Python OpenCV Edge Detection – The Art of Perception
Edge detection is a method used in image processing to identify the boundaries of objects within an image. It’s like outlining the edges of a drawing to make it more visible. This technique is commonly used in various applications like identifying objects, recognizing faces, and self-driving cars. OpenCV is a powerful tool that offers functions for edge detection. Edges are identified based on the changes in color or brightness of adjacent pixels.
Different techniques are used to identify edges, like Canny, Sobel, and Laplacian edge detection. By detecting edges in an image, we can extract useful information for further processing and analysis. This process is crucial in many computer vision applications.
Background
Before performing edge detection using filters like Sobel, Canny, or Laplacian in OpenCV, it’s important to consider the image background. The background refers to the areas of the image that are not of interest and can often include noise, textures, or patterns that can interfere with the edge detection process. To address this, preprocess the image by removing or reducing the effects of the background using techniques such as blurring, thresholding, or applying a mask. Once the background is reduced, edge detection can be performed to detect the edges and boundaries within the image for further processing.
How Edge Detection Works in Python OpenCV?
Edge detection in OpenCV looks for significant changes in intensity or color between adjacent pixels to identify edges and boundaries in an image. This is done using filters such as the Sobel, Canny, and Laplacian filters. The resulting output is a binary image where the edges are represented as white pixels. These edges can then be further processed for various applications in computer vision.
Types of Python OpenCV Edge Detection
Canny:-
Canny edge detection is a way to find the edges in a picture. It was created by John F. Canny in 1986 and is used a lot in computer vision. To use it, the picture is first made smoother to get rid of any noise. Then, the computer looks for places where the picture changes a lot and finds the direction of the edges. It gets rid of any weak edges and only keeps the strong ones. Finally, it turns the picture black and white so that the edges stand out. This technique is really good at finding edges accurately and is used for lots of things like finding objects in pictures or breaking up a picture into different parts.
Sobel:-
Sobel edge detection is a technique used by computers to find the edges in an image. It does this by looking at how the colors change from one part of the image to another. It uses two special filters, one for looking at changes in color horizontally and one for looking at changes in color vertically. When these filters are applied to the image, the areas where there are big color changes are highlighted as edges. This is useful for things like finding the outline of an object in an image. The Sobel edge detection technique is popular because it is simple and effective, and can be used for many different tasks like finding important features in an image.
Laplacian:-
Laplacian edge detection is a method used to find the edges in an image. It does this by looking for places where the image changes suddenly in intensity. This is done using a mathematical formula called the Laplacian operator. It’s good at finding edges that aren’t straight, but it can be tricked by noise in the image, which can cause it to find false edges. To make it more accurate, other techniques are often used alongside it.
Prerequisites for Edge Detection Using Python OpenCV
It is important to have a solid understanding of the Python programming language and the OpenCV library. Apart from this, you should have the following system requirements.
1. Python 3.7 and above
2. Any Python editor (VS code, Pycharm, etc.)
Download Python OpenCV Edge Detection Project
Please download the source code of Python OpenCV Edge Detection Project: Python OpenCV Edge Detection Project Code.
Installation
Open Windows cmd as administrator
1. To install the opencv library, run the command from the cmd.
pip install opencv-python
Let’s Implement It
To implement it, follow the below step.
1. First of all, we are importing all the necessary libraries that are required during implementation.
import cv2 import numpy as np
2. This line of code reads the image file named “apple.jpg located in the “Image” directory using the OpenCV library in Python.
img = cv2.imread("Image/apple.jpg")
3. This line of code resizes the image to a new width and height of 500 pixels using the resize() function provided by OpenCV.
img = cv2.resize(img, (500, 500))
4. This line of code converts the input image from the BGR color space to the grayscale color space using the cvtColor() function provided by OpenCV.
Gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
5. This line blurs the grayscale image using a filter to remove small details and noise that can interfere with edge detection. It keeps the edges of objects while smoothing the rest of the image. The filter size can be adjusted for different levels of smoothing.
blur = cv2.medianBlur(Gray_img, 5)
6. This line uses an adaptive thresholding method to separate the blurred image into black and white regions. This method calculates the threshold value for each pixel using the mean of neighbouring pixels, which adjusts to local changes in contrast and lighting. The resulting binary image has white pixels for values above the threshold and black pixels for values below it. The parameters define the maximum threshold value, the method used, the type of thresholding, and the neighbourhood size for calculating the threshold value.
threshold = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(blur, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 9, 9)
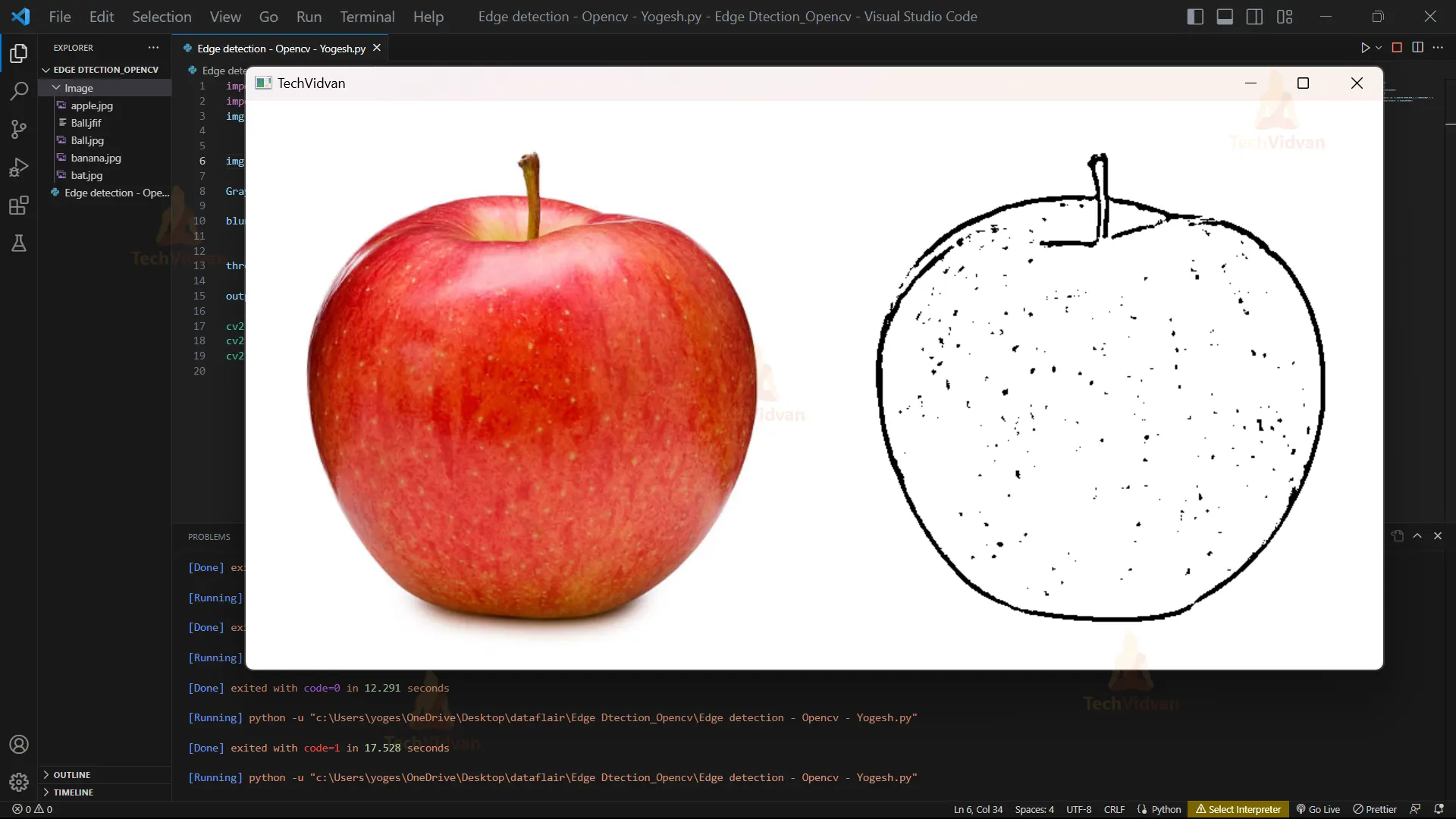
7. We can use the function np.hstack() to put two images side by side. First, we need to convert the grayscale threshold image into BGR color format using cv2.cvtColor(). Then, we can use np.hstack() to stack the original image and the color converted threshold image. This will result in an image showing the original image and its corresponding edges.
output = np.hstack((img, cv2.cvtColor(threshold, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)))
8. These lines of code show the edge of the image in a window with the title “TechVidvan” using OpenCV’s imshow() function. The waitKey(0) function waits until a key is pressed, allowing the user to view the image in the window. Finally, destroyAllWindows() closes all open windows and releases any resources used by OpenCV.
cv2.imshow("TechVidvan", threshold)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Fine-Tuning Edge Detection
To fine-tune edge detection in OpenCV, you can adjust the threshold value, apply filtering techniques such as Gaussian or bilateral filters, and blur the image to reduce noise. Higher thresholds detect fewer edges, while lower thresholds detect more. Blurring helps to reduce noise, but too much blurring can lead to the loss of important details.
Python OpenCV Edge Detection Output
Conclusion
Edge detection is a key technique in computer vision that can be used for different applications. OpenCV offers several methods for edge detection that can be improved by fine-tuning parameters like thresholding and filtering. The output can be further processed to extract useful information from the image. Edge detection using OpenCV is a powerful tool for analyzing images and can assist in various computer vision tasks.