PostgreSQL Performance Optimization and Scaling Services
When it is critical, you can count on us!
At Stormatics, we specialize in PostgreSQL optimization and scaling to ensure peak performance, no matter how your demands evolve. Whether you are dealing with slow queries, downtime, or scalability bottlenecks, our team of experts fine-tune your database for maximum efficiency and seamless growth using our signature methodology.
We don’t just support your database, we take ownership of its performance, so you can focus on growing your business.
Unlock the full potential of your PostgreSQL database with our expert optimization solutions today.

5 good reasons to get Performance Optimization

Customer Success Story
Compression time reduced from 72 minutes to 3 minutes, restoring automation and stability in production
Fraîcheur de Paris, the public utility operating Paris’s district cooling network, was facing severe performance issues in its Timescale DB environment after a large data backfill. The automated compression policy had stopped working, causing each chunk compression to take over 72 minutes and forcing the team into manual, time-consuming workarounds.
After engaging Stormatics, the issue was swiftly diagnosed and resolved through a structured remediation plan. The approach which involved policy resets, decompression, and full recompression of the hypertable was validated in staging and then applied successfully in production.
The transformative results with Stormatics included:
- Compression time reduced from 72 to just 3 minutes per chunk, restoring full automation.
- 24× improvement in throughput, ensuring efficient and reliable data compression at scale.
The Stormatics Signature Methodology
Our signature methodology for performance optimization, developed through years of hands-on experience with mission-critical databases, delivers lasting improvements by tackling performance challenges at their core.
Query Optimization
Query optimization significantly enhances performance by reducing resource consumption and delivering faster response times. We do query optimization in four steps.
Database Architecture Refinement
Architectural inefficiencies can lead to the sub-par performance of your Postgres database. We address these inefficiencies through load balancing and table partitioning.
Advanced Postgres Features
PostgreSQL offers numerous features designed for performance. We ensure you are leveraging features like HOT updates, TOAST, aggregates, and incremental sorting, etc.
Configuration Parameter Tuning
Proper configuration aligns database performance with workload requirements. Our focus includes identifying the available database resources and adjusting parameters for your workload and traffic patterns.
Importance of Performance Optimization for PostgreSQL: A Brief Guide
Infrastructure doesn’t come cheap, even if you are using the cloud, so be sure your database fully harnesses it. To maximize your ROI, it is crucial for your business to optimize your PostgreSQL Database for your workloads.
To showcase the possibilities, we ran some benchmarks and found cost savings of more than 75% in each optimization*. Now who wouldn’t want that?
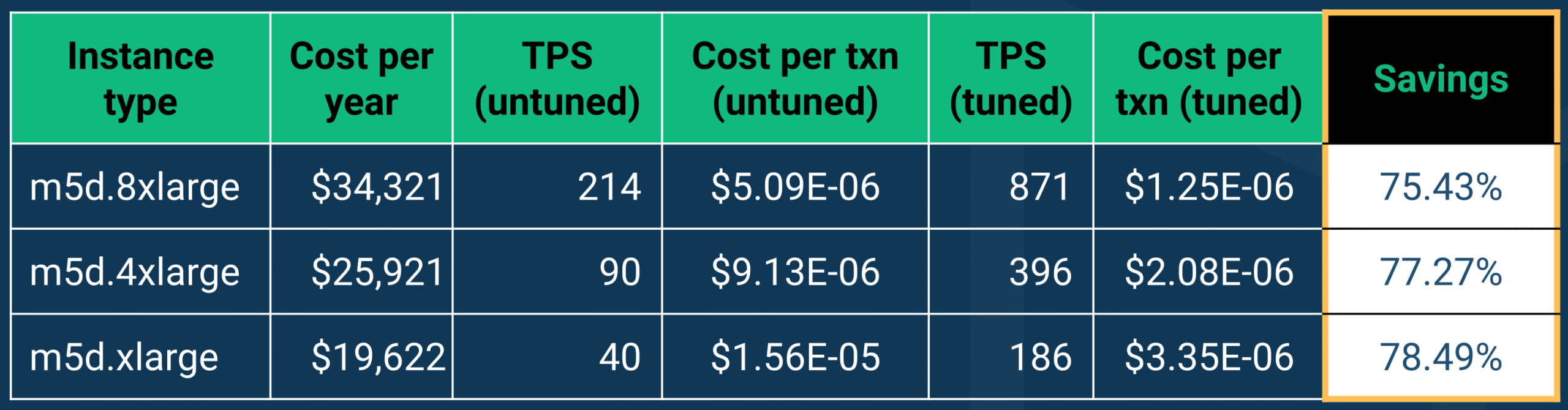
*using Resource Stresser dataset on BenchBase with a scale factor of 80,000 running over 3 hours with 50 concurrent terminals
Q. How to optimize PostgreSQL database performance?
Optimizing PostgreSQL performance involves several techniques including proper indexing, query tuning, adjusting configuration settings like `shared_buffers`, `work_mem`, and `maintenance_work_mem`, and ensuring efficient disk I/O. You can also leverage the `EXPLAIN` and `ANALYZE` commands to analyze query execution plans and identify bottlenecks.
Q. How can I make my PostgreSQL faster?
To make PostgreSQL faster, focus on optimizing queries, creating indexes on frequently queried columns, partitioning large tables, and tuning PostgreSQL configuration parameters. Regular maintenance tasks like `VACUUM` and `ANALYZE` are also essential.
Q. Does PostgreSQL optimize queries?
Yes, PostgreSQL has a built-in query optimizer that analyzes and optimizes SQL queries to determine the most efficient execution path. It uses statistics gathered from `ANALYZE` to make these decisions.
Q. How to measure performance in PostgreSQL?
You can measure PostgreSQL performance by using extensions like `pg_stat_statements` to track query performance, `EXPLAIN` to view query execution plans, and monitoring key performance indicators such as cache hit rate, CPU usage, and disk I/O. Third-party monitoring tools like `pgAdmin`, `Grafana`, and `Prometheus` can also help monitor performance.
Q. How do I fix PostgreSQL performance issues?
To resolve performance issues, start by identifying the problematic queries using `pg_stat_activity` or `pg_stat_statements`. Optimize these queries by adding indexes, rewriting inefficient joins, and tuning the PostgreSQL configuration settings. Ensure regular maintenance tasks like `VACUUM` are performed to prevent table bloat.
Q. Can PostgreSQL handle millions of rows?
Yes, PostgreSQL is designed to handle millions, even billions of rows efficiently. Partitioning, indexing, and tuning queries are crucial for handling large datasets.
Q. How to speed up vacuum in PostgreSQL?
To speed up `VACUUM`, increase the `maintenance_work_mem` and `autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit` parameters, and run `VACUUM` during off-peak hours.
Q. How to tune slow running queries in PostgreSQL?
Tune slow queries by analyzing the execution plan with `EXPLAIN ANALYZE`, identifying bottlenecks, and adjusting indexes or rewriting inefficient parts of the query. Make sure the database statistics are up to date using `ANALYZE`, and adjust memory settings like `work_mem` for better performance.
Q. Is PostgreSQL faster than MySQL?
The performance of PostgreSQL versus MySQL depends on the use case. PostgreSQL is generally better for complex queries, concurrency, and handling large datasets, while MySQL can perform faster in simpler, read-heavy workloads. For OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) and analytical workloads, PostgreSQL tends to excel.
Q. What is the fastest way to load data into PostgreSQL?
The fastest way to load data into PostgreSQL is by using the `COPY` command instead of multiple `INSERT` statements. Additionally, disabling indexes and constraints temporarily during the load process and batching transactions can further improve loading speed.
Q. How to improve cache hit rate in PostgreSQL?
Improve cache hit rate by increasing the size of `shared_buffers` to hold more data in memory. Regularly accessed data will then be served from memory rather than disk, enhancing performance.
Q. Why is my query running slow in PostgreSQL?
Slow queries in PostgreSQL can be caused by missing indexes, inefficient query execution plans, bloated tables, or insufficient memory allocation for queries. Use `EXPLAIN ANALYZE` to diagnose the slow parts of the query and optimize accordingly.
Q. How to monitor PostgreSQL database performance in Grafana?
Grafana, when paired with data sources like Prometheus or a PostgreSQL exporter, allows you to monitor key metrics such as query performance, CPU utilization, disk I/O, and cache hit rates in PostgreSQL through customizable dashboards.
Q. Does PostgreSQL scale well?
Yes, PostgreSQL scales well both vertically (by increasing resources on a single server) and horizontally (using replication and sharding techniques). Features like partitioning, replication, and connection pooling contribute to its scalability.
Q. What is the benchmark tool for PostgreSQL?
`pgbench` is a popular benchmarking tool for PostgreSQL. It can simulate client workloads and measure throughput, latency, and other performance metrics, helping to evaluate and tune PostgreSQL performance.