This document introduces functional programming in Scala. It notes that Scala code is more concise than Java. It discusses immutable data structures and pure functions without side effects as key aspects of functional programming. It provides examples of Scala code that uses options to avoid null pointers. The document also explains that Scala supports both functional and object-oriented programming. It concludes by recommending chapters in the Functional Programming in Scala textbook to learn more about functional programming.




![ElegantFunctionalProgrammingWay
val (openerO, wineO) = (Some(Opener), Some(Wine(vintage = 1997)))
val contentsO = for {
opener <- openerO
wine <- wineO
} yield opener.open(wine)
// contentsO: Option[Contents] = Some(contentsOfWine)
// no null, no NullPointerException
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyscala-170326171039/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-Review-of-Functional-Programming-in-Scala-Ch-1-5-2048.jpg)
![ElegantFunctionalProgrammingWay
val (openerO, wineO) = (Some(Opener), None)
val contentsO = for {
opener <- openerO
wine <- wineO
} yield opener.open(wine)
// contentsO: Option[Contents] = None
// no null, no NullPointerException
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyscala-170326171039/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-Review-of-Functional-Programming-in-Scala-Ch-1-6-2048.jpg)

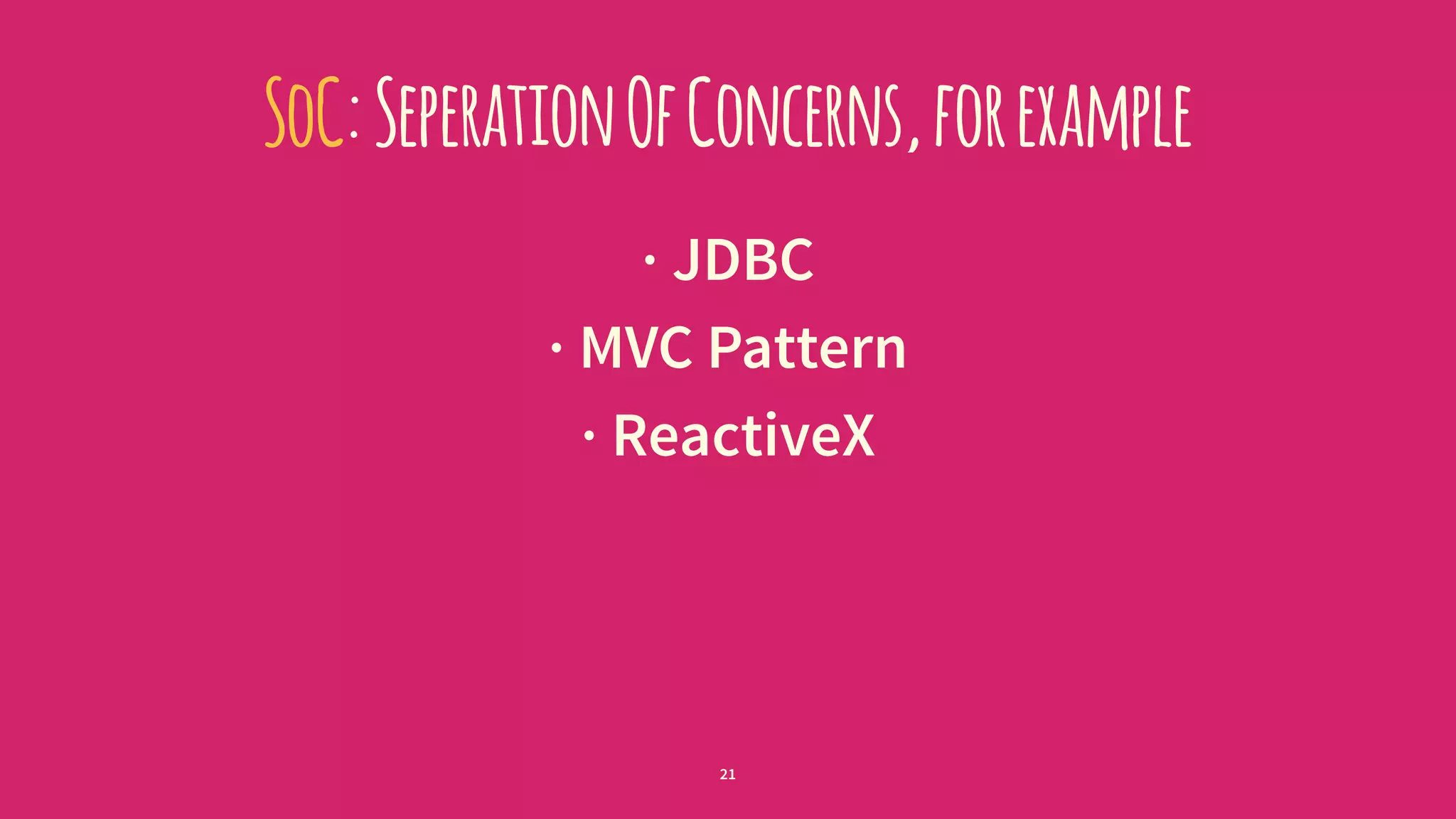
![…andViceVersa
// scala code
object Person {
val MALE = "m";
}
// java code
public class App {
public static void main(String argv[]) {
Person$ person = Person$.MODULE$;
System.out.println(person.MALE());
}
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyscala-170326171039/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-Review-of-Functional-Programming-in-Scala-Ch-1-9-2048.jpg)


![Immutability
// value, not variable
val a = 1
a = 2 // error: reassignment to val
// list
val ints1: List[Int] = 1 :: 2 :: Nil
val ints2: List[Int] = ints1 :+ 3
println(ints1) // List(1, 2)
println(ints2) // List(1, 2, 3)
println(ints2 == 1 :: 2 :: 3 :: Nil) // true
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyscala-170326171039/75/Functional-Programming-in-Scala-in-a-Nutshell-Review-of-Functional-Programming-in-Scala-Ch-1-12-2048.jpg)