free to surf to my page; www bong88
thank u for sharing this straightforward course, it was so helpful
so I would like to share another solution like :
instead of putting this code below :
it was very helpfull for me ,thank you for giving this golden oppurtunity.
It is possible to get input without having to end with an enter? I saw msvcrt is used, but it isn’t working in my code
How to ged rid of input question in output?
Understood the concepts easily.
Do you have link for file input ?
Could you please explain why did u do while: True …. else : break. I didn’t get this part.
Ans:- inside while loop if condition enters to ‘if’ statement and finds True then it skip that part and continue the loop again.
It keeps on skipping the value which holds true inside if condition.
Cómo puedeo eliminar el salto de linea \n después de un input, para evaluar la entrada y agregar un resultado en la misma linea:
tabla = 7 print('Mdo\t\tMdor\tProducto\tEvaluación') for i in range(12,0,-1): p = int(input(f'{tabla}\t x\t {i}\t =\t ')) if tabla * i == p: print('Bien') else: print('Mal')Cómo puedo eliminar el salto de línea después de un input?
tabla = 7 print('Mdo\t\tMdor\tProducto\tEvaluación') for i in range(12,0,-1): p = int(input(f'{tabla}\t x\t {i}\t =\t ')) if tabla * i == p: print('Bien') else: print('Mal')When I try to take input , I can only take integers as input …No alphabets are working …How can I fix it ???
Hey, Can you please post your code so I can look into it
Inputs are by-default strings, are you mentioning int before input ?
Sir can we hide while writing the input.
I mean let’s say :
password = input("Enter Password : ") print(f"{'*' * password}#after running it
Anyone can see the password while I’m printing it so can I hide it too while writing.
Python example to accept input from a user.
With this assignment, the last code
print (name, salary, company)Will not work in python 3.6
However
print (f"{name}, {salary}, {company}")
As f”” results in filling the inputs that the variable name, salary and company hold.
This article made me understand the input() and the input ([prompt]) better. Thank you.
Thank you Aglomasa Bill Clinton for your feedback and suggestion. I have tested code using 3.7 and it’s working as expected
Hi Vishal, with your Pynative, you did an excellent job .I’m from Italy, not longer a young boy 🙂 and i like Python and i would like to learn it well. I searched for tutorials in every corner and i must admit that yours is the best around. Continue on this path and….congratulations.
Franco
Thank you Franco A. Crispo for your kind words
Bro, where are the steps for parsing inputs from files as discussed in the title?
Thanks for the above explanations regarding manual inputs.
How do I write a statement that only allows letters not numbers?
while True: try: name_of_subject = str(input('Please input the name of the course \n')) print(' It\'s clear you want to calculate your average in ', name_of_subject) break except TypeError: print(' Letters only please. Subject names are not numbers\n') except ValueError: print(' Letters only please. Subject names are not numbers\n') except SyntaxError: print(' Letters only please. Subject names are not numbers\n')this was what I write but it doesn’t give me errors for inputing numbers when my intention was to allow only letters.
When you use the method
str(). it can take anything. When you have an integer it makes it a string. So your problem is there is no error for thatcan you please demonstrate the code for taking the dataFrame as input.
while using the input are there any other types which we can use other than int, float, string
Vishal
Thanks you so much. It is a really helpful resource for Python beginner.
Best Wishes.
Eeliena
Thank you Eeliena. I am glad you liked it.
Very beginner friendly…big thumbs
Thanks a lot.Your tutorials are really helpful for such a beginner like me.
Hey, Htet Arkar Thank You!
Though a fresh beginner, your articles appear to be informative. Thanks.
very well explained 🙂
Hey Abhimsh, Thank you.
Hi, Thanks for sharing nice articles…
How can i print space, num and len from one input? As a example like i got a user input that contains a line. In that line there are number, space and letter. Now i want print the number separately from that line and also want to conut all of the space that line contained. how can i do that?
Hi Tanvir, you can write a separate function to extract number and count total space
I don’t know much. Can you write down the function please. I’m a beginner in python.
ok bro
thank you
Shakti, I am glad it helped you:)
Can you give some suggestion, if we can give system input (no manual input) in python program?
Hey Probhat, Can you let me know what you are trying to say for system input. If you are talking about stdin then you can use fileinput module
fileinput will loop through all the lines in the input specified as file names given in command-line arguments, or the standard input if no arguments are provided.
Well explained
I am glad you liked it