Most testers assume scrolling in Selenium is simple—run a command and the page moves.
I thought so too, until a test suite kept failing because the element I needed wasn’t in view. One run would pass, the next would throw ElementNotInteractable, all because the page didn’t scroll reliably.
I tried adding waits, tweaking actions, even rewriting locators, but nothing fixed the inconsistency. What seemed like a basic interaction quickly turned into hours of frustration.
That’s when it hit me: scrolling isn’t just “moving the page.” Websites use dynamic layouts, infinite scroll, sticky headers, and lazy-loaded content—and Selenium needs the right scrolling method for each.
Overview
In Selenium, scrolling refers to programmatically moving a webpage’s viewport so elements outside the visible area come into view. This is typically done using JavaScript because Selenium can’t scroll on its own.
Scroll down a web page by a defined number of pixels
- Use JavascriptExecutor to scroll vertically by a specific pixel value.
- Useful when you know exactly how far down the page you want to move.
- Works well for fixed layouts and predictable page structures.
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollBy(0, 500)"); // scroll down 500pxScroll to the bottom of the webpage
- Scroll until the page’s document.body.scrollHeight is reached.
- Ideal for loading dynamic or infinite-scroll content.
- Ensures all elements at the bottom are rendered before interaction.
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight)");Scroll horizontally to a specific web element
- Use JavaScript to scroll the element into the horizontal view.
- Helpful for wide tables, carousels, or horizontally scrollable sections.
- Ensures the element is fully visible and interactable.
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight)");
In this guide, I’ll break down the simple, reliable ways to scroll with Selenium, whether it’s by pixels, to the bottom of the page, or directly to a specific element—so you don’t repeat the mistakes I did.
Why Scrolling Matters in Selenium
Scrolling is essential in Selenium because:
- Many elements load outside the visible viewport, and Selenium can’t interact with them until they’re scrolled into view.
- Modern websites use lazy loading, infinite scroll, and dynamic layouts, which require scrolling to trigger new content.
- Sticky headers and fixed sections can obstruct elements, making accurate interactions impossible without controlled scrolling.
- Failing to scroll often leads to errors like ElementNotInteractable or unexpected click failures.
- Replicates real user behavior, ensuring the test flows match how users naturally navigate long or complex pages.
According to Sarah Thomas, an expert in software testing, when scrolling up or down in Selenium, always scroll with a clear purpose—wait for the target element to be fully visible, account for sticky headers or dynamic content, and avoid hard-coded scroll values to keep tests stable across different screen sizes and browsers.
Since scrolling can behave differently across browsers, devices, and screen sizes, it’s important to test these interactions in real environments.
Platforms like BrowserStack Automate help you do exactly that by running your Selenium scripts on real browsers and devices, ensuring consistent and reliable scrolling behavior.
Methods to Scroll Down in Selenium
Now that you know why scrolling is essential for reliable Selenium tests, let’s look at the different ways to perform it in your scripts.
Depending on your page layout and testing needs, Selenium offers multiple scrolling techniques through JavaScript. Below are the most commonly used methods for scrolling in Selenium.
How to scroll down on a web page in Selenium by defining the number of pixels
Refer to the script below for performing Selenium scroll-down action on the Firefox browser.
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HandleScroll
{
@Test
public void scrollDown()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver","D://Selenium Environment//Drivers//geckodriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.navigate().to("Website URL");
//to perform Scroll on application using Selenium
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollBy(0,350)", "");
}
}Run Selenium Tests on Real Devices
Output: The code initializes the Geckodriver for Firefox. Then the Firefox browser is launched, and it navigates to the specified website URL. Once the website loads, the browser window is vertically scrolled down by 350 pixels.
If a user needs to scroll up, they just need to modify the pixel value of the second parameter (in this case 350) to a negative value (-350).
Refer to the script below:
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HandleScroll
{
@Test
public void scrollDown()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver","D://Selenium Environment//Drivers//geckodriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.navigate().to("Website URL"); // Specify the website URL
//to perform Scroll on application using Selenium
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollBy(0,-350)", "");
}
}How to scroll down to an element in Selenium until it is visible
Refer to the Selenium script below.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ScrollByVisibleElement {
WebDriver driver;
@Test
public void ByVisibleElement() {
System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver","D://Selenium Environment//Drivers//geckodriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
//Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.browserstack.com/guide/selenium-scroll-tutorial");
//Locating element by link text and store in variable "Element"
WebElement Element = driver.findElement(By.linkText("Try Selenium Testing For Free"));
// Scrolling down the page till the element is found
js.executeScript("arguments[0].scrollIntoView();", Element);
}
}Run Selenium Tests on Real Devices
Output: The above code when executed, will launch the Firefox browser, navigate to the defined URL (Selenium scroll tutorial). Further, it will perform the scroll down until the element with text – Try Selenium Testing For Free is found.
The Javascript method scrollIntoView() performs the scroll down operation until the mentioned element is completely visible.
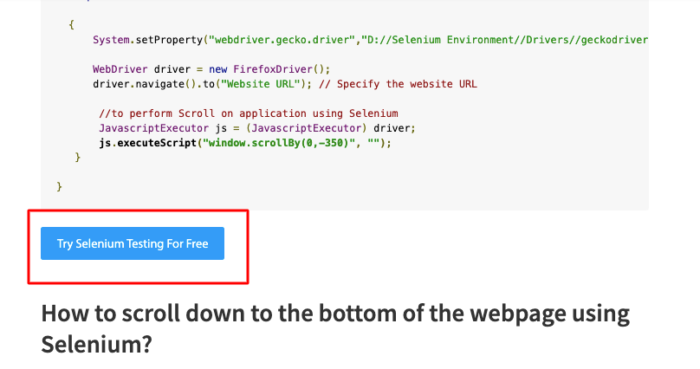
How to scroll down to the bottom of the webpage using Selenium?
Refer to the Selenium script below.
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HandleScroll
{
@Test
public void scrollDown()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver","D://Selenium Environment//Drivers//geckodriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.navigate().to("Website URL"); // Specify the Website URL
//to perform scroll on an application using Selenium
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("window.scrollBy(0,document.body.scrollHeight)");
}
}
Output: The code above will fetch the maximum height of the webpage from the Document Object Model, and then the scrollBy() method scrolls down to the bottom.
Pro Tip: Want to dive deeper into Selenium implementation on BrowserStack with free interactive courses and lab exercises? Visit Test University
How to scroll horizontally on a web page to a specific web element using Selenium
Refer to the Selenium script below:
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HandleScroll
{
@Test
public void ScrollHorizontally()
{
System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver","D://Selenium Environment//Drivers//geckodriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
// Launch the application
driver.get(" Website URL “); // Specify the website URL
WebElement Element = driver.findElement(By.linkText("Auto Testing"));
//This will scroll the page Horizontally till the element is found
js.executeScript("arguments[0].scrollIntoView();", Element);
}
}Output: The code above starts the Firefox browser and navigates to the specified URL. Once the page loads, Selenium will automatically detect the specified element on the web page and will scroll horizontally until the element is fully visible in the browser window.
With these scrolling techniques in place, the next step is ensuring they work consistently across different browsers, devices, and screen sizes. That’s where real-environment testing becomes essential.
Validate Scrolling on Real Devices with BrowserStack Automate
Scrolling can behave differently across browsers, operating systems, and device types. A scroll action that works flawlessly on desktop Chrome may behave unpredictably on mobile Safari or pages that rely on dynamic loading. Validating scrolling in real environments is essential for reliable Selenium tests.
BrowserStack Automate helps by providing:
- Access to 3,500+ real browser and device combinations to test scrolling exactly as users experience it.
- Consistent validation of scroll actions like pixel-based scrolls, scroll-to-element, infinite scroll, and horizontal scrolling.
- Accurate results across varying screen sizes and resolutions, ensuring your script handles real-world layout differences.
- Debugging support with video recordings, screenshots, console logs, and network insights to identify scroll-related failures quickly.
- Scalable parallel execution, allowing you to verify scrolling behavior across multiple environments at once.
By testing on real devices and real browsers, you can ensure your scrolling logic works smoothly across every environment your users rely on.
Conclusion
Scrolling may seem like a simple action, but in Selenium testing, it plays a critical role in ensuring elements are visible, interactable, and loaded correctly.
Whether you’re scrolling by pixels, moving to the bottom of the page, or bringing a specific element into view, choosing the right method helps you avoid flaky tests and align your scripts with real user behavior.
However, scroll behavior can vary across browsers, devices, and screen sizes. To validate your tests under real-world conditions, platforms like BrowserStack Automate let you run Selenium scripts on 3,500+ real browser and device combinations, ensuring consistent, reliable scrolling interactions every time.
Mastering these scrolling techniques—and testing them on real environments—will help you build more stable, accurate, and user-centric Selenium test suites.