VRSight: An AI-Driven Scene Description System to Improve Virtual Reality Accessibility for Blind People
Daniel Killough¹, Justin Feng¹*, Zheng Xue "ZX" Ching¹*, Daniel Wang¹*, Rithvik Dyava*, Yapeng Tian², Yuhang Zhao¹
1University of Wisconsin-Madison,
2University of Texas at Dallas
*Authors 2-5 contributed equally to this work.
Presented at UIST 2025 in Busan, Republic of Korea
VRSight provides spatial audio feedback for blind and low vision users in virtual reality (VR) environments by leveraging AI systems like real-time object detection, zero-shot depth estimation, and multimodal large language models. VRSight provides real-time audio descriptions and spatial interaction assistance without per-app developer integration, creating the first post hoc "3D screen reading" system for VR.
* Setup is not so quick and likely will require a sighted aide experienced with installing systems via command line. Expect 1 hour. Opportunity for future improvement.
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU with CUDA support (recommended) or Apple Silicon (MPS)
- RAM: Minimum 8GB, recommended 16GB+
- Storage: 2GB+ for models and dependencies
- VR Headset: Any VR headset should work as long as you can cast the output. We've tested with Quest line of headsets (2, 3, Pro) using Meta Quest Developer Hub.
- Corresponding casting utility for your VR Headset: e.g., Meta Quest Developer Hub, SteamVR mirror, etc.
- 3-key keyboard: e.g., this one (non-affiliate link)
- Long USB cables (3m+)
- PyTorch: Install version compatible with your CUDA version.
- Azure Models: Requires valid subscriptions to Microsoft Azure for OpenAI, Cognitive Services, and SpeechSynthesizer. Estimated cost $25/year.
- WebVR Utility: We use PlayCanvas (free), which you can clone this repo: https://playcanvas.com/project/1233172/overview/vr-scene
- Websocket Backend Utility: We use Render (free), which you can clone this repo: https://vrsight-backend.onrender.com/
Opportunity for future work: Using on-device VLMs, OCR, TTS instead of querying Azure. Would increase hardware requirements but reduce monetary cost.
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/MadisonAbilityLab/VRSight.git
cd VRSight/Recognition
# Create conda environment
conda create --name vrsight python=3.9
conda activate vrsight
# Install PyTorch (adjust for your CUDA version). Example:
pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
# Install other dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt# Create weights directory
mkdir -p weights
# Download VRSight model weights from HuggingFace
# Option 1: Using wget
wget -O weights/best.pt https://huggingface.co/UWMadAbility/VRSight/resolve/main/best.pt
# Option 2: Using curl
curl -L -o weights/best.pt https://huggingface.co/UWMadAbility/VRSight/resolve/main/best.pt
# Option 3: Manual download
# Visit: https://huggingface.co/UWMadAbility/VRSight/blob/main/best.pt
# Click "Download" and place in weights/best.pt
# Verify model download
python -c "
import torch
try:
model = torch.load('weights/best.pt', map_location='cpu')
print('✅ Model loaded successfully')
print(f'Model size: {os.path.getsize(\"weights/best.pt\") / (1024*1024):.1f} MB')
except Exception as e:
print(f'❌ Model loading failed: {e}')
"- Download the DepthAnythingV2 module and add to the Recognition/ folder
- Add your desired weights to Recognition/checkpoints
# Copy and edit environment configuration
cp .env.example .env
# Add your API keys to your .env
export AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY="your_openai_key"
export AZURE_COGNITIVESERVICES_KEY="your_azure_tts_key"
export AZURE_TTS_REGION="your_region"On your computer, launch your cloned webVR utility (e.g., https://playcanvas.com/project/1233172/overview/vr-scene) -> Launch.
If you're using a standalone headset like Meta Quest 3, open the built-in browser and navigate to the same Launch window. Then press the VR button to enter scene.
Once loaded in, you can safely return to menu and continue using your VR headset as normal, but do not quit the VR scene -- keep it running in the background.
Basic run with default settings:
python main.pyRun with specific camera index:
# Check available cameras
python -c "
import cv2
for i in range(5):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(i)
if cap.isOpened():
print(f'Camera {i}: Available')
cap.release()
else:
print(f'Camera {i}: Not available')
"
# Run with specific index:
python main.py --camera-index [index]Once VRSight is running:
- 1: Trigger ContextCompass (general scene descriptions using GPT)
- 2: Trigger SceneSweep (left-to-right spatial audio descriptions)
- 3: Trigger AimAssist (specific, targeted spatial audio descriptions near user's hand or pointer end)
- ESC or q: Exit the application
When running successfully, you should see:
- Real-time object detection, depth estimation, and edge detection preview windows
- Console output showing detected objects
- Audio feedback through configured TTS system
- WebSocket server running on localhost:8765
# config_manager.py - Environment-specific settings
from config_manager import get_config
config = get_config()
print(f"Running in {config.environment.value} mode")
print(f"Using device: {config.models.device}")camera:
width: 640
height: 640
webcam_index: 1
models:
yolo_model_path: "weights/best.pt"
depth_encoder: "vits" # vits, vitb, vitl, vitg
device: "auto" # auto, cuda, mps, cpu
performance:
memory_cleanup_threshold_mb: 1000
thread_heartbeat_timeout: 10
queue_max_size: 10
rate_limiting:
gpt_min_request_interval: 10
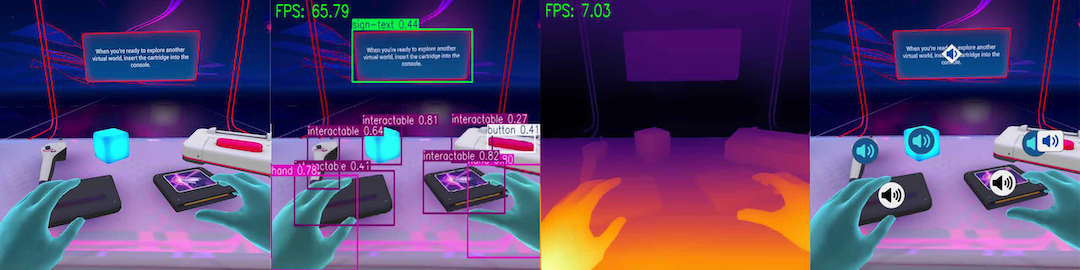
cooldown_interactables: 30VRSight achieves real-time performance:
- Frame Rate: 30+ FPS real-time processing
- Latency: End-to-end keypress-to-webVR feedback over websocket in as low as 2ms
- Memory Usage: 30% reduction through optimized buffering
- High Detection Accuracy: Custom YOLO model trained on DISCOVR dataset achieving 67.3% mAP50. Models trained on real-world objects (e.g., base YOLOv8 on COCO) rarely detected VR objects; see paper for more details.
VRSight is powered by the DISCOVR dataset, the first comprehensive VR object detection dataset.
- 30 Object Classes across 6 categories, including Avatars, Informational, Interactables, Safety, Seating Areas, and VR System.
- 15,207 Training Images
- 1,645 Validation Images
- 839 Test Images
- YOLOv8 Annotation Format
- Weights available on HuggingFace!
A full list of classes and their performance metrics can be found in Table 1 in the paper.
A full breakdown of annotation methodology can be found in the paper.
DISCOVR is available on HuggingFace at https://huggingface.co/datasets/UWMadAbility/DISCOVR under a CC-BY-4.0 License. If you use DISCOVR in your research, please cite the base VRSight paper using the citation at the bottom of the readme!
GPU Memory Errors
# Reduce memory usage
export VR_AI_ENV=development # Uses higher cleanup thresholdsModel Loading Failures
# Verify model file
python -c "import torch; torch.load('weights/best.pt')"
# Check CUDA availability
python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"Audio Issues
# Check Azure TTS configuration
python -c "import azure.cognitiveservices.speech as speechsdk; print('Azure TTS available')"For CPU-only systems:
# Force CPU mode in configuration
config.models.device = "cpu"
config.performance.queue_max_size = 5For high-performance systems:
# Enable optimizations
config.models.model_precision = "fp16"
config.performance.memory_cleanup_threshold_mb = 2000We welcome open-source contributions to improve VRSight!
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Push your code to the feature branch
- Submit a pull request with clear description of the changes
VRSight consists of a modular architecture as follows:
object_detection_engine.py: YOLO-based object detection with error recoverydepth_detection_engine.py: DepthAnythingV2 depth estimationedge_detection_engine.py: VR pointer/line detection for interactions
Object detection models can be easily swapped by updating the yolo_model_path constant in config.py to a different .pt weight file.
scene_sweep_processor.py: Comprehensive scene reading and descriptionaim_assist_processor.py: Hand/controller pointing command processingaim_assist_menu_pilot_processor.py: Additional handling for VR menu interaction (opportunity for future improvement)interaction_detection.py: Ray-casting and spatial interaction analysis
thread_manager.py: Unified thread coordination and resource managementmemory_manager.py: Advanced memory optimization with leak detectionconfig_manager.py: Environment-specific configuration managementunified_rate_limiter.py: Intelligent rate limiting across all services
geometry_utils.py: Spatial calculations and coordinate operationsaudio_utils.py: TTS synthesis and spatial audio management
- Multi-Modal Recognition: Object detection, depth estimation, edge detection, and OCR
- Real-time Processing: Optimized pipeline achieving 30+ FPS with automatic quality scaling
- Spatial Audio Feedback: 3D positional audio with Azure TTS integration
- VR Interaction Support: Hand/controller tracking with precise targeting assistance
- Advanced Analytics: Performance monitoring, memory management, and error recovery
- Multi-Environment Support: Development, production, and testing configurations
- Enterprise Quality: Comprehensive testing, benchmarking, and validation suite
- Modular Design: 11 specialized modules following SOLID principles
If you use VRSight or DISCOVR in your research, please cite our work:
@inproceedings{killough2025vrsight,
title={VRSight: An AI-Driven Scene Description System to Improve Virtual Reality Accessibility for Blind People},
author={Killough, Daniel and Feng, Justin and Ching, Zheng Xue and Wang, Daniel and Dyava, Rithvik and Tian, Yapeng and Zhao, Yuhang},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 38th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology},
pages={1--17},
year={2025}
}This project is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY-4.0) - see the LICENSE file for details.
You are free to share and adapt this work for any purpose as long as you provide appropriate attribution to the original authors.
We thank the University of Wisconsin-Madison Ability Lab, the University of Texas at Dallas, and all contributors to the DISCOVR dataset. Special thanks to the accessibility community for their invaluable feedback and testing.
Codebase refactored for release with help from Claude.ai
For questions and support, please open a GitHub Issue or contact Daniel Killough at the MadAbility Lab at UW-Madison.