External modules are collections of pre-written code created by other programmers. They add extra features for tasks like web development, working with data, machine learning or web scraping. Using these modules saves time and makes coding easier because you don’t have to write everything from scratch.
External modules can be easily installed and managed using Python’s package manager, pip. For example:
pip install requests
Popular External Python Modules
Here are some commonly used external modules in Python:
- Web Development: Django, Flask
- Data Analysis: pandas, numpy
- Machine Learning: scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch
- Data Visualization: matplotlib, seaborn
- Web Scraping: BeautifulSoup, Scrapy
- Networking and APIs: requests, socket
- Databases: SQLAlchemy, sqlite3
- Testing: pytest, unittest
- GUI Development: tkinter, PyQt
- Scientific Computing: SciPy, SymPy
Examples of External Modules
Example 1: Using requests to Fetch Data from an API
The "requests" module simplifies the process of making HTTP requests in Python. We can install this module by executing the below command in terminal.
pip install requests
This example shows how to connect to an API and check the response status.
import requests
response = requests.get("https://api.github.com")
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Successfully connected to GitHub API!")
else:
print("Failed to connect.")
Output
Successfully connected to GitHub API!
Explanation:
- requests.get() sends an HTTP GET request.
- response.status_code checks if the connection was successful.
Example 2: Using pandas to Read a CSV File
Pandas is a tool used for data manipulation and analysis in Python. Using pandas, we can handle vast datasets, manipulate data structures, and perform complex data operations with ease.
To install "pandas" module execute the below command in terminal.
pip install pandas
Below is a simple example showcasing reading a CSV file and displaying its first five rows:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("datafile.csv")
print(df.head())
Ouput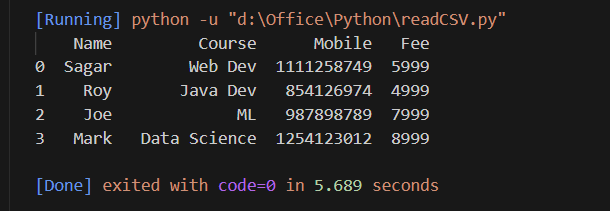
Explanation:
- pd.read_csv() loads the CSV into a DataFrame.
- df.head() displays the first 5 rows for a quick overview.
Example 3: Using numpy for Numerical Calculations
Numpy library is used for numerical computing in Python. It provides support for large multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a collection of mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
We can install this library by executing below command in our terminal.
pip install numpy
In the below code, we create a one dimensional array after that we print the mean of all the elements in an array using mean() function.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print("Mean:", np.mean(arr))
Output
Mean: 3.0
Explanation:
- np.array() creates a NumPy array.
- np.mean(arr) calculates the average of the array elements.
Example 4: Using matplotlib to Plot Data
Matplotlib is a plotting library that is used to visualize large datasets. To install "matplotlib" execute the below command in the terminal.
pip install matplotlib
In the below example, we draw a simple plot by using the sample data set.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
Output
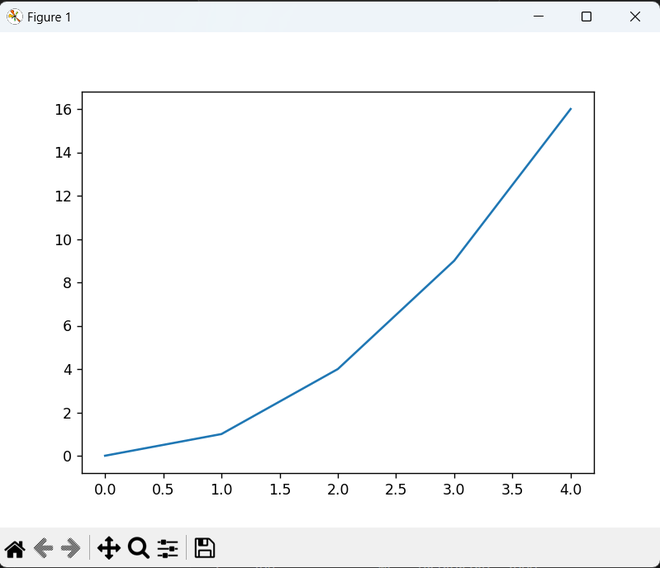
Explanation:
- plt.plot(x, y) plots the points.
- plt.show() displays the graph.
Example 5: Using Flask to Create a Simple Web App
Flask is a framework for web development in Python. It allows for the rapid development of web applications. We can install flask by executing the below command in terminal.
pip install flask
In the below example, we have written the script to display the message "Hello, Flask!" on the webpage.
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/home")
def home():
return "Hello, Flask!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()
Output
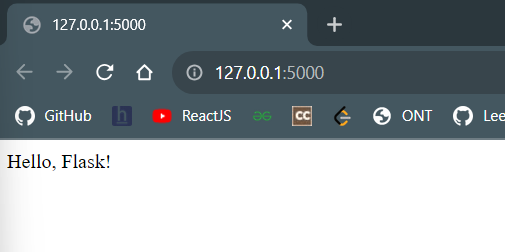
Explanation:
- Flask(__name__) creates the web app.
- @app.route() defines a URL path.
- app.run() starts the web server.