spring-data-rest in Action
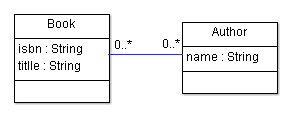
What is spring-data-rest? spring-data-rest , a recent addition to the spring-data project, is a framework that helps you expose your entities directly as RESTful webservice endpoints. Unlike rails, grails or roo it does not generate any code achieving this goal. spring data-rest supports JPA, MongoDB, JSR-303 validation, HAL and many more. It is really innovative and lets you setup your RESTful webservice within minutes. In this example i'll give you a short overview of what spring-data-rest is capable of. Initial Configuration I'm gonna use the new Servlet 3 Java Web Configuration instead of an ancient web.xml. Nothing really special here. public class WebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class <?>[] getRootConfigClasses () { return new Class <?>[]{ AppConfiguration . class }; } @Override protected Class <?>[] getServletConfigClasses () { return ...
