Java Collections Class | Java Collections Class MethodsLast Updated : 6 Jan 2026 The Java Collections class belongs to java.util package and provides static utility methods that operate on return collections, such as List, Set, and Map. These methods are mostly used to perform common operations such as sorting, searching, reversing and synchronization. The methods of this class all throw a NullPointerException if the collections or class objects provided to them are null. To read more Collections in Java 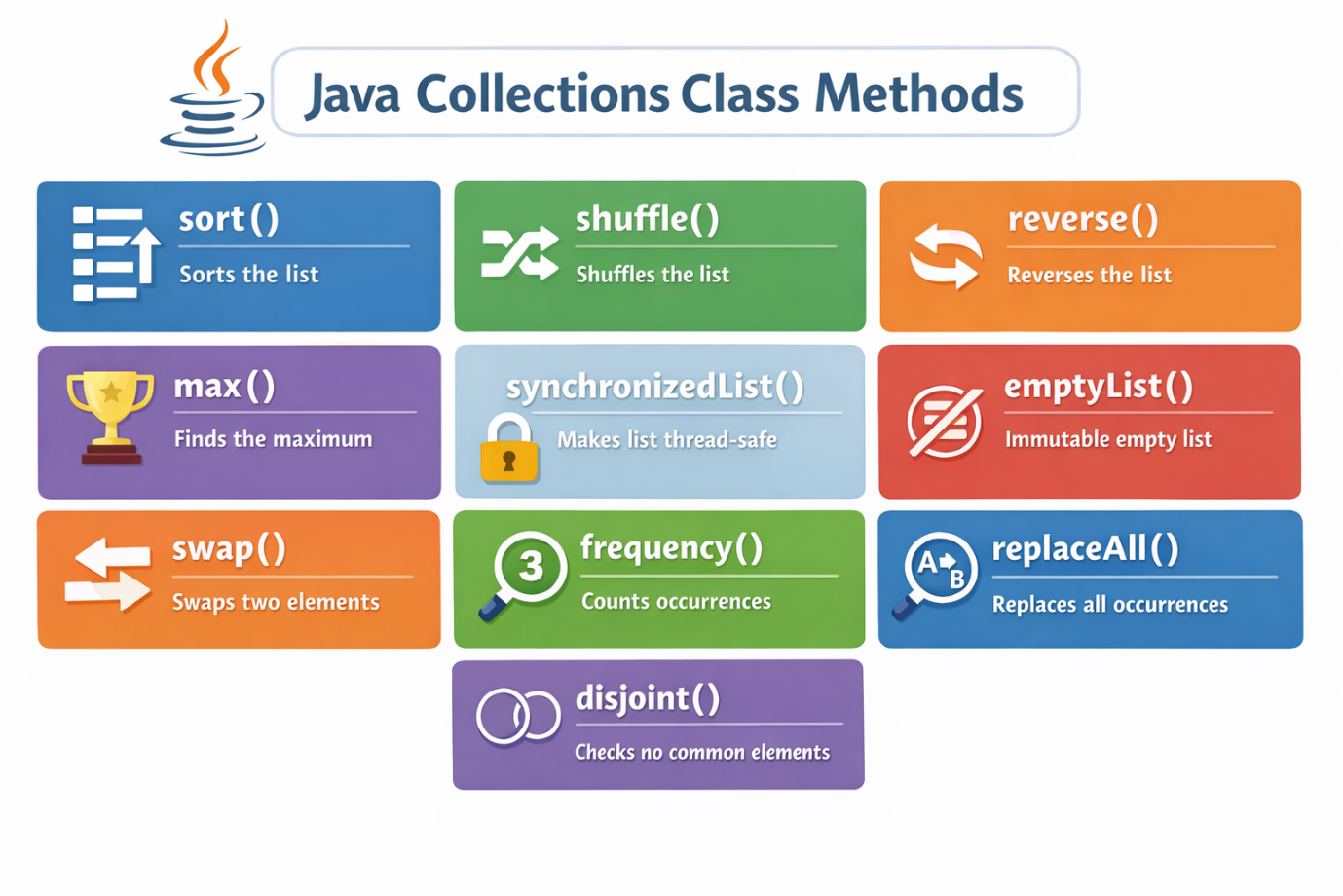 Java Collections Class Methods
Let's use some of the above methods in Java program. Java Collections Class Method ExamplesCollections.addAll() MethodThe method adds all of the specified elements to the specified collection. Elements to be added may be specified individually or as an array. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: Initial collection value:[C, Core Java, Advance Java] After adding elements collection value:[C, Core Java, Advance Java, Servlet, JSP] After adding array collection value:[C, Core Java, Advance Java, Servlet, JSP, C#, .Net] Collections.max() MethodThis method returns the maximum element from the given collection. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: Value of maximum element from the collection: 67 Explanation In the above code, we have a list of numbers [46, 67, 24, 16, 8, 12]. The collection.max() method is used to find the largest number in the list which is 67. It works based on the natural order of integers. The method then prints the minimum value. It is the easiest way to find the biggest item in any collection. Collections.min() MethodThis method returns the minimum element from the given collection. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: Value of minimum element from the collection: 8 Explanation In the above code, we have a list of numbers [46, 67, 24, 16, 8, 12]. The collection.min() method finds the smallest number in the list which is 8. It works based on the natural order of integers. The method then prints the minimum value. It is the easiest way to find the smallest item in any collection. Collections.sort() MethodThe methos is used to sort the given elements. If the elements do not implement Comparable, this method throws a ClassCastException. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [5, 7, 11, 14] Explanation In the above code, we create a list of integers (14, 5, 11, 7) using Arrays.asList(). The Collections.sort() method is used to sort the list in ascending order based on their natural order (i.e., from smallest to largest). After sorting, the System.out.println() method displays the sorted list: [5, 7, 11, 14]. Collections.reverse() MethodThe method modifies the original list directly which makes it simple way to reverse collection without the need of custom code. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [Kiwi, Pineapple, Banana] Explanation In the above code, we have created a list of fruits ("Banana", "Pineapple", "Kiwi") using Arrays.asList() and wrap it with an ArrayList. The Collections.reverse() method is then called to reverse the order of elements in the list. This method modifies the original list directly, so the order changes from [Banana, Pineapple, Kiwi] to [Kiwi, Pineapple, Banana]. Hence, the reversed list is printed to console. This method is simple and efficient to make it easy to reverse collections. Collections.shuffle() MethodThis method randomly reorders the elements in the given list using default randomness. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [8, 7, 5, 9, 6] Explanation In the above code we have created a list of integers (5, 6, 7, 8, 9) using ArrayList() and wrap it with an ArrayList. The collection.shuffle() method is then used to randomly shuffle the elements in the list, introducing randomness to their order. After shuffling, the list might appear as [8, 7, 5, 9, 6] the order will change each time when we run the code. This method is helpful in scenarios like card games or any case where we need to rearrange a collection of items randomly. Collections.swap() MethodSwaps the elements at the specified positions in the specified list. (If the specified positions are equal, invoking this method leaves the list unchanged.) Syntax: Parameters: list: The list in which to swap elements. i: the index of one element to be swapped. j: the index of the other element to be swapped. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [Georgia, Ginny, Daisy] Explanation It the above code, we have created a list of names: "Daisy", "Ginny" and "Georgia". The Collections.swap() method is used to swap the elements at position 0 and 2 which means "Daisy" and "Georgia" switch places. After swapping, the list becomes [Georgia, Ginny, Daisy]. This method is useful when we want to change the order of specific elements quickly in a list without writing extra code. Collections.copy() MethodThe copy () method copies elements from one list to another. The destination list must be large enough to hold all elements from the source list. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [A, B, C] Explanation In the above code, we have two lists: one is the source list ("A", "B", "C") and the other is destination list ("X", "Y", "Z"). The collections.copy() method copies all elements from the source list into the destination list, replacing the existing values from each position. After the copy, the destination list becomes [A, B, C]. Collections.emptyList() MethodThe emptyList() method creates a list that has no elements and cannot be changed. This means we cannot add, remove, or update anything in the list. Syntax: ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [] Explanation In this example, we used Collection.emptyList() to make an empty list. It is a read only list, so no one can add or remove anything from it. This is useful when we need to return an empty list from a method, and we want to make sure it stays empty and safe from changes. Collections.singletonList() MethodThe method returns an immutable list containing only the specified object. The returned list is serializable. It returns an immutable list containing only the specified object. Syntax: Where, T: the class of the objects in the list o: the sole object to be stored in the returned list. ExampleCompile and RunOutput: [Hello] Explanation The above method in Java is used to create a list that contains only one item and that cannot be changed. This means that we cannot add, remove or replace any element in it. It is helpful when we need a fixed, single-value list for quick use. The above example shows the list contains only the word "Hello", and when printed, it shows [Hello]. This method is often used when we want to return a one-item list without worrying that someone might modify it later. ConclusionThe Collections class in Java gives us many easy-to-use tools for working with collections like lists, sets, and maps. It has built-in methods to do common tasks such as sorting, reversing, shuffling and copying. These methods help us to write less code and make the program simpler and easier to understand. Working with collections class can save time. Next TopicSorting Collection |
Subscribe to Tpoint Tech
We request you to subscribe our newsletter for upcoming updates.







