Inheritance in JavaLast Updated : 2 Jan 2026 Inheritance in Java is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object. It is an important part of OOPs (Object Oriented programming system). The idea behind inheritance in Java is that we can create new classes that are built upon existing classes. When we inherit methods from an existing class, we can reuse methods and fields of the parent class. However, we can add new methods and fields in your current class also. What is Inheritance?Inheritance in Java enables a class to inherit properties and actions from another class, called a superclass or parent class. A class derived from a superclass is called a subclass or child group. Through inheritance, a subclass can access members of its superclass (fields and methods), enforce reuse rules, and encourage hierarchy. Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship. Why Use Inheritance in Java?The inheritance is used for the following important reasons:
Terms used in InheritanceHere are the important terms (terminologies) that are used in inheritance:
The extends KeywordThe extends keyword is used to create a new class (subclass) that derives from an existing class (superclass). It allows the subclass to inherit fields and methods from the superclass. SyntaxIt has the following syntax: Java Inheritance Example As displayed in the above figure, Programmer is the subclass and Employee is the superclass. The relationship between the two classes is Programmer IS-A Employee. It means that Programmer is a type of Employee. This example demonstrate the single inheritance in Java, where the Programmer class inherits the salary variable from the Employee class and also defines its own bonus. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: Programmer salary is:40000.0 Bonus of programmer is:10000 In the above example, Programmer object can access the field of own class as well as of Employee class i.e. code reusability. Types of InheritanceThere are several types of inheritance supported in Java:
In Java, multiple inheritance and hybrid inheritance are supported only through interfaces, because Java does not allow multiple inheritance with classes directly. We will learn more about interfaces later. Single InheritanceWhen a class inherits another class, it is known as a single inheritance. In the example given below, Dog class inherits the Animal class, so there is the single inheritance.  Let us take an example to demonstrate the single inheritance in Java. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: barking... eating... Multilevel InheritanceWhen there is a chain of inheritance, it is known as multilevel inheritance. As you can see in the example given below, BabyDog class inherits the Dog class which again inherits the Animal class, so there is a multilevel inheritance.  Here, we are going to take an example to demonstrate the working of multilevel inheritance in Java. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: weeping... barking... eating... Hierarchical InheritanceWhen two or more classes inherits a single class, it is known as hierarchical inheritance. In the example given below, Dog and Cat classes inherits the Animal class, so there is hierarchical inheritance. 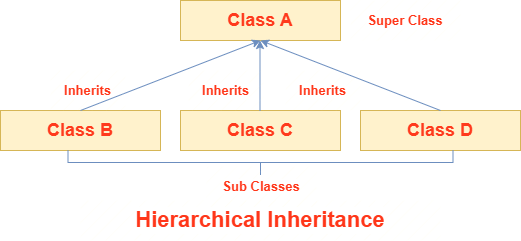 Here, we are going to take an example to demonstrate the working of hierarchical inheritance in Java. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: meowing... eating... Multiple InheritanceMultiple Inheritance A class's capacity to inherit traits from several classes is referred to as multiple inheritances. This notion may be quite helpful when a class needs features from many sources.  However, Multiple inheritances can result in issues like the diamond problem, which occurs when two superclasses share the same method or field and causes conflicts. Java uses interfaces to implement multiple inheritances in order to prevent these conflicts. Here, we are going to take an example to demonstrate the working of multiple inheritance in Java. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: Warrior attacks with a sword. Warrior uses a sword. Mage attacks with a wand. Mage uses a wand. Hybrid Inheritance in JavaThe hybrid inheritance is the composition of two or more types of inheritance. The main purpose of using hybrid inheritance is to modularize the code into well-defined classes. It also provides the code reusability.  The hybrid inheritance can be achieved by using the following combinations:
Here, we are going to take an example to demonstrate the working of hybrid inheritance in Java. ExampleOutput: D FAQs about Inheritance1. Why multiple inheritance is not supported in Java?To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in Java. Suppose there are three classes A, B, and C. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and we call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class. It is called diamond problem. To read more Diamond Problem in Java Since compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So, whether you have same method or different, there will be compile time error. Output: Compile Time Error 2. How to achieve Multiple Inheritance in Java?Java supports multiple inheritance through interfaces only, where a class can implement multiple interfaces. Multiple inheritance in Java is not possible by class, but it is possible through interfaces. Next TopicAggregation in java (HAS-A) |
Subscribe to Tpoint Tech
We request you to subscribe our newsletter for upcoming updates.







